In the rapidly evolving field of embodied artificial intelligence (AI), agents—whether physical robots or virtual avatars—must understand complex indoor environments from their own first-person perspective and respond to human instructions in natural language. Traditional 3D scene understanding benchmarks, however, often rely on static, global, or top-down views that poorly reflect the dynamic, partial, and sequential observations real agents encounter.
Enter EmbodiedScan: a comprehensive, multi-modal, ego-centric 3D perception suite designed explicitly to bridge this gap. Developed by OpenRobotLab and introduced at CVPR 2024, EmbodiedScan provides both a large-scale dataset and a set of benchmark tasks that mirror the real-world challenges faced by embodied agents operating in indoor spaces. By fusing first-person RGB-D observations with rich language annotations and dense 3D semantics, EmbodiedScan enables developers and researchers to train, evaluate, and deploy models that truly “see and understand” the world as an agent would.
If you’re working on robotics, spatial computing, AR/VR, or vision-language systems that require grounded reasoning in 3D environments, EmbodiedScan offers a uniquely practical and holistic foundation.
What Makes EmbodiedScan Different?
Unlike conventional 3D datasets like ScanNet or Matterport3D—which primarily capture complete, stationary reconstructions—EmbodiedScan is built from the agent’s point of view. Its core innovation lies in its ego-centric data collection paradigm, which aligns perception with embodiment.
Key verified features include:
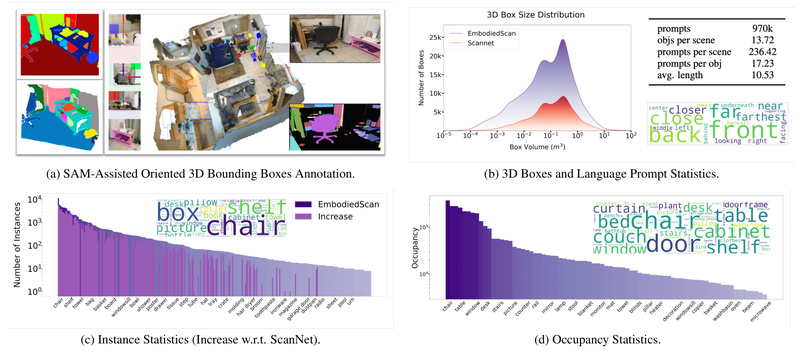
- Over 5,000 real-world indoor scans, sourced from established datasets like ScanNet, 3RScan, and ARKitScenes.
- 1 million ego-centric RGB-D views, simulating the partial, sequential observations an agent gathers while moving through a space.
- 1 million human-written language prompts, each tied to specific 3D locations or objects, enabling language-grounded perception.
- 160,000+ 3D-oriented bounding boxes spanning 760 object categories (partially aligned with LVIS), offering fine-grained object-level annotations.
- Dense semantic occupancy maps for 80 common categories, providing voxel-level understanding of scene geometry and semantics.
Together, these elements support not just detection or segmentation, but holistic scene understanding grounded in both space and language—a critical requirement for agents that must follow instructions like “bring me the red mug on the kitchen counter.”
Ideal Use Cases
EmbodiedScan is purpose-built for teams and researchers tackling problems where perception, language, and embodiment intersect. Here are a few high-impact scenarios:
- Training embodied agents: Robots or AR/VR avatars that navigate homes, offices, or warehouses and respond to natural language commands benefit directly from EmbodiedScan’s aligned vision-language-3D data.
- Developing vision-language models (VLMs) for 3D: If your model needs to ground phrases like “the chair near the window” in a 3D coordinate system, EmbodiedScan provides the necessary training signals and evaluation protocols.
- Benchmarking multi-view 3D perception: The suite includes standardized tasks for multi-view 3D object detection, visual grounding, and occupancy prediction—ideal for comparing algorithmic approaches under realistic conditions.
- Prototyping spatial AI applications: Smart home assistants, inventory robots, or assistive technologies can leverage EmbodiedScan’s data to simulate and validate real-world performance early in development.
In short, if your project involves understanding indoor 3D scenes through the eyes of an agent, EmbodiedScan offers a rare combination of scale, realism, and multi-modal alignment.
Solving Real Pain Points
Before EmbodiedScan, practitioners faced several persistent challenges:
- Lack of first-person 3D-language alignment: Most datasets provide either global 3D meshes or 2D image captions—but not ego-centric trajectories with per-view language tied to 3D coordinates. EmbodiedScan solves this by co-collecting RGB-D sequences and spatially grounded prompts.
- Difficulty evaluating language-guided 3D reasoning: While 2D visual grounding benchmarks exist (e.g., RefCOCO), their 3D counterparts were scarce. EmbodiedScan introduces a multi-view 3D visual grounding benchmark, complete with evaluation scripts and submission tools.
- Simulation-to-reality gap: Synthetic datasets (e.g., AI2-THOR) simplify perception but lack real-world sensor noise, occlusion, and lighting variation. EmbodiedScan’s use of real RGB-D scans ensures models trained on it generalize better to physical deployments.
By directly addressing these issues, EmbodiedScan reduces the friction between theoretical research and deployable embodied AI systems.
Getting Started
EmbodiedScan is open-source and designed for technical users who want to run experiments quickly. The official repository provides clear, step-by-step guidance:
- Environment setup: Requires Ubuntu 20.04, CUDA 12.0, Python 3.8, and PyTorch 1.11.
- Installation: A single
install.pyscript handles dependencies (including PyTorch3D and Minkowski Engine), though users should anticipate potential build complexities with these packages. - Data access: Researchers can apply to download the full dataset via a form; sample data is publicly available for immediate testing.
- Pretrained models: The Embodied Perceptron baseline is provided with checkpoints for tasks like multi-view 3D detection and visual grounding.
- Inference & evaluation: Simple commands like
tools/test.pyallow users to run models on custom scans or evaluate against benchmarks. Visualization utilities are also included for debugging and analysis.
For technical decision-makers, this means you can assess EmbodiedScan’s fit for your pipeline within hours—not weeks.
Current Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, EmbodiedScan isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Be aware of the following constraints:
- Indoor focus: All scans come from indoor environments (homes, offices), limiting applicability to outdoor or industrial settings.
- Non-commercial license: The dataset and code are released under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0, which prohibits commercial use without separate permission—critical for enterprise teams to note.
- Installation complexity: Dependencies like PyTorch3D and Minkowski Engine can be tricky to compile, especially on non-standard systems.
- Evolving benchmarks: The team notes in their TODO list that APIs and benchmarks are still being polished, meaning some interfaces may change in future releases.
These factors don’t diminish EmbodiedScan’s value but help set realistic expectations during technical evaluation.
Summary
EmbodiedScan fills a crucial gap in the embodied AI ecosystem by delivering a large-scale, ego-centric, multi-modal 3D perception suite that aligns real-world agent observations with natural language. With its rich annotations, standardized benchmarks, and practical baseline models, it empowers developers and researchers to build agents that don’t just “see” 3D scenes—but understand and act within them based on human instructions. For anyone working at the intersection of robotics, spatial AI, and vision-language grounding, EmbodiedScan is a compelling, production-ready resource worth serious consideration.