Locating the precise files or functions that need modification when addressing a bug report or feature request is one of the most time-consuming—and error-prone—tasks in software maintenance. Developers routinely struggle to bridge high-level natural language descriptions (e.g., GitHub issue titles or user bug reports) with the exact code entities that require changes, especially in large, interdependent codebases. Traditional static analysis tools lack semantic understanding, while standard Large Language Models (LLMs) often fail because they treat code as flat text, ignoring its rich structural and dependency relationships.
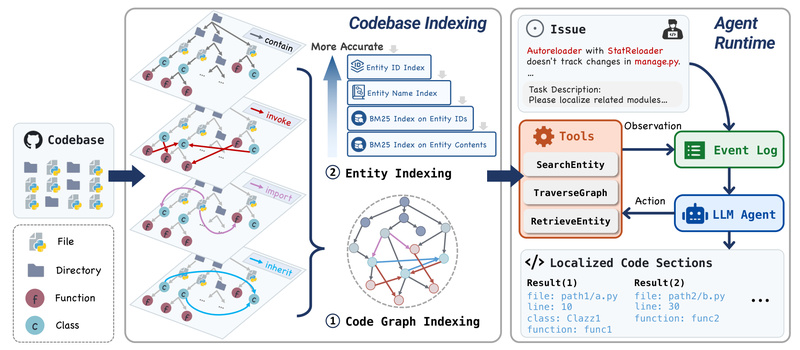
Enter LocAgent: a novel framework that dramatically improves code localization by combining the structural awareness of code graphs with the reasoning power of LLM agents. Instead of guessing based on keyword matching or isolated code snippets, LocAgent enables LLMs to "navigate" the codebase like a map—performing intelligent, multi-hop reasoning across files, classes, functions, and their dependencies.
Why Code Localization Is Hard—and Why It Matters
In real-world software engineering, a single issue description rarely maps cleanly to a single file. Consider a bug report like “User authentication fails when logging in via OAuth.” To fix this, a developer might need to inspect:
- The authentication controller
- The OAuth client wrapper
- Configuration files for third-party integrations
- User session management logic
Without understanding how these components connect, even state-of-the-art LLMs may miss critical files or waste effort on irrelevant ones. Existing approaches—whether rule-based indexers or dense vector retrievers—struggle to capture cross-file dependencies such as imports, method calls, or inheritance chains. This structural blindness leads to low precision and poor downstream task performance (e.g., automated patch generation).
How LocAgent Works: Graphs + LLMs = Smart Navigation
LocAgent solves this by first converting a codebase into a directed heterogeneous graph. Nodes represent structural elements (files, classes, functions), while edges encode semantic relationships (e.g., calls, imports, inherits_from). This graph is lightweight yet expressive—designed specifically to support efficient traversal during LLM-guided search.
The core innovation lies in how the LLM agent interacts with this graph:
- Step 1: Given a natural language issue, the agent starts by retrieving candidate entry points (e.g., via BM25 keyword search).
- Step 2: It then explores the graph neighborhood of these candidates, asking the LLM to reason about relevance (“Does this function influence OAuth login?”).
- Step 3: Through iterative, multi-hop queries, the agent prunes irrelevant paths and converges on the most probable target files.
This graph-guided approach mimics how expert developers mentally traverse a codebase—but at machine speed and scale.
Proven Performance: Accuracy, Cost, and Real-World Impact
LocAgent isn’t just theoretically elegant—it delivers measurable gains:
- 92.7% file-level localization accuracy on benchmark datasets like Loc-Bench V1 and SWE-Bench Lite—rivaling proprietary models.
- 86% lower inference cost compared to leading commercial systems, achieved by fine-tuning open-source models like Qwen-2.5-Coder-Instruct-32B.
- 12% higher Pass@10 success rate in downstream GitHub issue resolution, meaning teams using LocAgent are significantly more likely to generate a correct fix within 10 attempts.
These results demonstrate that LocAgent isn’t just an academic prototype—it’s a practical tool that boosts developer productivity and AI-assisted coding reliability.
Ideal Use Cases: Where LocAgent Shines
You should consider LocAgent if your workflow involves:
- Automated triage of GitHub issues in open-source or enterprise repositories.
- Enhancing AI coding assistants (e.g., GitHub Copilot alternatives) with structural awareness for better edit suggestions.
- Accelerating software maintenance in legacy or monolithic codebases where dependency tracing is non-trivial.
- Benchmarking or researching code understanding systems, thanks to its support for standard datasets like SWE-Bench.
It’s particularly valuable when issue descriptions are vague, high-level, or lack precise technical keywords—situations where naive retrieval fails.
Getting Started: Simple Setup, Flexible Integration
LocAgent is designed for quick adoption:
-
Clone and install:
git clone [email protected]:gersteinlab/LocAgent.git cd LocAgent conda create -n locagent python=3.12 conda activate locagent pip install -r requirements.txt
-
(Optional) Pre-build graph indexes for your target repository to speed up inference:
python dependency_graph/batch_build_graph.py --dataset 'czlll/Loc-Bench_V1' --split 'test' --download_repo
-
Set environment variables for graph and BM25 indexes:
export GRAPH_INDEX_DIR='{your_index_dir}/graph_index_v2.3' export BM25_INDEX_DIR='{your_index_dir}/BM25_index' -
Run localization with your preferred LLM—whether open-source (e.g., Qwen-Coder) or via API (e.g., GPT-4o):
python auto_search_main.py --dataset 'czlll/SWE-bench_Lite' --model 'azure/gpt-4o' --localize --use_function_calling
Options like --simple_desc and --use_function_calling let you tailor behavior to your model’s strengths.
Limitations and Practical Notes
While powerful, LocAgent has boundaries to keep in mind:
- Language support: Current benchmarks and parsing focus on Python codebases. Extending to other languages would require adapting the graph construction pipeline.
- Graph construction overhead: For massive repositories, building the initial graph may take time—though batch pre-processing mitigates this.
- Scope: LocAgent specializes in localization only—it identifies where changes should go but doesn’t generate patches. It’s best used as a front-end to downstream code generation or repair systems.
Summary
LocAgent redefines code localization by giving LLMs a structural "map" of the codebase, enabling them to reason like seasoned developers. With industry-leading accuracy, significant cost savings over proprietary alternatives, and seamless integration into existing AI coding workflows, it’s a compelling choice for teams and researchers tackling real-world software maintenance challenges. If you’re building or evaluating tools that bridge natural language and code, LocAgent offers a robust, open, and empirically validated foundation.