Battery degradation is a critical bottleneck in the deployment of electric vehicles (EVs), grid-scale energy storage, and portable electronics. Engineers and researchers struggle with “range anxiety,” unexpected battery failures, and inefficient maintenance schedules—problems rooted in the inability to accurately predict a battery’s remaining useful life (RUL) or state of health (SOH). While machine learning (ML) holds promise for modeling these complex electrochemical processes, bridging domain knowledge in battery science with modern ML techniques remains a major hurdle.
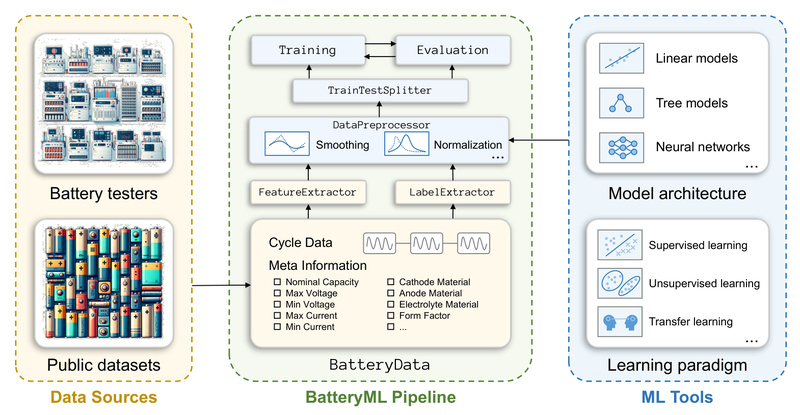
Enter BatteryML: an open-source, end-to-end platform developed by Microsoft that unifies data ingestion, preprocessing, feature engineering, and model deployment for battery degradation prediction. Designed for both battery scientists with limited ML experience and data scientists new to electrochemistry, BatteryML removes the friction of building custom pipelines from scratch—enabling faster iteration, reproducible benchmarks, and cross-disciplinary collaboration.
Why Battery Degradation Prediction Matters
Lithium-ion batteries degrade due to intricate physical processes—solid electrolyte interface (SEI) growth, lithium plating, and loss of active material—each influenced by usage patterns, temperature, and chemistry. In real-world applications, this degradation manifests as reduced driving range in EVs or power instability in renewable energy storage systems.
Traditional physics-based models are often too slow or require detailed internal parameters that are hard to measure. Purely data-driven approaches, meanwhile, suffer from inconsistent data formats, lack of standardized benchmarks, and fragmented tooling. BatteryML directly addresses these pain points by offering a unified, community-driven platform where researchers can focus on modeling—not data wrangling.
All-in-One Tool for Battery + ML: What Makes BatteryML Stand Out
BatteryML is built around four core capabilities that streamline the entire ML workflow for battery data:
- Integrated data preprocessing and feature engineering: Automatically transforms raw cycling data into structured, ML-ready features like QdLinear (discharge capacity curves).
- Comprehensive model library: Includes both classical baselines (e.g., Ridge Regression, PLSR, XGBoost) and deep learning architectures (LSTM, Transformer, CNN).
- Extensible architecture: Offers clean Python interfaces for adding new datasets, features, or models without overhauling the codebase.
- Community-driven and open-source: Hosted on GitHub under MIT license, inviting contributions from both battery and ML communities.
This integration ensures that battery experts can apply powerful ML models without becoming ML engineers—and that ML practitioners can work with real battery data without needing a PhD in electrochemistry.
Comprehensive, Ready-to-Use Battery Datasets Out of the Box
One of BatteryML’s biggest time-savers is its native support for seven major public battery datasets, covering diverse chemistries (LFP, NMC, NCA, LCO), cycling conditions, and cell counts:
- CALCE (LCO/graphite)
- MATR and HUST (LFP/graphite)
- HNEI (NMC_LCO/graphite)
- RWTH (NMC/carbon)
- SNL (multi-chemistry)
- UL_PUR (NCA/graphite)
Beyond individual datasets, BatteryML also provides combined benchmarks like CRUH, CRUSH, and MIX, which merge data across sources to test model generalizability—a crucial requirement for real-world deployment where battery types vary widely. All datasets are preprocessed into a consistent BatteryData format, eliminating weeks of manual cleaning and alignment.
From Raw Cycler Data to ML-Ready Format in Minutes
Many labs generate battery data using commercial cyclers like ARBIN or NEWARE, but raw outputs are rarely structured for ML. BatteryML includes built-in parsers for these formats, controlled via simple YAML configuration files.
For example, converting ARBIN data requires just:
batteryml preprocess ARBIN /raw/data/path /processed/data/path --config /configs/cycler/ARBIN.yaml
The platform already supports ARBIN and NEWARE, with Biologic, LANDT, and Indigo formats under active development. If your cycler isn’t fully supported yet, you can customize the YAML mapping to align your fields—making BatteryML adaptable to proprietary lab setups.
Benchmarked Models and Easy Experimentation
Reproducing published results or testing new ideas is as simple as editing a config file. BatteryML ships with predefined YAML configs for all baseline models used in its ICLR 2024 paper—from the simple “variance” model to full Transformer architectures.
To train and evaluate the variance model on MATR data:
batteryml run configs/baselines/sklearn/variance_model/matr_1.yaml --workspace ./workspace/test --train --eval
This config-driven approach ensures full reproducibility and lowers the barrier to entry. Users can compare 15+ models across 8 datasets using standardized metrics, making it easy to identify the best approach for their specific use case.
Who Should Use BatteryML—and Who Might Need to Think Twice
Ideal users include:
- Battery researchers seeking ML-powered RUL/SOH prediction without building ML infrastructure.
- Data scientists entering the energy or EV sectors who need curated, domain-specific datasets.
- R&D teams in automotive or energy storage companies looking to prototype predictive maintenance systems.
Considerations:
- Deep learning models require PyTorch (not included by default).
- Support for non-ARBIN/NEWARE cyclers is still expanding—users may need to contribute configs for less common formats.
- Large-scale training (e.g., on the full MIX dataset) demands adequate GPU resources, which BatteryML doesn’t provide—it’s a software toolkit, not a cloud service.
Getting Started in Under 5 Minutes
Installation is straightforward:
pip install -r requirements.txt pip install .
Then download and preprocess a dataset:
batteryml download MATR ./raw batteryml preprocess MATR ./raw ./processed
Finally, run a baseline:
batteryml run configs/baselines/sklearn/variance_model/matr_1.yaml --workspace ./test --train --eval
The CLI and config system ensure that even non-experts can achieve reliable, repeatable results—fast.
Summary
BatteryML solves a real, cross-disciplinary problem: the disconnect between battery science and scalable machine learning. By providing standardized data, built-in preprocessing, benchmarked models, and an extensible framework, it empowers researchers to focus on innovation—not infrastructure. Whether you’re predicting EV battery life or optimizing grid storage, BatteryML offers a proven, open foundation to accelerate your work.