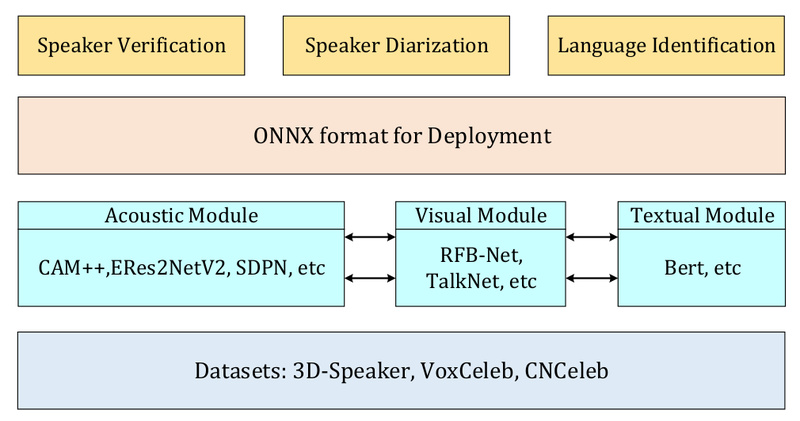
Speaker analysis—whether for verifying identity, recognizing who’s speaking, or separating voices in a multi-person conversation—is a fundamental task in speech processing. Yet, traditional systems often falter in real-world conditions: background noise, overlapping speech, or limited speaker data can severely degrade performance. Enter 3D-Speaker-Toolkit, an open-source, multimodal toolkit purpose-built to tackle these challenges head-on.
Developed for both academic researchers and industrial practitioners, 3D-Speaker-Toolkit uniquely integrates acoustic, semantic, and visual signals to deliver robust speaker verification and diarization. By fusing voice characteristics, linguistic context, and facial cues, it significantly outperforms single-modality approaches—especially in complex scenarios like meetings or crowded environments.
Beyond its technical innovation, the toolkit ships with state-of-the-art pre-trained models, a large-scale dataset covering over 10,000 speakers, and ready-to-run recipes for supervised, self-supervised, and multimodal workflows. All models are accessible via ModelScope, and the codebase is designed for easy experimentation and deployment.
Why Multimodal Speaker Analysis Matters
Most speaker verification systems rely solely on audio—extracting voice embeddings from speech signals. While effective in controlled settings, they struggle when voices overlap, accents vary, or audio quality degrades.
3D-Speaker-Toolkit addresses this by introducing a three-dimensional understanding of speakers:
- Acoustic module: Uses advanced architectures like ERes2NetV2, CAM++, and ECAPA-TDNN to extract high-quality speaker embeddings from raw audio. Supports both fully supervised and self-supervised learning (e.g., SDPN, RDINO).
- Semantic module: Leverages large language models to interpret spoken content and linguistic patterns, helping distinguish speakers based not just on how they sound, but what they say.
- Visual module: Applies lightweight face detection and recognition to video streams, enabling speaker diarization even when multiple people talk simultaneously.
This fusion enables more accurate, reliable, and context-aware speaker analysis—critical for applications where precision is non-negotiable.
Key Features and Capabilities
State-of-the-Art Speaker Verification Models
The toolkit includes training and inference recipes for multiple leading architectures, benchmarked across VoxCeleb, CN-Celeb, and the native 3D-Speaker dataset. Notable models include:
- ERes2NetV2 (17.8M parameters): Achieves 0.61% EER on VoxCeleb1-O and 6.14% on CN-Celeb—the best among evaluated models.
- CAM++: Delivers 0.65% EER on VoxCeleb with only 7.2M parameters, balancing accuracy and efficiency.
- ECAPA-TDNN, ResNet34, and Res2Net: Fully supported with optimized training pipelines.
Self-supervised options like SDPN and RDINO enable speaker embedding learning without labeled data—ideal for low-resource languages or private datasets.
Multimodal Speaker Diarization
3D-Speaker-Toolkit goes beyond audio-only diarization. Its multimodal pipeline combines:
- Voice activity detection (VAD)
- Overlap-aware speech segmentation
- Speaker embedding extraction (from audio)
- Facial tracking and speaker-face alignment (from video)
- Clustering with optional overlap handling
Benchmark results show clear advantages: on the Aishell-4 dataset, it achieves 10.30% DER, outperforming pyannote.audio (12.2%) and DiariZen_WavLM (11.7%). On in-house Chinese meeting data (Meeting-CN_ZH-1/2), it consistently leads rival systems.
Language Identification and Dataset Support
The toolkit also supports language identification, with models trained on phonetic-aware representations for Mandarin and English.
Crucially, it introduces the 3D-Speaker Dataset—a large-scale, diverse corpus of over 10,000 speakers—designed to advance research in speech representation disentanglement. This addresses a long-standing gap in public speaker data, particularly for non-English and multilingual contexts.
Solving Real-World Pain Points
3D-Speaker-Toolkit directly tackles four common industry challenges:
- Poor generalization in noisy or overlapping speech: Multimodal fusion (audio + video + semantics) dramatically improves robustness.
- Lack of accessible, large-scale speaker datasets: The 3D-Speaker Dataset fills this void, enabling better model training and evaluation.
- Complexity of deploying SOTA models: Pre-trained models on ModelScope and simple inference scripts (e.g.,
infer_sv.py,infer_diarization.py) let users go from installation to prediction in minutes. - High barrier to multimodal integration: The toolkit provides end-to-end diarization recipes that seamlessly combine audio and video—no need to build pipelines from scratch.
Getting Started in Minutes
Installation is straightforward:
git clone https://github.com/modelscope/3D-Speaker.git cd 3D-Speaker conda create -n 3D-Speaker python=3.8 conda activate 3D-Speaker pip install -r requirements.txt
For inference, simply load a pre-trained model from ModelScope:
# Example: CAM++ for speaker verification model_id = "iic/speech_campplus_sv_zh-cn_16k-common" python speakerlab/bin/infer_sv.py --model_id $model_id
Diarization is equally simple:
python speakerlab/bin/infer_diarization.py --wav /path/to/audio.wav --out_dir ./results
The repository includes extensive examples for speaker verification, diarization (audio-only or multimodal), and language identification under the egs/ directory.
Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, users should note:
- Language coverage: Most pre-trained models are optimized for Mandarin and English. Performance on other languages may require fine-tuning.
- Multimodal dependencies: Video-based diarization requires additional dependencies (e.g., face detectors) and increases computational load.
- Privacy compliance: When processing real-world recordings—especially video—ensure adherence to data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
Summary
3D-Speaker-Toolkit redefines what’s possible in speaker analysis by unifying acoustic, semantic, and visual intelligence in a single, open-source framework. With cutting-edge models, a large public dataset, and plug-and-play inference, it empowers developers and researchers to deploy reliable speaker verification and diarization systems—even in the messiest real-world scenarios. Whether you’re building secure voice authentication, meeting transcription tools, or forensic audio analysis pipelines, this toolkit offers a compelling foundation for next-generation speech applications.