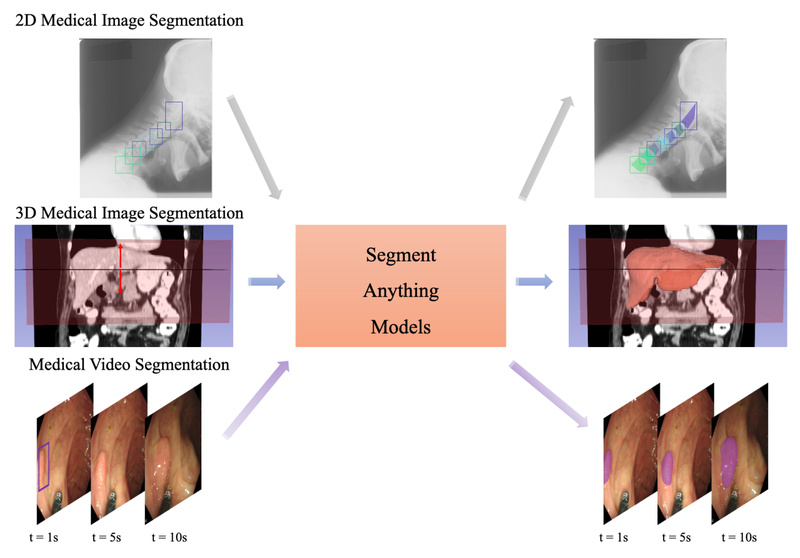
Medical image segmentation—the process of delineating anatomical structures or pathologies in scans like CT, MRI, or ultrasound—is foundational to diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical navigation. Yet, deploying robust, general-purpose segmentation tools in clinical or research settings has historically required massive annotated datasets and specialized deep learning expertise.
Enter MedSAM (Segment Anything in Medical Images): an open-source, prompt-based segmentation model built by fine-tuning Meta’s Segment Anything Model (SAM) specifically for medical imaging. Unlike generic foundation models that struggle with the unique intensity distributions, low contrast, and domain-specific semantics of clinical data, MedSAM delivers high-quality segmentation across 11 medical modalities, including 2D/3D images and videos—right out of the box.
Designed with both researchers and technical product teams in mind, MedSAM combines the flexibility of prompt-driven inference with the reliability needed for real-world medical applications. Whether you’re prototyping a radiology annotation tool or building an AI assistant for intraoperative guidance, MedSAM offers a rare blend of performance, accessibility, and deployment readiness.
Why General-Purpose SAM Falls Short in Medicine—And How MedSAM Fixes It
The original Segment Anything Model (SAM) revolutionized natural image segmentation by enabling zero-shot inference from points, boxes, or text prompts. However, when applied directly to medical images, SAM often fails due to fundamental differences:
- Medical scans are often grayscale, lack texture, and exhibit modality-specific intensity ranges (e.g., Hounsfield units in CT).
- Anatomical structures may appear with low contrast or ambiguous boundaries.
- Domain shift between natural photos and clinical data leads to poor generalization.
MedSAM addresses these gaps through domain-specific fine-tuning on diverse medical datasets. The result? A model that retains SAM’s interactive, prompt-based interface while achieving significantly higher accuracy on clinical data—without requiring users to curate large labeled datasets from scratch.
Recent updates (MedSAM2, released April 2025) extend support to 3D volumetric data and medical videos, making it one of the few open models capable of consistent temporal and spatial segmentation in dynamic or multi-slice scenarios.
Key Features That Make MedSAM Developer- and Clinician-Friendly
MedSAM isn’t just accurate—it’s built for real-world usability. Here’s what sets it apart:
Multiple Inference Interfaces for Every Workflow
- Command line: Run inference in seconds with
python MedSAM_Inference.py -i input.jpg -o output.png --box x1 y1 x2 y2. - GUI: A lightweight PyQt-based interface lets clinicians or annotators draw bounding boxes interactively—no coding required.
- Jupyter Notebook: Step-by-step tutorials (including on Colab) enable rapid experimentation and integration into data pipelines.
- 3D Slicer Plugin & Gradio API: For hospital IT teams or research labs, MedSAM integrates directly into clinical visualization platforms and web services.
Speed Optimizations for Practical Deployment
The introduction of LiteMedSAM (January 2024) delivers a 10x inference speedup over the original model—critical for time-sensitive applications like intraoperative imaging or large-scale screening.
Pre-Trained and Ready to Use
MedSAM provides publicly available checkpoints trained on multi-organ abdominal CT scans (from the MICCAI FLARE22 challenge). Users can skip training entirely and start segmenting immediately—ideal for proof-of-concept validation or MVP development.
Ideal Use Cases for Technical Teams and Researchers
MedSAM shines in scenarios where interactive, precise, and rapid segmentation is needed, but full automation isn’t feasible—or desirable. Consider these applications:
- Rapid annotation tooling: Accelerate label generation for new medical AI datasets by letting human experts provide simple bounding boxes instead of pixel-perfect masks.
- Clinical decision support: Embed MedSAM into radiology workflows to segment organs (e.g., liver, kidneys, tumors) on-demand during review sessions.
- Challenge participation: Leverage MedSAM as a strong baseline for competitions like the CVPR 2024 “MedSAM on Laptop” or CVPR 2025’s interactive 3D segmentation challenges.
- Edge deployment prototyping: Use LiteMedSAM to test feasibility of lightweight AI tools on portable or resource-constrained devices in point-of-care settings.
Because MedSAM supports bounding box prompts (rather than requiring complex contour drawing), it aligns well with clinician behavior—making adoption smoother in real clinical environments.
Getting Started Is Simpler Than You Think
You don’t need a PhD in deep learning—or a GPU cluster—to use MedSAM. Here’s the minimal path to your first segmentation:
-
Set up the environment:
conda create -n medsam python=3.10 -y conda activate medsam pip install torch torchvision # PyTorch 2.0+ git clone https://github.com/bowang-lab/MedSAM cd MedSAM && pip install -e .
-
Download the pre-trained checkpoint (e.g.,
medsam_vit_b) and place it in your working directory. -
Run inference:
- Via command line on any image with a bounding box.
- Via
gui.pyfor interactive exploration. - Via
tutorial_quickstart.ipynbfor programmatic integration.
Training from scratch is optional—and only recommended if you have access to multi-GPU resources (the official training used 20 A100 GPUs). For most teams, fine-tuning isn’t necessary to achieve strong results.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While MedSAM is powerful, it’s not a magic bullet. Keep these constraints in mind:
- Prompt dependency: MedSAM requires at least a bounding box to generate a mask—it is not fully automatic. This is by design (to ensure clinical controllability), but may not suit fully unsupervised pipelines.
- Training resource intensity: Re-training or fine-tuning on new modalities demands significant GPU memory and compute—likely beyond a single workstation for large 3D datasets.
- Modality coverage: Although benchmarked on 11 modalities, performance on rare or highly specialized imaging types (e.g., histopathology, OCT) may vary. Always validate on your target domain.
- No native text prompting (yet): Unlike newer multimodal models, MedSAM currently relies on spatial prompts (boxes/points), not natural language.
These trade-offs reflect a pragmatic balance: MedSAM prioritizes reliability, speed, and ease of integration over speculative generality.
Summary
MedSAM bridges the gap between foundation models and clinical reality. By adapting SAM to the nuances of medical imaging—and packaging it with GUIs, APIs, and speed-optimized variants—it empowers technical teams to deploy high-quality segmentation without months of model development. Whether you’re in a research lab, a health tech startup, or a hospital innovation unit, MedSAM offers a rare combination of scientific rigor, open accessibility, and real-world practicality.
If your project involves medical image analysis and could benefit from interactive, accurate, and ready-to-deploy segmentation, MedSAM is well worth a try.