Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become a cornerstone technique for grounding language models in factual knowledge. However, traditional RAG pipelines struggle when paired with Small Language Models (SLMs)—models with under 4 billion parameters—due to their limited semantic comprehension and high computational overhead. This performance gap has made it difficult to deploy effective RAG systems on mobile phones, edge devices, or other resource-constrained environments.
Enter MiniRAG: a radically simplified RAG framework engineered specifically for SLMs. By rethinking how knowledge is indexed and retrieved, MiniRAG bypasses the need for deep language understanding during retrieval while slashing storage requirements to just 25% of conventional systems. The result? SLMs like Phi-3.5-mini or GLM-Edge-1.5B can now achieve RAG performance that rivals or even surpasses larger models in realistic, on-device scenarios.
Built with developers and researchers in mind, MiniRAG is open-source, easy to install, and supports multiple graph databases out of the box—making it a practical, future-ready solution for lightweight AI applications.
Why Traditional RAG Fails with Small Models
Most existing RAG systems assume access to powerful Large Language Models (LLMs) capable of rich semantic parsing, complex query rewriting, and nuanced document ranking. But SLMs lack the capacity for such tasks. When forced into standard RAG workflows, they often produce incoherent retrievals or fail to connect relevant facts, especially for multi-hop or compositional queries.
This isn’t just a theoretical limitation—it’s a real barrier to deploying AI on everyday devices. If your application must run offline on a smartphone or embedded system, you can’t afford a 7B+ parameter model. Yet without an effective RAG strategy, your SLM remains shallow and unreliable.
MiniRAG directly addresses this mismatch by shifting intelligence from the language model to the knowledge index itself.
Two Innovations That Make MiniRAG Work
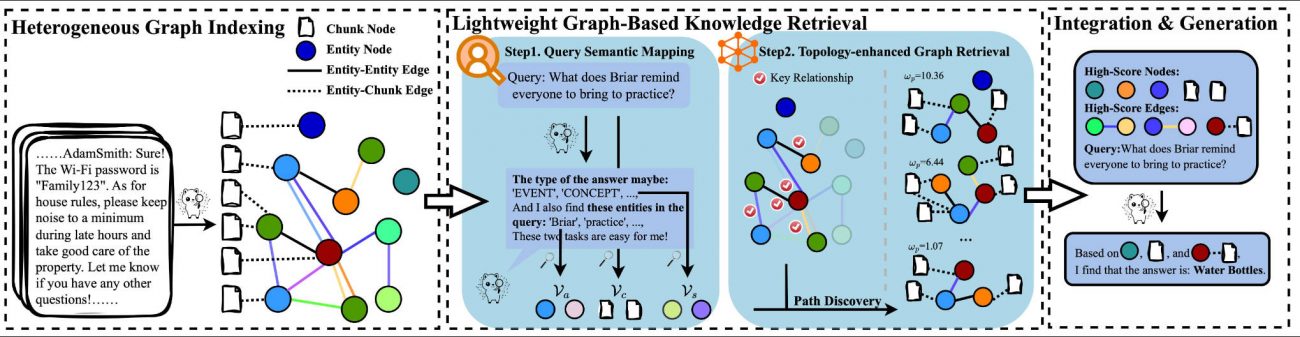
Semantic-Aware Heterogeneous Graph Indexing
Instead of treating documents as isolated text chunks, MiniRAG constructs a heterogeneous knowledge graph that unifies two types of nodes:
- Text chunks (e.g., paragraphs from a document)
- Named entities (e.g., people, locations, dates extracted via lightweight NER)
Edges connect entities to the chunks where they appear, and chunks to each other based on co-occurrence or proximity. This structure encodes semantic relationships without requiring the SLM to infer them at query time.
For example, if a user asks, “What did LiHua say about Kyoto in spring?”, MiniRAG can directly traverse from the entity Kyoto → relevant chunks → seasonal context, bypassing ambiguous keyword matching or fragile embedding similarity.
Lightweight Topology-Enhanced Retrieval
Rather than relying on dense vector embeddings or complex re-rankers, MiniRAG uses graph topology to guide retrieval. When a query arrives, it’s parsed into key entities (using a minimal extractor), which seed a subgraph expansion. The system then retrieves the most central or well-connected nodes in this subgraph—effectively letting the graph’s structure do the “reasoning.”
This approach requires no fine-tuned encoders, no cross-attention over long contexts, and minimal GPU memory. It’s fast, interpretable, and highly efficient.
Proven Performance on Real-World Tasks
MiniRAG was evaluated on LiHua-World, a new benchmark simulating on-device RAG with a year’s worth of chat logs from a virtual user. The dataset includes:
- Single-hop questions (direct fact lookup)
- Multi-hop questions (requiring chaining of facts)
- Summary queries (synthesizing information across documents)
Results show MiniRAG consistently outperforms NaiveRAG and LightRAG—and often approaches LLM-level accuracy—when using SLMs:
- Phi-3.5-mini-instruct: 53.29% accuracy with MiniRAG vs. 41.22% with NaiveRAG
- GLM-Edge-1.5B-Chat: 52.51% vs. 42.79%
- Even gpt-4o-mini achieves 68.43% on multi-hop queries with MiniRAG, beating GraphRAG and LightRAG
Crucially, MiniRAG achieves this while using only 25% of the storage space of traditional RAG systems—thanks to compact graph representations and reduced reliance on large embedding caches.
Getting Started Is Simple
MiniRAG is designed for rapid adoption:
- Install via PyPI:
pip install minirag-hku
- Prepare data: Place your documents (or use the included
LiHuaWorld.zip) in the./datasetfolder. - Index and query with two scripts:
python ./reproduce/Step_0_index.py python ./reproduce/Step_1_QA.py
The framework supports 10+ heterogeneous graph databases, including Neo4j, PostgreSQL, and TiDB, and offers API and Docker deployment for production use.
Whether you’re building a mobile assistant, an offline knowledge bot, or an edge-based QA system, MiniRAG integrates smoothly into your stack.
When to Use (and Not Use) MiniRAG
Ideal for:
- On-device AI applications (mobile, IoT, embedded systems)
- Low-latency RAG where model size and speed are critical
- Structured or semi-structured knowledge bases (e.g., personal notes, technical docs, chat logs)
- Teams prioritizing efficiency over open-ended creativity
Less suitable for:
- Tasks requiring deep, open-ended reasoning beyond factual grounding
- Domains with minimal named entities or highly abstract concepts
- Scenarios where full multi-hop reasoning must be handled entirely by the language model (some SLMs still show limitations here, as noted by “/” entries in benchmark tables)
MiniRAG isn’t meant to replace LLM-based RAG in research labs—it’s built to empower real-world deployment where resources are tight and reliability matters.
Summary
MiniRAG redefines what’s possible with Small Language Models in retrieval-augmented settings. By offloading semantic reasoning into a lightweight, heterogeneous graph index and using topology-aware retrieval, it eliminates the biggest bottlenecks that plague SLMs in traditional RAG pipelines.
With strong benchmark results, minimal storage footprint, broad database compatibility, and a simple installation process, MiniRAG offers a compelling path forward for developers building efficient, on-device AI systems.
If you’re working on a project where every megabyte and millisecond counts—but you still need accurate, knowledge-grounded responses—MiniRAG is worth trying today.