Multimodal AI models like OpenAI’s CLIP have transformed how developers build systems that understand both images and text. But there’s a catch: these models are trained primarily on English-language data. When applied to Chinese-language applications—like e-commerce search, content moderation, or user-generated image tagging—standard CLIP models often underperform due to language mismatch.
Chinese CLIP solves this problem head-on. Developed by OFA-Sys, it’s a vision-language foundation model explicitly pre-trained on approximately 200 million Chinese image-text pairs. Built on the proven CLIP architecture but optimized for Chinese, it enables zero-shot image-text retrieval, cross-modal search, and zero-shot image classification—all without requiring any labeled training data for your specific task.
For teams working on Chinese-language products or research, Chinese CLIP removes the biggest barrier to deploying multimodal AI: the need for large, task-specific labeled datasets. Instead, you can leverage rich semantic alignment between Chinese text and images out of the box.
Why Chinese CLIP Stands Out
Built for Chinese, Not an Afterthought
Unlike generic multilingual models that treat Chinese as one of many languages, Chinese CLIP is purpose-built for the Chinese linguistic and visual context. Its training data comes from large-scale, publicly available Chinese image-text datasets, ensuring culturally and linguistically relevant embeddings.
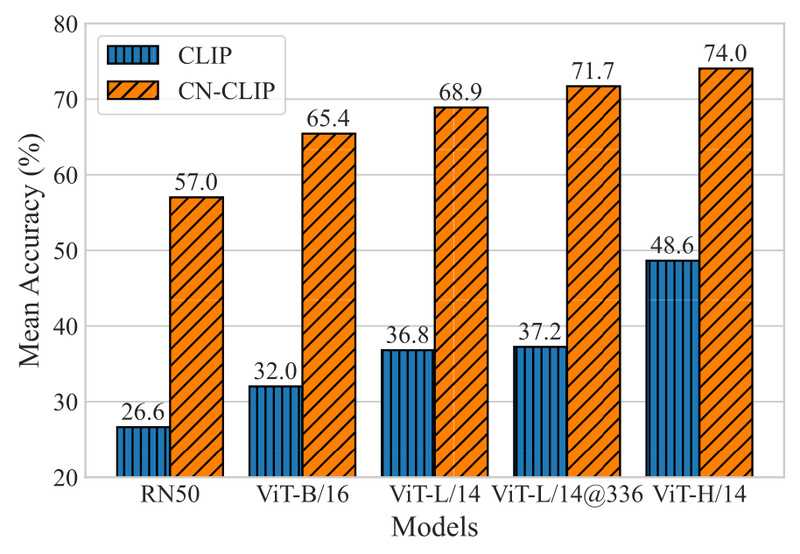
This focus pays off: Chinese CLIP consistently outperforms other Chinese vision-language models (like Wukong and R2D2) on standard benchmarks such as MUGE, Flickr30K-CN, and COCO-CN—both in zero-shot and fine-tuned settings.
Flexible Model Sizes for Real-World Constraints
Not every project has access to high-end GPUs or cloud budgets. Chinese CLIP offers five model variants, ranging from lightweight to large-scale:
- chinese-clip-rn50 (77M parameters) – ideal for edge or mobile deployment
- chinese-clip-vit-base-patch16 (188M)
- chinese-clip-vit-large-patch14 (406M)
- chinese-clip-vit-large-patch14-336px (407M, higher resolution)
- chinese-clip-vit-huge-patch14 (958M) – for maximum accuracy
This allows teams to trade off performance versus resource usage based on their specific needs.
Two-Stage Pretraining for Better Alignment
Behind the scenes, Chinese CLIP uses a two-stage training strategy:
- First, the vision encoder is frozen, and only the text encoder is trained.
- Then, all parameters are jointly optimized.
This approach stabilizes early training and leads to stronger cross-modal alignment, especially critical when working with a high-resource language pair like Chinese text and images.
Practical Use Cases for Teams
Chinese CLIP isn’t just a research artifact—it’s designed for production-ready applications. Here’s how teams can use it today:
1. Chinese E-Commerce Visual Search
Allow users to search product catalogs using natural Chinese queries like “红色连衣裙 with 蕾丝袖子” and instantly retrieve matching images—no manual tagging required.
2. Content Moderation for Chinese Social Platforms
Automatically detect mismatches between image content and user-provided Chinese captions (e.g., misleading or harmful posts) by measuring semantic similarity.
3. Zero-Label Image Tagging
Generate descriptive Chinese tags for user-uploaded photos in apps or archives, enabling organization and search without any labeled data.
4. Multimodal Assistants for Chinese Users
Build AI systems that understand prompts like “找出这张图里穿蓝色衣服的人” by jointly processing image features and Chinese instructions.
These scenarios share a common thread: they require robust understanding of Chinese language in visual contexts, and they benefit from zero-shot capabilities—exactly where Chinese CLIP excels.
Getting Started in Minutes
Adopting Chinese CLIP is straightforward, especially if you’re already familiar with the original CLIP API.
Installation
Install the official package via pip:
pip install cn_clip
Basic Inference
Load a pre-trained model and compute similarity between an image and Chinese text prompts:
import torch
from PIL import Image
import cn_clip.clip as clip
from cn_clip.clip import load_from_name
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model, preprocess = load_from_name("ViT-B-16", device=device, download_root='./')
model.eval()
image = preprocess(Image.open("photo.jpg")).unsqueeze(0).to(device)
text = clip.tokenize(["杰尼龟", "皮卡丘", "小火龙"]).to(device)
with torch.no_grad():image_features = model.encode_image(image)text_features = model.encode_text(text)# Normalize featuresimage_features /= image_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)text_features /= text_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)# Compute similaritylogits_per_image, _ = model.get_similarity(image, text)probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=-1).cpu().numpy()
print("Predicted probabilities:", probs)
The model automatically downloads weights from ModelScope or Hugging Face on first use. The API mirrors OpenAI’s CLIP, so migration is seamless.
Deployment-Ready Optimizations
For production, Chinese CLIP supports:
- ONNX and TensorRT export for accelerated inference
- FlashAttention to reduce memory and speed up training
- Gradient checkpointing for large-batch training under memory constraints
These features significantly lower the barrier to deploying at scale.
Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, Chinese CLIP has practical constraints to consider:
- Language specificity: It is optimized only for Chinese. Performance on English or other languages is not guaranteed.
- Fine-tuning complexity: Although inference is simple, full fine-tuning requires converting datasets into LMDB format with base64-encoded images and JSONL text annotations—a non-trivial preprocessing step.
- High-resolution models (e.g., ViT-L/14-336) demand significant GPU memory, which may limit use on consumer hardware.
- Training from scratch is not practical without access to large-scale Chinese image-text data and distributed infrastructure.
For most teams, however, using the pre-trained models out of the box is sufficient for high-impact applications.
Summary
Chinese CLIP bridges a critical gap in the multimodal AI ecosystem: it brings the power of contrastive vision-language learning to Chinese-language applications without requiring labeled data. With multiple model sizes, strong zero-shot performance, and production-ready tooling, it’s a practical choice for developers, researchers, and product teams building AI systems for Chinese users.
Whether you’re enhancing search, automating moderation, or enabling new multimodal interactions, Chinese CLIP gives you a head start—right out of the box.