If you’re building computer vision systems that rely on pixel-perfect understanding—like autonomous driving, medical imaging analysis, or retail scene parsing—you’ve likely hit a wall with standard semantic segmentation models. They often struggle when objects appear in complex, real-world contexts because their context modeling is too rigid or shallow.
Enter IDRNet (Intervention-Driven Relation Network), a NeurIPS 2023-accepted approach that rethinks how contextual relationships between pixels are learned. Unlike traditional methods that depend on handcrafted assumptions or fixed similarity rules, IDRNet uses a data-driven intervention strategy—inspired by causal inference—to dynamically discover and leverage meaningful semantic relations. The result? Consistent accuracy gains across diverse benchmarks without overhauling your existing pipeline.
For engineers and technical decision-makers, IDRNet isn’t just another academic model—it’s a practical upgrade that plugs into real-world workflows with minimal friction and maximum reward.
How IDRNet Works: Beyond Predefined Context Assumptions
Most semantic segmentation models improve performance by aggregating context—e.g., using multi-scale features or attention maps based on pixel similarity. But these approaches often encode strong priors: assumptions about what “context” should look like before seeing the data. When those assumptions mismatch reality (e.g., in cluttered urban scenes or ambiguous medical scans), performance plateaus.
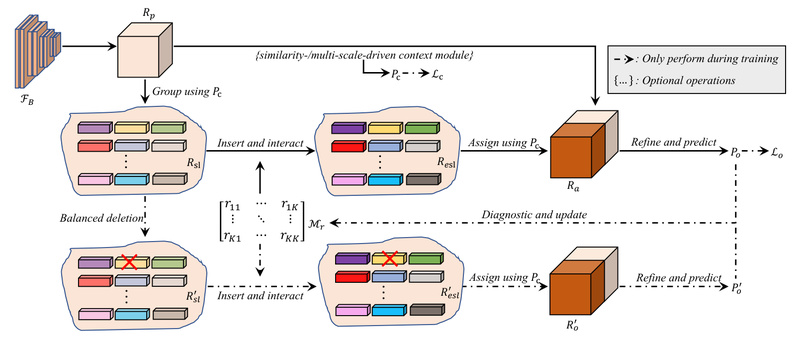
IDRNet takes a different route. It introduces a deletion diagnostics procedure—a technique borrowed from interpretability and causal analysis—to actively probe how removing certain semantic groups affects the model’s output. Here’s the workflow:
- Semantic grouping: Pixel-level features are grouped into semantic-level representations using pseudo-label guidance.
- Feature enhancement: These grouped representations are sharpened to increase inter-class distinguishability.
- Intervention-driven relation modeling: The model simulates “what if this semantic group were removed?” and observes the impact on predictions. This reveals which semantic groups are contextually relevant to each other.
- Context-guided refinement: The learned relations are used to let semantic groups interact, and the refined representations are fused back to enhance original pixel-level features for final prediction.
This process avoids reliance on fixed spatial or similarity priors. Instead, context is discovered through intervention, making it adaptive to the input scene.
Key Strengths for Practitioners
IDRNet shines not because it’s radically new in architecture, but because it delivers measurable, plug-and-play improvements to existing systems:
- Consistent performance gains: When integrated into leading frameworks (e.g., OCRNet, UPerNet), IDRNet reliably lifts mIoU scores across Cityscapes, ADE20K, COCO-Stuff, PASCAL-Context, and LIP.
- Minimal integration overhead: As part of the SSSegmentation toolbox—a PyTorch-based, modular segmentation library—IDRNet requires no exotic dependencies and supports popular backbones like ResNet, SwinTransformer, and ConvNeXt.
- Production-friendly: Unlike prompt-based or zero-shot models (e.g., SAM), IDRNet is designed for supervised, high-accuracy dense prediction in controlled environments where labeled data is available—an ideal fit for industrial applications.
Ideal Use Cases
IDRNet is particularly valuable when your segmentation task involves:
- Complex co-occurrent patterns: Urban driving scenes (Cityscapes) where cars, pedestrians, and traffic signs appear in varied configurations.
- Fine-grained human parsing: Fashion or healthcare applications (LIP, CIHP) requiring precise delineation of body parts or clothing layers.
- Dense indoor/outdoor understanding: Scene parsing in ADE20K or PASCAL-Context, where object relationships are critical for disambiguation (e.g., “a cup on a table” vs. “a cup in a sink”).
In these scenarios, off-the-shelf models often blur boundaries or mislabel regions due to poor contextual reasoning. IDRNet’s intervention-driven relations help disentangle these ambiguities by learning which semantics truly influence each other—on the fly.
Getting Started Quickly
You don’t need to rebuild your system to try IDRNet. It’s natively supported in SSSegmentation, an open-source toolbox that unifies dozens of segmentation algorithms under a consistent interface.
- Pre-trained models are available for standard datasets.
- Documentation is comprehensive, with inference examples and training recipes.
- Backbone flexibility: Works with ResNet, HRNet, SwinTransformer, and more—so you can slot it into your current feature extractor.
- Lightweight integration: Adding IDRNet typically means swapping in a few modules or config lines, not rewriting your pipeline.
This makes it an ideal candidate for A/B testing: deploy your baseline model alongside an IDRNet-enhanced version and measure real-world gains in accuracy or robustness.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
IDRNet isn’t a silver bullet. Keep these points in mind:
- It assumes supervised learning with labeled data—not suitable for zero-shot or annotation-free setups.
- It’s not a standalone model, but a context-enhancement module meant to augment existing segmentors. Compatibility with your chosen backbone and head should be verified.
- While it reduces reliance on priors, it still operates within the limits of the underlying segmentation framework. Garbage in (e.g., poor pseudo-labels during grouping) can affect relation quality.
That said, for teams already using semantic segmentation in production or research, IDRNet represents a low-risk, high-value optimization path.
Summary
IDRNet solves a quiet but pervasive problem in semantic segmentation: the inefficiency of static, prior-heavy context modeling. By grounding relation learning in an intervention-driven diagnostic process, it adapts context dynamically to each image—leading to more accurate, robust predictions.
For technical decision-makers, it offers a rare combination: academic rigor (NeurIPS 2023), engineering practicality (modular, PyTorch-native), and measurable impact (consistent gains on major benchmarks). If your project demands pixel-level precision in complex scenes—and you’re already using supervised segmentation—IDRNet is a smart, low-friction upgrade worth evaluating.