For teams building real-world AI applications that combine vision and language—whether it’s parsing scanned documents, analyzing instructional videos, or creating interactive agents—efficiency and capability must go hand in hand. Enter Kimi-VL, an open-source vision-language model (VLM) developed by Moonshot AI that delivers state-of-the-art multimodal reasoning while activating just 2.8 billion parameters during inference.
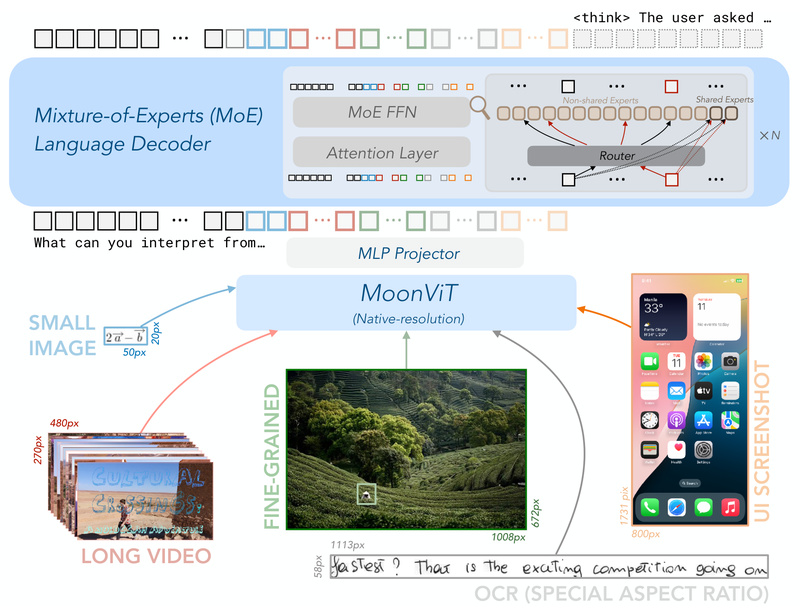
Unlike proprietary alternatives such as GPT-4o, Kimi-VL is fully open, enabling full control, customization, and deployment without vendor lock-in. Built on a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture and powered by the MoonViT native-resolution vision encoder, Kimi-VL excels across diverse tasks—from college-level visual math to navigating desktop environments like a human user—without the computational bloat of dense 10B+ models.
With a 128K-token context window, support for ultra-high-resolution images (up to 1792×1792), and specialized variants for both general perception and deep reasoning, Kimi-VL offers a rare balance: high performance, low inference cost, and full transparency.
Why Kimi-VL Stands Out
1. Efficient MoE Architecture with Strong Capabilities
Kimi-VL’s language decoder is a 16-billion-parameter MoE model, but only ~3B parameters are activated per query. This design dramatically reduces memory and compute requirements during inference while preserving advanced reasoning power. For engineering teams managing cost-sensitive deployments—especially on edge devices or in cloud environments with strict quotas—this efficiency is transformative.
Despite its lean active footprint, Kimi-VL competes with or outperforms larger models like Qwen2.5-VL-7B, Gemma-3-12B-IT, and even GPT-4o-mini on specialized benchmarks, including:
- MathVista (80.1) and MathVision (56.9) for visual math reasoning
- InfoVQA (83.2) for document understanding with dense text
- LongVideoBench (64.5) for long-form video comprehension
- OSWorld (52.5) for interactive desktop agent tasks
2. Native High-Resolution Vision Understanding
Most VLMs downscale images before processing, losing critical details in diagrams, maps, or dense documents. Kimi-VL uses MoonViT, a vision encoder that processes images at native resolution, supporting up to 3.2 million pixels per image (1792×1792)—4× higher than its initial release.
This capability enables reliable OCR, fine-grained object recognition, and accurate grounding in UI navigation tasks, as demonstrated by its 52.8 score on ScreenSpot-Pro and 83.2 on the V* Benchmark—all without external tools.
3. 128K Context for Long and Complex Inputs
Kimi-VL handles long multimodal sequences with ease. Whether it’s a 50-page PDF, a 10-minute instructional video, or a multi-turn agent session with image and text history, the 128K-token context window ensures coherent understanding across the entire input. This makes it uniquely suited for:
- Legal or financial document analysis
- Academic paper summarization with figures
- Video surveillance timeline reasoning
- Multi-step software automation via visual feedback
4. Two Optimized Variants for Different Needs
Kimi-VL offers two main model variants, both with 16B total parameters and 3B activated:
- Kimi-VL-A3B-Instruct: Optimized for general perception, OCR, and fast responses. Use with
temperature=0.2. - Kimi-VL-A3B-Thinking-2506: Enhanced with long chain-of-thought (CoT) fine-tuning and reinforcement learning, this version excels at complex reasoning, problem-solving, and video comprehension. Use with
temperature=0.8.
Notably, the 2506 Thinking variant doesn’t sacrifice general performance—it matches or exceeds the Instruct version on benchmarks like MMBench (84.4) and RealWorldQA (70.0), while also setting new open-source records on VideoMMMU (65.2).
Practical Use Cases for Your Projects
Kimi-VL isn’t just a research prototype—it’s engineered for real-world deployment:
- Document Intelligence: Extract and reason over text, tables, and diagrams in scanned contracts, academic papers, or invoices using its strong OCR and long-context capabilities.
- AI Agents for Desktop Automation: Build agents that interpret UI screenshots and perform multi-step tasks (e.g., filling forms, debugging workflows) via the OSWorld framework.
- Educational Tools: Solve visual math problems, explain scientific diagrams, or tutor students using step-by-step reasoning.
- Video Analysis: Summarize long videos, detect anomalies in surveillance footage, or extract procedural steps from tutorials.
- Multi-Image Comparison: Analyze before/after medical scans, architectural revisions, or product design iterations.
Getting Started Is Straightforward
Kimi-VL integrates seamlessly with standard open-source tooling:
Inference with Hugging Face Transformers
Load the model in just a few lines using transformers. Support for FlashAttention-2 further reduces memory usage and speeds up generation.
Fine-Tuning with LLaMA-Factory
Customize Kimi-VL on your domain data using LoRA—achievable on a single GPU with 50GB VRAM. Full fine-tuning is also supported via DeepSpeed ZeRO-2 across multiple GPUs.
Production Deployment via vLLM
Deploy Kimi-VL at scale with vLLM, which supports:
- Offline batch inference
- OpenAI-compatible API servers (enabling drop-in replacement for GPT-4o in your apps)
- Configurable multi-image limits (up to 512 images per prompt) and extended context handling
This ecosystem ensures you can prototype quickly, iterate with fine-tuning, and deploy reliably—all without leaving the open-source stack.
Current Limitations and Best Practices
While Kimi-VL is highly capable, practical deployment requires awareness of its constraints:
- Total model size is 16B parameters, so GPU memory must accommodate the full model (though only ~3B activate per token).
- High-resolution or long-context inputs benefit from ≥24GB VRAM and FlashAttention-2 for optimal speed.
- For reasoning-heavy tasks (e.g., math, logic puzzles), always use the Thinking-2506 variant with
temperature=0.8. - For fast, factual responses (e.g., OCR, object identification), use the Instruct variant with
temperature=0.2.
Performance gains assume proper environment setup—Python 3.10, PyTorch 2.5.1, and Transformers 4.51.3 are recommended.
Why Choose Kimi-VL Over Alternatives?
Compared to closed models like GPT-4o or larger open models like Qwen2.5-VL-7B, Kimi-VL offers a compelling value proposition:
- Open and inspectable: Full code and weights on GitHub—no black-box surprises.
- More efficient: 3B active parameters vs. 7B–12B dense models, reducing inference cost by 2–4×.
- Stronger in key domains: Outperforms GPT-4o on InfoVQA, MathVista, and OS agent tasks.
- Future-proof: Actively maintained with community tooling (vLLM, LLaMA-Factory) and new capabilities like video support.
For teams that need production-ready, high-accuracy multimodal AI without the cost or opacity of proprietary APIs, Kimi-VL is a strategic choice.
Summary
Kimi-VL redefines what’s possible for efficient, open-source vision-language models. By combining a sparse MoE architecture, native-resolution vision, and a 128K context window, it delivers flagship-level performance on real-world tasks—from document parsing to desktop automation—while keeping resource demands manageable. With robust tooling for inference, fine-tuning, and deployment, it empowers engineers and researchers to build, adapt, and scale multimodal applications with confidence. If you’re evaluating VLMs for your next project, Kimi-VL deserves serious consideration.