Image restoration—recovering clean, high-resolution images from degraded inputs—is a foundational task in computer vision with applications ranging from smartphone photography to medical imaging. Traditional deep learning approaches often rely on Vision Transformers (ViTs) for global context awareness or CNNs for local efficiency, but struggle to achieve both simultaneously. Enter MambaIR, a modern image restoration framework built on state-space models (SSMs) that delivers strong performance with remarkable computational efficiency. Its latest iteration, MambaIRv2, further overcomes a core limitation of early SSM-based designs by introducing non-causal, globally attentive modeling—enabling richer pixel interactions without sacrificing speed or model size.
For engineers, researchers, and product teams weighing architectural trade-offs, MambaIR offers a compelling balance: ViT-level restoration quality with CNN-like inference speed and a lighter parameter footprint than leading alternatives like HAT or SRFormer. Whether you’re enhancing legacy photos, cleaning noisy sensor data, or restoring compressed web images, MambaIR provides a robust, ready-to-deploy solution optimized for real-world constraints.
What Makes MambaIR Different?
From Causal to Attentive: The MambaIRv2 Breakthrough
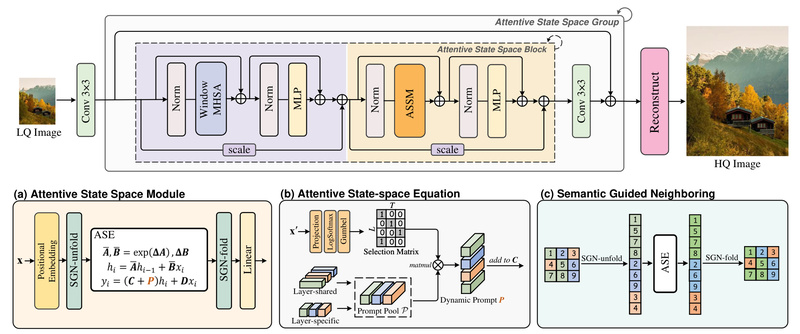
The original Mamba architecture processes sequences in a causal manner—each token can only attend to previous tokens in the scan order. While efficient, this limits global context utilization in 2D images, where pixels far apart may share critical structural or semantic relationships.
MambaIRv2 addresses this by redefining the state-space equation to support non-causal modeling. Its attentive state-space mechanism allows every pixel to interact with others beyond its scan-path predecessors—effectively mimicking the global receptive field of ViTs—yet retains the linear complexity advantage of SSMs. This is achieved with just a single image scan, avoiding the multi-directional passes used in some prior work.
Semantic-Guided Pixel Interaction
Beyond global reach, MambaIRv2 introduces a semantic-guided neighboring mechanism that encourages communication between distant but visually or semantically similar pixels. For example, it can connect sky regions across opposite corners of an image or align repetitive textures, significantly improving restoration coherence in complex scenes.
Proven Efficiency and Performance
Benchmark results speak volumes:
- On lightweight super-resolution (lightSR ×2), MambaIRv2 outperforms SRFormer by +0.35 dB PSNR while using 9.3% fewer parameters.
- On classic super-resolution (SR ×4), it surpasses the strong HAT baseline by up to +0.29 dB PSNR.
- It consistently leads across Gaussian denoising, real-world denoising (SIDD), and JPEG compression artifact reduction tasks.
All this is achieved without inflating computational cost—making MambaIRv2 not just more accurate, but also more deployable.
Real Problems MambaIR Solves
MambaIR targets practical degradation scenarios commonly encountered in real systems:
- Blurriness from upscaling: Restoring fine details in low-resolution images (e.g., surveillance footage, archival photos) via classic or lightweight super-resolution.
- Sensor noise in low-light conditions: Removing noise from smartphone or IoT camera outputs using models trained on real (SIDD) or synthetic (Gaussian) noise patterns.
- Compression artifacts: Reversing blocky distortions and blurring caused by aggressive JPEG encoding—crucial for web media or legacy image databases.
Because MambaIR models are compact and fast, they’re well-suited for edge deployment (e.g., mobile apps, embedded vision systems) where latency and memory are constrained, yet quality cannot be compromised.
Ideal Use Cases
Based on the officially supported tasks, MambaIR is best applied when you need:
- Classic super-resolution (×2/×3/×4): For high-fidelity enhancement of general images (e.g., digital archives, broadcast media).
- Lightweight super-resolution: When model size and speed are priorities (e.g., real-time video upscaling on mobile).
- Image denoising: Both real-world (camera sensor noise) and synthetic (Gaussian) variants.
- JPEG artifact reduction: Restoring images degraded by lossy compression, common in web and social media pipelines.
It is not designed for high-level vision tasks like object detection, segmentation, or classification—its strength lies squarely in low-level pixel reconstruction.
Getting Started: Practical Adoption
MambaIR is developer-friendly and integrates smoothly into existing workflows:
- Quick inference: Use pretrained weights (available on GitHub and Hugging Face) with simple test scripts. Just point to your input image and config file—no complex setup needed.
- Custom training: Retrain on your own data using provided YAML configuration files for each task (SR, denoising, JPEG CAR). The codebase is built on BasicSR, a widely used framework in restoration research.
- Zero-install experimentation: Try the model instantly via the online Jupyter Notebook demo, eliminating environment setup for initial evaluation.
The repository includes detailed installation instructions for CUDA 11.7/PyTorch 2.0.1, with fallback options (e.g., offline WHLs) for dependency issues with mamba_ssm or causal_conv1d.
Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, MambaIR has important boundaries:
- Task scope: Focused exclusively on image restoration—no support for classification, detection, or generation.
- Hardware dependencies: Optimal performance requires specific CUDA/PyTorch versions. Newer CUDA versions (e.g., 12.x) may need manual library adjustments.
- Scanning-based processing: Although MambaIRv2 enables non-causal attention, it still relies on sequential scanning of the image grid. This differs from fully parallel ViTs and may influence design choices for certain latency-critical applications.
Nonetheless, for its target domain, MambaIR sets a new standard for efficiency-quality trade-offs.
Summary
MambaIR—and its enhanced successor MambaIRv2—redefines what’s possible in efficient image restoration. By combining the global modeling power of attention-like mechanisms with the linear complexity of state-space models, it delivers state-of-the-art results across super-resolution, denoising, and artifact reduction, all while using fewer parameters and less computation than leading alternatives. Its modular design, pretrained models, and clear documentation make it accessible for both rapid prototyping and production deployment. If your project demands high-quality image recovery under real-world constraints, MambaIR is a framework worth adopting.