Semantic segmentation of urban remote sensing imagery—such as aerial photos from drones or satellites—is essential for applications like land cover mapping, urban planning, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure assessment. However, many existing deep learning models face a critical trade-off: high accuracy often comes at the cost of slow inference speed, while lightweight models sacrifice contextual understanding for efficiency.
UNetFormer directly addresses this dilemma. Introduced in the paper “UNetFormer: A UNet-like Transformer for Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Urban Scene Imagery”, it is a purpose-built architecture that blends the best of convolutional and transformer-based design. By combining a lightweight CNN encoder (like ResNet18) with a novel global-local attention mechanism in the decoder, UNetFormer delivers both real-time performance and competitive accuracy—making it uniquely suited for practitioners who need deployable, reliable segmentation in resource-constrained settings.
Why UNetFormer Stands Out
Built for Urban Remote Sensing—Not General Images
Unlike generic segmentation models trained on natural scene datasets (e.g., Cityscapes or ADE20K), UNetFormer is explicitly designed and evaluated on urban remote sensing benchmarks such as UAVid, LoveDA, Vaihingen, and Potsdam. These datasets feature high-resolution aerial views with complex spatial patterns, small object instances, and fine-grained class distinctions (e.g., impervious surfaces vs. buildings). UNetFormer’s architecture accounts for these characteristics, ensuring relevance and robustness in real-world geospatial workflows.
Speed Meets Accuracy—No Compromise
A standout achievement of UNetFormer is its inference efficiency without severe accuracy degradation. On a single NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU, it achieves 322.4 FPS on 512×512 inputs when paired with ResNet18—making it feasible for near real-time drone video analysis or rapid large-scale mapping. At the same time, it reports 67.8% mIoU on UAVid and 52.4% mIoU on LoveDA, outperforming other lightweight alternatives.
Moreover, when enhanced with a stronger backbone like Swin Transformer, UNetFormer reaches 84.1% mIoU and 91.3% F1 on Vaihingen, demonstrating its scalability across hardware budgets. This flexibility allows teams to choose between deployment-ready speed (with ResNet18) or peak accuracy (with Swin) based on their project constraints.
Efficient Global-Local Context Modeling
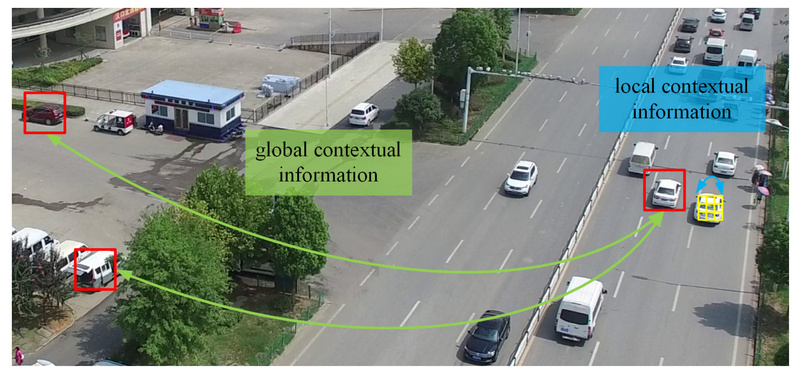
Traditional CNNs excel at capturing local texture and edge details but struggle with long-range dependencies—critical for distinguishing similar urban classes (e.g., road vs. parking lot). Pure Vision Transformers address global context but are computationally heavy.
UNetFormer introduces an efficient global-local attention mechanism in its decoder that selectively fuses fine-grained local features from lower encoder stages with coarse global representations from deeper layers. This hybrid approach ensures that both spatial precision and semantic coherence are preserved, directly tackling a core weakness of prior remote sensing segmentation models.
Practical Use Cases
UNetFormer is ideal for scenarios where speed, accuracy, and urban scene specificity intersect:
- Urban Change Detection: Rapidly segment historical and current aerial images to identify new constructions or land use shifts.
- Disaster Response Mapping: Deploy on edge devices to generate real-time flood or damage assessments from drone footage.
- Environmental Monitoring: Automate green space or water body delineation across cities for sustainability reporting.
- Economic Infrastructure Analysis: Extract road networks, buildings, and industrial zones to support policy or investment decisions.
Its compatibility with standard remote sensing datasets and ability to run on consumer-grade GPUs (e.g., RTX 3090) lowers the barrier for municipal agencies, startups, or academic labs without access to large compute clusters.
Getting Started with UNetFormer
The model is implemented in GeoSeg, an open-source PyTorch-based toolbox designed for remote sensing segmentation. Thanks to PyTorch Lightning and the timm library, the codebase is modular, readable, and easy to extend.
Step-by-Step Workflow
-
Environment Setup: Create a Python 3.8+ environment and install dependencies via
requirements.txt. Mamba support is optional but available for newer models. -
Data Preparation: Use provided scripts to preprocess standard datasets. For example:
- Convert LoveDA mask labels to training-compatible IDs.
- Split large Vaihingen or Potsdam images into 1024×1024 patches with configurable stride.
-
Training: Launch training with a single command pointing to a config file:
python GeoSeg/train_supervision.py -c GeoSeg/config/uavid/unetformer.py
Config files define backbone, decoder settings, optimizer, and augmentation—making experimentation straightforward.
-
Inference: Run predictions on test sets or full-resolution images:
python GeoSeg/inference_uavid.py -i 'data/uavid/uavid_test' -c GeoSeg/config/uavid/unetformer.py -o results --rgb -t 'lr'
Options include test-time augmentation (
'lr'for horizontal flip,'d4'for multi-scale) and RGB mask output for visualization.
Notably, GeoSeg also supports inference on huge images (e.g., full orthophotos) via sliding-window tiling, enabling application beyond benchmark datasets.
Limitations and Considerations
While UNetFormer excels in urban remote sensing, it is not a general-purpose segmentation model. Its design and training focus on aerial urban scenes; performance may degrade on non-urban or non-aerial imagery (e.g., medical or satellite non-urban landscapes).
Additionally, optimal results require careful data preprocessing—particularly mask label conversion and patch splitting—as the model expects standardized input formats. Teams should also note that top-tier accuracy on Vaihingen/Potsdam requires Swin Transformer backbones, which demand more GPU memory than ResNet18.
Finally, like all deep learning models, UNetFormer’s performance depends on data quality and class balance. Urban datasets with rare classes (e.g., cars in UAVid) may still pose challenges without tailored loss functions or sampling strategies.
Summary
UNetFormer successfully bridges the gap between speed and accuracy in semantic segmentation for urban remote sensing. By integrating an efficient global-local attention decoder with flexible backbones, it offers a practical solution for real-world geospatial applications where latency, hardware constraints, and domain specificity matter. With its open-source implementation in GeoSeg, clear documentation, and support for major remote sensing datasets, UNetFormer empowers developers and researchers to quickly prototype, validate, and deploy high-performance segmentation pipelines—without reinventing the wheel.
For teams working on drone analytics, urban mapping, or environmental monitoring, UNetFormer represents a compelling balance of innovation, efficiency, and accessibility.