In industrial quality control, detecting defects—like cracks in concrete, scratches on metal, or deformities in packaged goods—is critical. Yet traditional industrial anomaly detection (IAD) systems face a recurring bottleneck: they output anomaly scores, not decisions. Users must manually tune thresholds to distinguish “normal” from “abnormal,” a process that’s time-consuming, error-prone, and often requires expert calibration.
Enter AnomalyGPT, the first Large Vision-Language Model (LVLM) purpose-built for industrial anomaly detection. Unlike conventional methods, AnomalyGPT doesn’t just score images—it directly answers whether an anomaly exists, pinpoints its location, and explains what’s wrong in natural language. And remarkably, it can do this even with only a single example of a normal item, making it ideal for scenarios where labeled anomaly data is scarce or nonexistent.
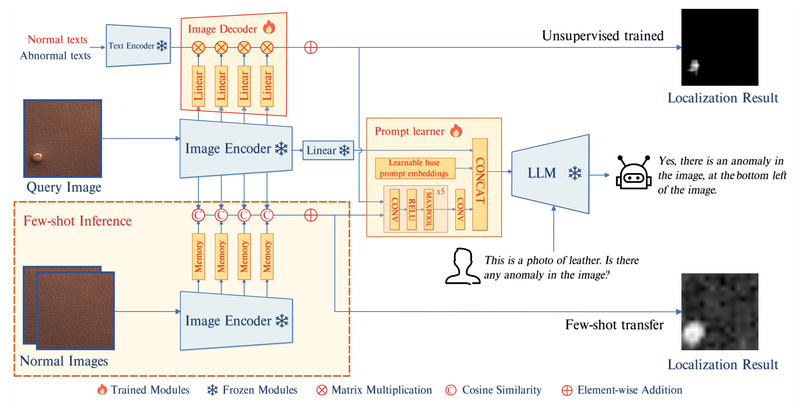
Developed by researchers at CASIA-IVA-Lab, AnomalyGPT leverages the power of multimodal foundation models—combining visual understanding from ImageBind and language reasoning from Vicuna—while introducing novel components like a lightweight image decoder and a prompt learner to adapt LVLMs to the fine-grained demands of industrial inspection. The result is a system that bridges the gap between cutting-edge AI and real-world deployment needs.
Why AnomalyGPT Stands Out
No Manual Thresholds, No Ambiguity
Traditional IAD methods (e.g., reconstruction-based or feature-matching approaches) produce heatmaps or scalar anomaly scores. Operators then set thresholds—often through trial and error—to classify images. This step introduces subjectivity and delays deployment, especially across new product lines.
AnomalyGPT eliminates this entirely. It outputs a clear verdict: “This bottle has a crack near the base,” or “The fabric is defect-free.” This declarative response removes ambiguity and integrates smoothly into automated inspection pipelines.
Precise Localization with Semantic Context
Beyond binary classification, AnomalyGPT localizes anomalies at the pixel level while providing natural language descriptions. For instance, given an image of a hazelnut, it might respond: “There’s a cut on the left side of the nut.” This dual output—spatial + semantic—is invaluable for root-cause analysis, operator training, and audit trails.
Strong Few-Shot Performance
AnomalyGPT excels in few-shot settings. On the widely used MVTec-AD benchmark, it achieves 86.1% accuracy, 94.1% image-level AUC, and 95.3% pixel-level AUC using just one normal example per category. This makes it uniquely suited for low-data or rapid-deployment scenarios—common in custom manufacturing or small-batch production.
Interactive Multi-Turn Dialogue
Thanks to its LVLM backbone, AnomalyGPT supports follow-up questions. After detecting a defect, an operator can ask, “Is this defect dangerous?” or “Has this type appeared before?”—enabling dynamic human-AI collaboration during inspection.
Real-World Applications
AnomalyGPT shines in industrial environments where:
- Anomaly types are unknown or evolving: Since it doesn’t require pre-labeled anomalies, it adapts to new defect patterns without retraining.
- Speed-to-deployment matters: With only normal samples needed, factories can onboard new products in hours, not weeks.
- Explainability is required: Quality engineers need more than a heatmap—they need actionable insights. AnomalyGPT delivers both visual and linguistic explanations.
Use cases include:
- Detecting micro-cracks in concrete or ceramics
- Identifying surface scratches on metal or plastic parts
- Verifying integrity of sealed bottles or capsules
- Inspecting textile weave consistency
These tasks often suffer from imbalanced data (few defects, many normals)—a regime where AnomalyGPT’s design thrives.
How It Works (Without the Heavy Lifting)
AnomalyGPT builds on existing foundation models but tailors them for IAD:
- Image Encoding: Uses ImageBind to extract rich visual features.
- Prompt Learning: A trainable prompt learner injects task-specific semantics into the language model (Vicuna), guiding it to focus on anomaly-relevant details.
- Image Decoder: A lightweight module aligns visual and textual features to produce precise anomaly maps.
- Training Strategy: Leverages synthetic anomalies—generated by perturbing normal images—paired with descriptive captions, enabling supervision without real defect labels.
This architecture avoids end-to-end retraining of massive models, instead using efficient fine-tuning via delta weights (building on PandaGPT). The result is high performance with manageable compute.
Getting Started
Running AnomalyGPT is straightforward for teams with basic ML infrastructure:
- Clone the official repository.
- Install dependencies via
pip install -r requirements.txt. - Download required checkpoints:
- ImageBind (for vision encoding)
- Vicuna (base LLM, e.g., 7B or 13B)
- PandaGPT delta weights (as initialization)
- AnomalyGPT fine-tuned weights (available for MVTec-AD, VisA, or multi-dataset supervised training)
- Launch the web demo with
python web_demo.py.
For custom use cases, users can train on their own data using scripts provided for MVTec-AD or VisA formats. Training has been validated on 2×RTX 3090 GPUs, making it accessible to well-equipped labs or small engineering teams.
Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, AnomalyGPT has practical constraints:
- License: Released under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0, meaning it’s free for research and non-commercial use but not for commercial deployment without permission.
- Dependency on External Models: Relies on Vicuna (which has its own licensing terms) and ImageBind—users must comply with their respective usage policies.
- Hardware Requirements: Training requires multi-GPU setups (~24–48 GB VRAM per GPU for Vicuna-7B+ImageBind). Inference is lighter but still benefits from modern GPUs.
- Domain Sensitivity: Performance may degrade on images with extreme lighting, occlusion, or domain shifts far from training data (e.g., medical or agricultural images).
That said, for industrial visual inspection within its design scope, AnomalyGPT offers a rare combination of accuracy, usability, and adaptability.
Summary
AnomalyGPT redefines industrial anomaly detection by replacing opaque scores with clear, explainable, and localized insights—no manual thresholds required. Its few-shot capability, natural language interface, and strong performance on standard benchmarks make it a compelling choice for quality engineers, automation developers, and AI researchers working in manufacturing. While mindful of its non-commercial license and hardware needs, technical evaluators will find it a practical and forward-looking tool for next-generation visual inspection systems.