Creating lifelike, animated human faces used to require complex pipelines—motion capture rigs, professional voice actors, or hours of post-production. But what if you could generate high-fidelity portrait animations using only a still photo and an audio file? That’s exactly what AniPortrait delivers.
AniPortrait is an open-source framework developed by researchers at Tencent that synthesizes temporally smooth, photorealistic talking-head videos directly from a reference portrait image and an audio clip. Unlike traditional methods that demand extensive datasets or specialized hardware, AniPortrait simplifies the process into a lightweight, controllable workflow—ideal for developers, content creators, and product teams exploring AI-driven media generation.
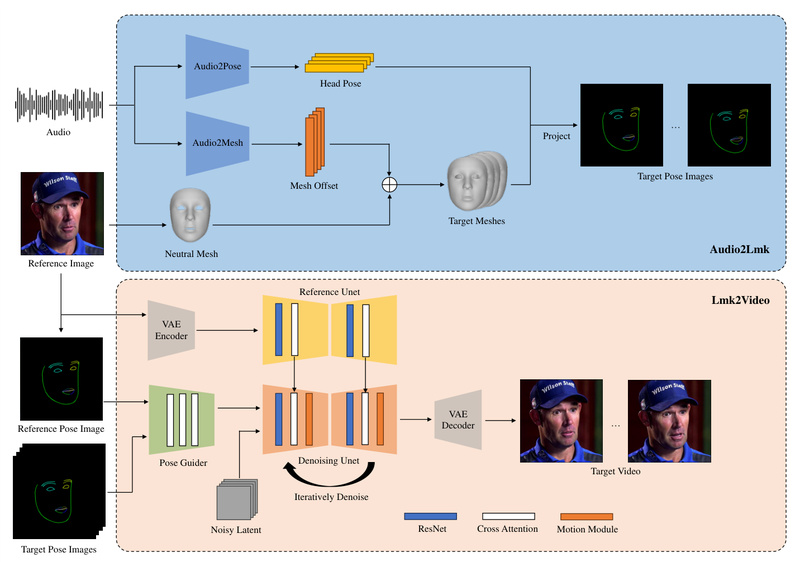
The core innovation lies in its two-stage pipeline: first, it converts audio into 3D facial motion representations and projects them into a sequence of 2D facial landmarks; then, a diffusion-based generator—enhanced with a dedicated motion module—renders these landmarks into coherent, high-resolution video frames that preserve identity, expression, and lip-sync accuracy. The result? Natural, expressive animations that feel authentic, not robotic.
Key Capabilities That Enable Real-World Adoption
Audio-to-Video Synthesis from a Single Image
At its most basic, AniPortrait takes one front-facing portrait image and an audio recording (e.g., speech or narration) and outputs a synchronized talking-head video. This eliminates the need for source video footage—making it perfect for generating avatars from profile pictures or historical photos.
Face Reenactment with Pose Flexibility
Beyond audio-driven animation, AniPortrait supports face reenactment: you provide a source video (which defines the target motion and head pose) and a reference image (which defines the identity), and the model transfers the motion onto the new face. Recent updates enable handling of significant pose differences between the source video and reference image—greatly expanding creative control.
Explicit Head Pose Control
Want your AI avatar to nod, tilt, or turn while speaking? AniPortrait allows head pose control via a pose template (a .npy file generated from a short reference video). This decouples facial expression from head motion, enabling expressive animations that go beyond lip-syncing.
Accelerated Inference with Frame Interpolation
Generating high-quality videos can be slow. AniPortrait addresses this with a built-in frame interpolation module (enabled via the -acc flag). By leveraging a lightweight FILM network (film_net_fp16.pt), it reduces generation time without sacrificing visual quality—critical for rapid prototyping or iterative design.
Interactive Demo via Gradio
For quick experimentation, the project includes a Gradio web interface. With a single command (python -m scripts.app), users can test audio-driven animation, face reenactment, or head pose control in a browser—no coding required. An official demo is also hosted on Hugging Face Spaces.
Practical Applications Across Industries
AniPortrait isn’t just a research novelty—it solves tangible problems:
- AI Avatars & Virtual Assistants: Generate personalized, expressive agents for customer service, education, or gaming using only a user-uploaded photo and text-to-speech audio.
- Dubbing & Localization: Automatically animate faces in dubbed videos so lip movements match translated dialogue—without reshooting scenes.
- Low-Budget Content Creation: Indie creators can produce animated explainers, narrated tutorials, or interactive stories without hiring talent or renting studios.
- Digital Heritage & Accessibility: Bring historical figures to life using archival photos and synthetic speech, or create sign-language avatars with synchronized facial expressions.
These use cases share a common thread: reducing dependency on live performers while maintaining emotional realism.
Getting Started: A Streamlined Evaluation Workflow
AniPortrait is designed for usability from day one:
- Prepare Inputs: Gather a clean, frontal portrait image (preferably with neutral expression) and a clear audio file (
.wavrecommended). - Choose a Mode: Decide between:
- Audio-driven (
scripts/audio2vid) - Self-driven (animate the reference image using its own motion, via
scripts/pose2vid) - Face reenactment (
scripts/vid2vid)
- Audio-driven (
- Configure: Edit the corresponding YAML config file (e.g.,
animation_audio.yaml) to point to your assets. - Run Inference: Execute the command with optional flags like
-W 512 -H 512 -accfor resolution and acceleration. - Optional Pose Control: Generate a custom
pose_temp.npyfrom a short video clip usingscripts.generate_ref_poseto dictate head movement.
Pretrained models—including Stable Diffusion v1.5 backbone, wav2vec2 for audio encoding, and custom motion modules—are provided, so you don’t need to train from scratch.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While powerful, AniPortrait has real-world constraints that evaluators should consider:
- Model Size & Dependencies: You’ll need to download ~2–3 GB of weights, including Stable Diffusion v1.5 components, VAE, image encoder, and audio models. Disk space and bandwidth matter.
- Input Quality Sensitivity: Best results require front-facing, well-lit reference images and clear, noise-free audio. Profile views or muffled speech degrade output quality.
- Hardware Requirements: Inference relies on GPU acceleration (CUDA 11.7+ recommended). Even with
-acc, generation can take minutes per second of video on consumer hardware. - Pose Retargeting Complexity: In face reenactment, extreme pose mismatches may still require manual pose template tuning for optimal alignment.
These aren’t dealbreakers—but they inform whether AniPortrait fits your infrastructure and quality bar.
Summary
AniPortrait stands out as a practical, open-source solution for photorealistic portrait animation driven by audio or video. By combining audio-to-pose modeling with diffusion-based rendering, it delivers expressive, temporally consistent results without complex pipelines. Its support for head pose control, face reenactment, and accelerated inference makes it adaptable across entertainment, education, and human-AI interaction. While it demands careful input preparation and GPU resources, the payoff—a lifelike animated face from a single image and voice—can transform how teams approach digital character creation. For technical decision-makers seeking to prototype or deploy talking-head generation, AniPortrait is a compelling starting point.