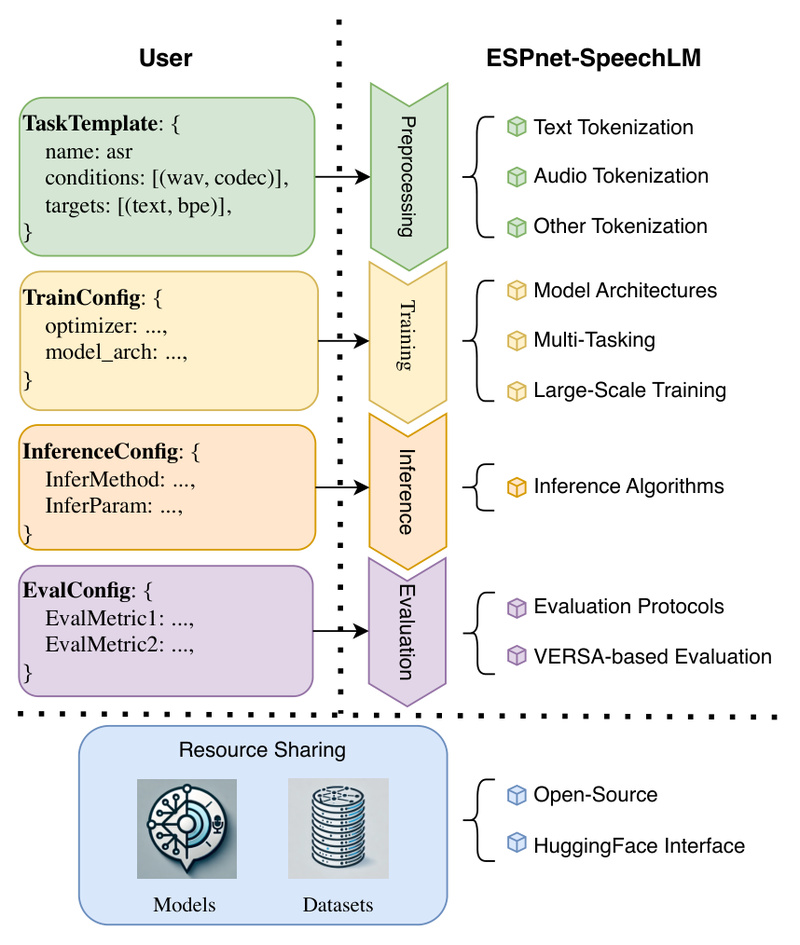
Building speech language models (SpeechLMs)—systems that jointly understand and generate both speech and text—is rapidly becoming essential for next-generation voice assistants, multimodal agents, and human-centric AI applications. However, the process is often fragmented, requiring custom pipelines for data handling, pre-training, inference, and evaluation across diverse speech tasks.
Enter ESPnet-SpeechLM: an open-source toolkit built on the mature ESPnet framework that standardizes the entire SpeechLM development lifecycle. Designed for both researchers and practitioners, it treats all speech processing tasks—from automatic speech recognition (ASR) to spoken language understanding (SLU)—as universal sequential modeling problems. This unification dramatically simplifies experimentation, deployment, and scaling, while ensuring full reproducibility through transparent, community-vetted recipes.
Whether you’re prototyping a 1.7B-parameter multimodal model or fine-tuning a lightweight voice agent, ESPnet-SpeechLM provides the structure, flexibility, and efficiency needed to turn ideas into working systems—without reinventing the wheel.
Why ESPnet-SpeechLM Stands Out
Unified Sequential Modeling for All Speech Tasks
Traditional speech toolkits often treat ASR, TTS, ST, and SLU as separate domains, each with its own data formats, training scripts, and evaluation protocols. ESPnet-SpeechLM eliminates this fragmentation by reframing every task as a sequence-to-sequence problem. This abstraction enables:
- Consistent data preprocessing pipelines
- Shared pre-training objectives across modalities (e.g., speech and text)
- Reusable inference and decoding strategies
- Unified evaluation metrics and benchmarking
As a result, you can pre-train a single model on mixed speech-text corpora and seamlessly adapt it to multiple downstream tasks—accelerating development and improving cross-task generalization.
End-to-End, Reproducible Workflow
ESPnet-SpeechLM delivers a cohesive workflow covering four critical stages:
- Data Preprocessing: Automatically handles audio-text alignment, tokenization, and feature extraction using ESPnet’s battle-tested Kaldi-style recipes.
- Pre-Training: Supports scalable pre-training of large models (including the demonstrated 1.7B-parameter architecture) on heterogeneous datasets.
- Inference: Offers flexible decoding options (e.g., beam search, streaming) with minimal configuration.
- Task Evaluation: Integrates standardized benchmarks for ASR, SLU, ST, and more, ensuring fair model comparison.
Every step is configurable through YAML-based recipes, and all components are open-sourced on GitHub, guaranteeing full transparency and reproducibility.
Flexibility Without Complexity
Despite its power, ESPnet-SpeechLM prioritizes usability. Users define high-level task templates (e.g., “speech-to-intent” for SLU or “text-to-speech” for TTS) and adjust key settings via intuitive configuration files. Under the hood, the toolkit automatically selects appropriate architectures—such as Transformers, Conformers, or RWKV—while abstracting away boilerplate code.
This design empowers teams to:
- Rapidly prototype new SpeechLM variants
- Share and reproduce experiments across institutions
- Scale from small academic datasets to industrial-scale corpora
Ideal Use Cases
ESPnet-SpeechLM is particularly valuable in the following scenarios:
- Multimodal Agent Development: Teams building voice-driven AI agents that must process spoken commands, reason over context, and generate natural responses benefit from the toolkit’s joint speech-text modeling capabilities.
- Research on Unified Speech Models: Researchers exploring cross-modal pre-training (e.g., training on LibriSpeech and Common Voice alongside text corpora) can leverage ESPnet-SpeechLM’s standardized data and training infrastructure.
- Production Voice Assistant Pipelines: Engineers deploying commercial voice interfaces can use the provided recipes to train, evaluate, and deploy competitive SpeechLMs—complete with support for speaker adaptation, multilingualism, and streaming inference.
The toolkit’s demonstration of a 1.7B-parameter model pre-trained on both speech and text tasks proves its capacity to support state-of-the-art systems, while its modular design ensures smaller projects remain equally well-served.
Getting Started
Starting with ESPnet-SpeechLM is straightforward:
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/espnet/espnetand switch to thespeechlmbranch. - Install dependencies via
pip install "espnet[all]"(PyTorch required). - Navigate to an example recipe (e.g.,
egs2/librispeech/speechlm1) and modify the configuration YAML to define your task template and model size. - Run training with a single command—the toolkit handles data loading, model construction, and logging automatically.
Pre-trained models and detailed documentation are available in the ESPnet Model Zoo, and all recipes are designed to run out-of-the-box on CPUs, GPUs, or multi-node clusters.
No deep expertise in speech processing is required—just a basic understanding of sequence modeling and configuration files.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While powerful, ESPnet-SpeechLM does come with realistic constraints:
- Learning Curve: Users new to the broader ESPnet ecosystem may need time to understand its recipe structure and data conventions. However, extensive tutorials and community support mitigate this barrier.
- Resource Requirements: Training large models (e.g., the 1.7B-parameter example) demands significant GPU memory and storage. For smaller teams, fine-tuning smaller variants or leveraging pre-trained checkpoints is recommended.
- Dependency on ESPnet: The toolkit inherits ESPnet’s architecture and conventions, which may limit interoperability with non-ESPnet pipelines.
That said, for users already in the ESPnet ecosystem—or those seeking a standardized, end-to-end solution—these trade-offs are well worth the gains in reproducibility and development speed.
Summary
ESPnet-SpeechLM solves a critical pain point in modern speech AI: the lack of a unified, reproducible framework for building speech language models. By standardizing data, training, and evaluation across tasks—and providing highly configurable yet intuitive workflows—it dramatically lowers the barrier to developing competitive, multimodal voice systems.
For researchers, developers, and teams building the next generation of voice-driven applications, ESPnet-SpeechLM isn’t just a toolkit—it’s a catalyst for faster, more reliable innovation in speech-language modeling.