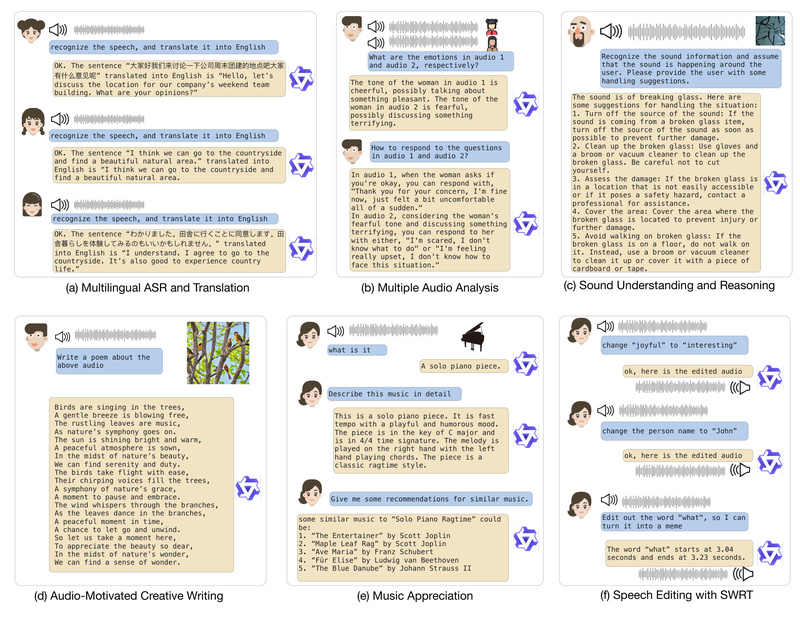
Audio is one of the richest yet most fragmented modalities in artificial intelligence. Traditional systems often require separate models for speech recognition, sound classification, music analysis, or audio captioning—each trained on isolated datasets and fine-tuned for narrow tasks. This fragmentation increases engineering complexity, maintenance costs, and deployment latency.
Enter Qwen-Audio, a universal audio-language model developed by Alibaba Cloud as part of the Qwen (Tongyi Qianwen) large model series. Unlike conventional approaches, Qwen-Audio is designed from the ground up to understand diverse audio types—including human speech, natural sounds, music, and songs—within a single, unified architecture. Remarkably, it achieves state-of-the-art results across more than 30 audio tasks without any task-specific fine-tuning, offering a true “one model fits (almost) all” solution for audio understanding.
For technical decision-makers evaluating multimodal AI systems, Qwen-Audio represents a significant leap toward simplifying audio processing pipelines while delivering robust, generalizable performance.
Why Qwen-Audio Stands Out
A Truly Universal Audio Foundation
Most audio models today are specialists: one for transcription, another for emotion detection, yet another for instrument identification. Qwen-Audio breaks this pattern by unifying these capabilities into a single pretrained model. It accepts both audio and text inputs and outputs natural language responses, enabling cross-task reasoning and knowledge transfer.
This universality stems from its large-scale pretraining on a heterogeneous mix of over 30 audio-related tasks, covering multiple languages and audio domains. Instead of treating each dataset in isolation, Qwen-Audio uses a hierarchical multi-task training framework that conditions the decoder on structured tags (e.g., task type, language, audio category). This design encourages knowledge sharing while preventing interference between dissimilar tasks—a critical innovation that enables stable, high-quality performance across diverse benchmarks.
State-of-the-Art Performance Out of the Box
Qwen-Audio doesn’t just claim versatility—it delivers results. On widely accepted benchmarks, it consistently outperforms or matches specialized models:
- ASR: Achieves 1.2% WER on Aishell1 (dev) and 1.3% on test, setting a new SOTA.
- Sound Classification: Reaches 79.5% accuracy on Cochlscene, far surpassing prior work.
- Vocal Sound Recognition: Hits 92.89% accuracy on VocalSound, a dramatic improvement over CLAP (49.45%) and Pengi (60.35%).
- Audio Question Answering: Scores 74.9% on binary ClothoAQA, demonstrating strong reasoning over audio content.
- Speech-to-Text Translation: Delivers strong BLEU scores across seven language pairs in CoVoST2, including 41.5 for en→zh.
Crucially, these results are achieved without task-specific fine-tuning, making Qwen-Audio immediately useful in production scenarios where retraining isn’t feasible.
Two Models for Two Use Cases
The Qwen-Audio series includes two variants tailored to different needs:
- Qwen-Audio (Base): A pretrained multi-task audio understanding model built by initializing the language decoder from Qwen-7B and the audio encoder from Whisper-large-v2. Ideal for batch inference, evaluation, or custom downstream adaptation.
- Qwen-Audio-Chat: An instruction-tuned, conversational agent that supports multi-turn dialogues with mixed audio and text inputs. Perfect for interactive applications like voice assistants, accessibility tools, or audio analysis dashboards.
Both models support multiple audio inputs in a single query and can reason about timing, semantics, and context—e.g., answering “When does the bird chirp start?” or “What instrument plays the melody?”
Real-World Applications for Technical Teams
Qwen-Audio’s generalization capabilities translate into tangible engineering and product advantages:
- Unified Voice Assistants: Build assistants that not only transcribe speech but also recognize background sounds (e.g., “Is that a fire alarm?”) and respond contextually—without integrating separate sound classifiers.
- Automated Audio Captioning: Generate rich, descriptive captions for videos, podcasts, or surveillance footage to improve accessibility and searchability.
- Customer Experience Analytics: Analyze support call recordings for emotion (via MELD benchmark performance), key phrases, and speaker intent in a single pass.
- Multilingual Meeting Transcription & Translation: Transcribe and translate cross-language meetings in real time using one model instead of chaining ASR + MT systems.
- Music & Creative Tools: Identify instruments, analyze musical structure, or answer questions like “What key is this song in?” using the NSynth benchmark capabilities.
By replacing multiple specialized models with one general-purpose system, teams reduce infrastructure overhead, simplify version control, and accelerate iteration.
Getting Started in Minutes
Qwen-Audio is designed for easy adoption. Official support is provided via Hugging Face Transformers and ModelScope, with clear examples for both inference and chat.
Basic Inference with Qwen-Audio (Base)
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen-Audio", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen-Audio", device_map="cuda", trust_remote_code=True
).eval()
audio_path = "sample.flac"
prompt = "<|startoftranscription|><|en|><|transcribe|><|en|><|notimestamps|><|wo_itn|>"
query = f"<audio>{audio_path}</audio>{prompt}"
audio_info = tokenizer.process_audio(query)
inputs = tokenizer(query, return_tensors='pt', audio_info=audio_info).to(model.device)
output = model.generate(**inputs, audio_info=audio_info)
response = tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=False, audio_info=audio_info)
print(response)
Interactive Dialogue with Qwen-Audio-Chat
query = tokenizer.from_list_format([{'audio': 'meeting_clip.wav'},{'text': 'What language is being spoken, and what is the main topic?'}
])
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, query=query, history=None)
print(response)
# Follow-up: "Summarize the key decisions made."
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, "Summarize the key decisions made.", history=history)
Requirements are standard: Python ≥3.8, PyTorch ≥1.12, and FFmpeg for audio preprocessing. Full evaluation scripts are publicly available to reproduce all benchmark results.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While powerful, Qwen-Audio has realistic constraints that technical evaluators should consider:
- Audio Length: Optimized for clips under 30 seconds. Longer inputs may degrade performance or increase memory usage significantly.
- Hardware: Requires a CUDA-capable GPU for efficient inference (BF16/FP16 recommended). CPU-only mode is supported but slow for real-time use.
- Memory Footprint: Based on Qwen-7B, the model demands substantial VRAM (~14–20 GB depending on precision).
- No Built-in Streaming: Designed for offline or chunked processing, not real-time streaming ASR.
These limitations are typical for large multimodal models, but they mean Qwen-Audio is best suited for batch processing, on-demand analysis, or conversational applications with bounded audio inputs—not always-on embedded systems.
Summary
Qwen-Audio redefines what’s possible in audio-language modeling by delivering broad, high-quality understanding across speech, sound, and music in a single, pretrained system. Its ability to excel on diverse tasks without fine-tuning solves a critical pain point in audio AI: the costly, fragile ecosystem of specialized models. For engineers and researchers building next-generation voice interfaces, accessibility tools, or audio analytics platforms, Qwen-Audio offers a compelling path toward simplicity, scalability, and state-of-the-art performance—all while being openly available for commercial and research use.
With clear documentation, reproducible evaluations, and straightforward integration via Hugging Face or ModelScope, Qwen-Audio lowers the barrier to adopting universal audio understanding in real-world projects.