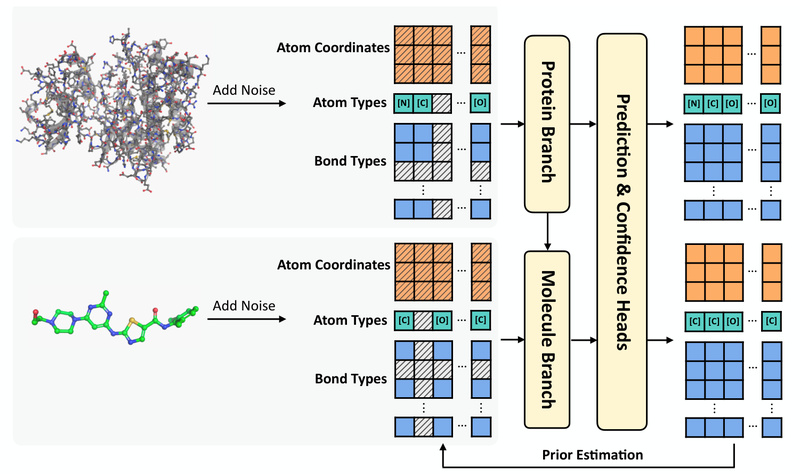
PharMolixFM is an all-atom foundation model purpose-built for molecular modeling and generation, jointly developed by PharMolix Inc. and the Institute for AI Industry Research (AIR) at Tsinghua University. Unlike many academic prototypes, PharMolixFM is engineered for practical adoption in structural biology and early-stage drug discovery. It operates directly on atomic coordinates—modeling proteins, small molecules, and antibodies in a unified framework—and delivers competitive accuracy with dramatically faster inference than leading alternatives like AlphaFold3.
Integrated into the OpenBioMed ecosystem, PharMolixFM isn’t just a model; it’s a production-ready tool that enables researchers to generate binding poses, design novel drug candidates, and explore molecular conformations with minimal computational overhead. For teams seeking to accelerate discovery without sacrificing physical realism, PharMolixFM offers a rare balance of speed, accuracy, and versatility.
What Makes PharMolixFM Different?
Unified All-Atom Representation Across Biomolecules
PharMolixFM treats every biomolecule—whether a protein, antibody, or small organic compound—as a set of atoms with explicit 3D coordinates. This all-atom approach preserves critical structural details often lost in coarse-grained representations, enabling physically plausible modeling of interactions at binding sites. By unifying diverse molecular types under a single generative framework, the model eliminates the need for modality-specific pipelines.
Docking Performance That Balances Speed and Accuracy
In protein–small-molecule docking (given a known binding pocket), PharMolixFM achieves 83.9% of predictions with RMSD < 2Å—a metric widely used to assess pose accuracy. While AlphaFold3 reports 90.2% on the same benchmark, PharMolixFM accomplishes its results with significantly improved inference speed, making it far more practical for high-throughput virtual screening or iterative design cycles.
Broad Applicability Across Molecular Tasks
Beyond docking, PharMolixFM supports a suite of downstream applications critical to drug discovery:
- Structure-based drug design: Generate novel molecules that fit a specified protein pocket.
- Peptide design: Create or optimize peptide sequences with desired structural properties.
- Molecular conformation generation: Sample realistic 3D conformers for flexible molecules.
These capabilities stem from a generalized denoising framework that incorporates task-specific priors, allowing the same core model to adapt to diverse objectives without retraining.
Seamless Integration into Scientific Workflows
PharMolixFM is natively supported in OpenBioMed, a Python toolkit that provides APIs for data loading, model inference, and workflow orchestration. Users can chain PharMolixFM with tools for ADMET prediction, pocket detection (via P2Rank), or visualization—all within a single environment. For advanced users, the platform also enables LLM-driven “AutoPilot” agents that autonomously compose multi-step research protocols.
Practical Use Cases for Technical Teams
Accelerating Hit Identification
Traditional docking relies on physics-based scoring or slow sampling methods. PharMolixFM replaces these with a fast, learned generative process that produces accurate binding poses in seconds, enabling teams to screen thousands of compounds in hours rather than weeks.
De Novo Molecule Design with Structural Constraints
When a target protein pocket is known (e.g., from cryo-EM or homology modeling), researchers can use PharMolixFM to generate entirely new molecules tailored to that site. This is especially valuable in lead optimization, where subtle structural changes can dramatically improve affinity or selectivity.
Rapid Conformational Exploration
For flexible drug-like molecules, generating low-energy 3D conformers is essential for accurate binding prediction. PharMolixFM’s conformation modeling module samples diverse, realistic geometries orders of magnitude faster than molecular dynamics, supporting quick iteration in computational pipelines.
Getting Started with PharMolixFM
PharMolixFM is publicly available through the OpenBioMed GitHub repository. To begin:
- Set up the environment: Install dependencies using the provided
condaandpipcommands (CUDA 11.7 is recommended). - Run inference: Use OpenBioMed’s high-level APIs to perform tasks like docking or structure-based generation. For example, the
Protein-molecule Rigid Dockingtool accepts a protein pocket and a SMILES string, returning a 3D binding pose. - Validate quickly: Jupyter notebook tutorials demonstrate end-to-end workflows, including visualization of protein–ligand complexes and integration with downstream property predictors.
- Scale with agents: For complex tasks, compose multi-tool workflows or deploy LLM agents via the OpenBioMed Agent Platform to automate hypothesis-driven exploration.
Pre-trained models, including PharMolixFM-Diff, are included, and no fine-tuning is required for standard inference.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While powerful, PharMolixFM has important constraints that users should understand:
- Requires a pre-defined binding pocket: The model assumes the binding site is known and provided as input. It does not perform blind docking across the entire protein surface.
- Environment setup complexity: Installation involves multiple scientific Python packages and CUDA dependencies, which may require IT support in some institutional settings.
- Part of a larger framework: Standalone use of PharMolixFM still depends on OpenBioMed’s data structures and utilities, so full isolation is not trivial.
- Not for clinical deployment: Like other research-grade AI models, PharMolixFM is intended for scientific exploration and hypothesis generation—not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or public-facing applications without rigorous validation.
Users should also review the project’s Acceptable Use Policy and MIT License before deployment.
Summary
PharMolixFM bridges the gap between cutting-edge foundation models and real-world structural biology needs. By delivering all-atom accuracy at practical speeds—and embedding that capability into a flexible, open-source toolkit—it empowers research teams to iterate faster, design smarter molecules, and reduce reliance on costly simulations. For those evaluating AI tools for drug discovery or molecular design, PharMolixFM represents a compelling option that prioritizes both scientific fidelity and engineering usability.