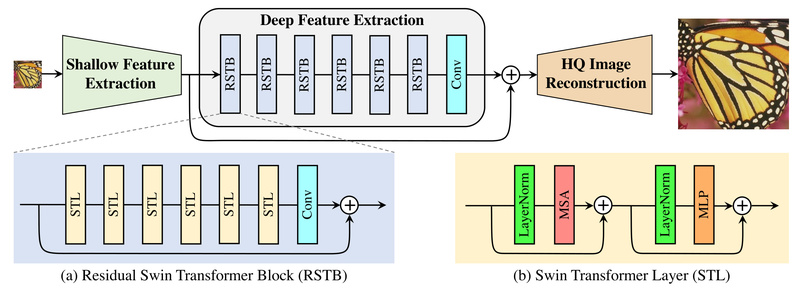
Image quality degradation—whether from compression, noise, or low resolution—is a persistent challenge across industries ranging from medical imaging to consumer photography. Traditional deep learning approaches rely heavily on convolutional neural networks (CNNs), but a new generation of models is proving that vision transformers can deliver superior results with greater efficiency. Enter SwinIR: a powerful, open-source image restoration framework built on the Swin Transformer architecture.
SwinIR isn’t just another academic prototype—it’s a practical, battle-tested solution that consistently outperforms prior methods across multiple low-level vision tasks while using up to 67% fewer parameters. Whether you’re enhancing surveillance footage, restoring archival photos, or building a mobile photo-editing app, SwinIR offers a ready-to-deploy toolkit that balances performance, flexibility, and resource efficiency.
What Problems Does SwinIR Solve?
In real-world applications, images often suffer from one or more of the following issues:
- Low resolution: Images appear blurry or pixelated when upscaled—common in legacy media, satellite imagery, or mobile-captured photos.
- Noise: Grain or speckles degrade image clarity, especially in low-light conditions (e.g., smartphone night mode or medical scans).
- JPEG compression artifacts: Blocky distortions and color bleeding occur when images are heavily compressed—a frequent problem in web publishing and streaming.
SwinIR directly addresses these pain points through a unified architecture that handles super-resolution, denoising, and compression artifact reduction—all without requiring you to train separate models for each task.
Core Capabilities and Supported Tasks
SwinIR is designed around three major image restoration scenarios, each with tailored model variants:
1. Image Super-Resolution (SR)
SwinIR supports three SR settings:
- Classical SR: Upscaling images degraded by idealized bicubic downsampling.
- Lightweight SR: Optimized for edge devices with a compact “SwinIR-S” model (ideal for mobile apps).
- Real-World SR: Handles complex, realistic degradations using the BSRGAN degradation model—crucial for enhancing user-uploaded photos that don’t follow synthetic assumptions.
2. Image Denoising
- Grayscale denoising: For scientific or historical images.
- Color denoising: For natural photos across varying noise levels (e.g., ISO 1600–6400 equivalents).
3. JPEG Compression Artifact Reduction
- Works on both grayscale and color images.
- Uses a window size of 7 (aligned with JPEG’s 8×8 block structure) for optimal artifact suppression.
Each task comes with pretrained models that automatically download when you run the provided inference scripts—no dataset preparation required for basic usage.
Why SwinIR Stands Out
SwinIR’s architecture combines the global modeling power of transformers with the efficiency of shifted window attention, a key innovation from the Swin Transformer. This design enables:
- Higher restoration quality: Gains of 0.14–0.45 dB in PSNR over state-of-the-art CNN-based methods.
- Reduced model size: Up to 67% fewer parameters than comparable models like RCAN, lowering storage and memory overhead.
- Scalable deployment: Choose from small (S), middle (M), and large (L) model sizes based on your hardware constraints and quality requirements.
For example, the lightweight SwinIR-S variant delivers strong performance with minimal compute, while SwinIR-L achieves maximum fidelity for high-stakes applications like medical or forensic imaging.
Getting Started in Minutes
You don’t need deep expertise in transformers to use SwinIR. The repository provides:
- Pretrained models for all major tasks, automatically fetched during inference.
- Simple command-line scripts to run restoration on your own images. For instance:
python main_test_swinir.py --task real_sr --scale 4 --model_path model_zoo/swinir/003_realSR_BSRGAN_DFO_s64w8_SwinIR-M_x4_GAN.pth --folder_lq your_lowres_images/
- Ready-to-use demos:
- A Colab notebook for browser-based testing (no GPU required).
- A PlayTorch demo for integrating SwinIR into React Native mobile apps.
Even without training data, you can test SwinIR on the included testsets (~20 MB) or your own images immediately.
Practical Limitations to Consider
While SwinIR excels in quality and efficiency, be mindful of these trade-offs:
- Memory usage: Large images may exceed GPU memory. Use the
--tileoption to process images in chunks (e.g.,--tile 400). - Inference speed: Slower than some CNNs (e.g., RCAN takes 0.18s vs. SwinIR’s 0.54s on a 256×256 image)—a consideration for real-time systems.
- Real-world SR dependency: The real-world super-resolution models assume degradation aligned with the BSRGAN model; results may vary on images with unknown or atypical distortions.
Summary
SwinIR redefines what’s possible in image restoration by merging transformer-based global reasoning with practical engineering considerations. It offers higher quality, smaller models, and broader task coverage than most alternatives—all while being open-source, well-documented, and easy to integrate. For developers, researchers, and engineers looking to enhance image quality without reinventing the wheel, SwinIR is a compelling, production-ready choice that lowers the barrier to professional-grade restoration.