Time series forecasting is essential across industries—from predicting energy demand and stock trends to managing supply chains and monitoring IoT sensor networks. Yet despite the rise of powerful deep learning models like Transformers, practitioners consistently face a critical trade-off: accuracy versus efficiency. Transformers, while effective at capturing long-range dependencies, are notoriously resource-intensive, making them impractical for long-horizon forecasting or deployment in constrained environments.
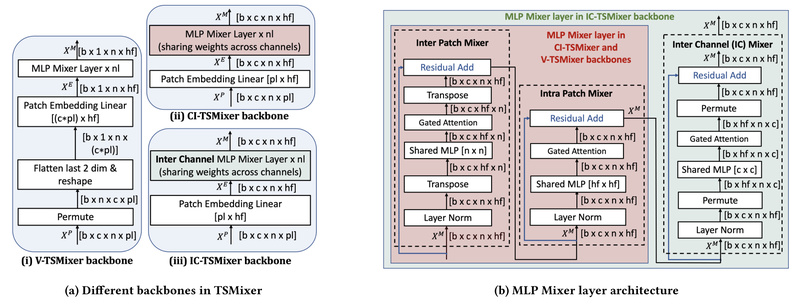
Enter TSMixer, a novel, lightweight neural architecture designed specifically for multivariate time series forecasting. Built entirely from multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs), TSMixer delivers state-of-the-art accuracy—outperforming both MLP-based and Transformer-based models by 8–60%—while slashing memory usage and runtime by 2–3× compared to recent Patch-Transformer models. Developed by IBM researchers and released as PatchTSMixer in the Hugging Face Transformers library, TSMixer offers a compelling solution for teams seeking performance without the computational overhead.
Why TSMixer Solves Real Forecasting Pain Points
Traditional forecasting models struggle with three key challenges:
- High computational cost: Transformer-based models scale quadratically with sequence length, making long-horizon forecasts slow and expensive.
- Memory bottlenecks: Attention mechanisms require storing large attention matrices, limiting deployment on edge devices or in cost-sensitive cloud setups.
- Poor generalization across diverse datasets: Many models overfit to specific domains and fail to transfer effectively.
TSMixer directly addresses these issues. By replacing attention with a streamlined MLP-Mixer backbone adapted for time series, it eliminates the need for heavy matrix operations. This design enables faster training, lower memory consumption, and easier scaling to long forecast horizons—all while achieving higher accuracy across a wide range of real-world datasets.
Key Features That Make TSMixer Stand Out
Pure MLP Architecture, Optimized for Time Series
Inspired by the MLP-Mixer from computer vision, TSMixer processes time series in “patches”—short segments of temporal data—which are then mixed across time and variables using separate MLPs. This dual mixing (time mixing and channel mixing) efficiently captures both temporal patterns and inter-variable relationships without attention.
Online Reconciliation Heads
A standout innovation in TSMixer is its online reconciliation heads. These lightweight modules are attached to the backbone to explicitly model time series properties like hierarchical structures (e.g., daily vs. weekly patterns) and cross-channel correlations (e.g., how temperature affects energy load). This leads to more coherent and physically plausible forecasts.
Hybrid Channel Modeling with Gating
To handle noisy or irrelevant channel interactions—common in real-world sensor or financial data—TSMixer introduces a simple gating mechanism within its Hybrid channel modeling. This improves robustness and generalization across diverse forecasting tasks without adding significant complexity.
Modular and Foundation-Model Ready
TSMixer’s architecture is inherently modular. It supports both supervised forecasting and masked self-supervised pre-training, making it an ideal building block for Time Series Foundation Models (TSFMs). This flexibility enables effective transfer learning: pre-train on large public datasets, then fine-tune on domain-specific data with minimal labeled examples.
Ideal Use Cases for TSMixer
TSMixer excels in scenarios where accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability are critical:
- Long-horizon multivariate forecasting: Predicting 24+ hours of electricity demand across dozens of substations.
- Resource-constrained deployments: Running on edge devices in smart factories or low-cost cloud instances for IoT analytics.
- Cross-domain transfer learning: Leveraging pre-trained models for quick adaptation to new domains like retail sales or logistics, even with limited historical data.
- High-throughput applications: Batch forecasting thousands of time series simultaneously—common in finance, energy, and e-commerce—where runtime and memory directly impact operational cost.
It is particularly well-suited for applications involving structured, multivariate signals, such as:
- Energy load and renewable power forecasting
- Financial market and risk modeling
- Supply chain and inventory optimization
- Industrial sensor and telemetry monitoring
How to Get Started with TSMixer
Getting started with TSMixer is straightforward thanks to its integration with Hugging Face and the open-source TSFM (Time Series Foundation Models) repository.
- Access pre-trained models: TSMixer is available as
PatchTSMixerin the Hugging Face Transformers library, with pre-trained checkpoints ready for inference or fine-tuning. - Run example notebooks: The official GitHub repository (
ibm/tsfm) includes ready-to-run notebooks for:- Basic inference with
PatchTSMixer - Transfer learning on custom datasets
- Comparison with other models like
PatchTSTandTinyTimeMixer
- Basic inference with
- Experiment in Colab: Google Colab tutorials allow instant experimentation without local setup—ideal for rapid prototyping.
- Fine-tune or pre-train: Using the provided utilities, users can adapt TSMixer to their specific forecasting horizons, variable counts, and data distributions.
Installation is simple via pip, with support for Python 3.10–3.12. The codebase is designed for clarity and ease of modification, making it accessible even to teams new to time series deep learning.
Limitations and Considerations
While TSMixer offers compelling advantages, it’s important to understand its current scope:
- Designed for multivariate time series: It is not optimized for univariate forecasting tasks.
- Relies on patched input representation: Time series must be segmented into patches, which may require tuning for very short sequences.
- Not ideal for ultra-low-latency regimes: Though efficient, it may still be overkill for simple, short-term predictions where classical models (e.g., ARIMA or exponential smoothing) suffice.
- Community-supported, not productized: As noted in IBM’s disclosure, the code is released “as-is” under an open-source license, without guaranteed long-term maintenance or enterprise support.
Nonetheless, for teams balancing performance, cost, and scalability, TSMixer represents a significant step forward in practical time series modeling.
Summary
TSMixer redefines what’s possible in efficient time series forecasting. By replacing complex attention mechanisms with a lean, MLP-based architecture enhanced with reconciliation heads and gating, it achieves superior accuracy with dramatically lower computational demands. Its compatibility with modern foundation model workflows—pre-training, transfer learning, and modular deployment—makes it a strategic choice for engineers and researchers building next-generation forecasting systems. If your project involves multivariate, long-horizon forecasting under real-world constraints, TSMixer is worth serious consideration.