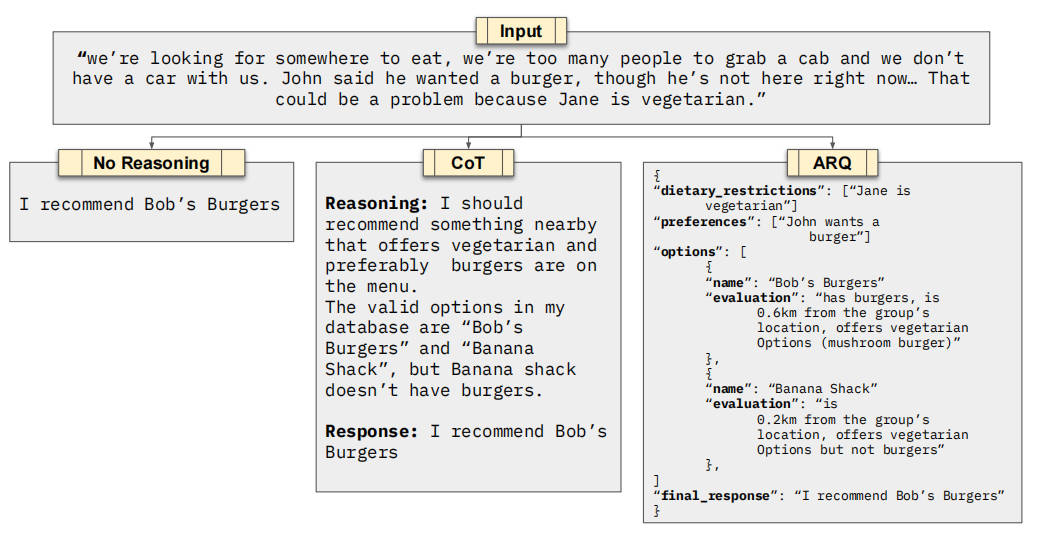
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across a wide range of tasks—from answering questions to generating code. However, when deployed in real-world, multi-turn interactions—especially in customer-facing or compliance-sensitive environments—they often struggle to consistently follow complex, domain-specific instructions. This inconsistency can lead to hallucinations, instruction drift, or outright failure to comply with critical operational guidelines.
Enter Attentive Reasoning Queries (ARQs): a structured reasoning method designed to significantly improve how LLMs interpret and adhere to instructions throughout extended conversations. Unlike generic prompting strategies, ARQs embed targeted, step-by-step queries directly into the reasoning process to actively reinstate key instructions at critical decision points. The result? Higher reliability, fewer errors, and stronger alignment with business requirements.
What Are Attentive Reasoning Queries (ARQs)?
At their core, ARQs are a systematic prompting technique that guides LLMs through a predefined reasoning blueprint tailored to a specific domain or use case. Rather than leaving reasoning entirely open-ended—as with standard prompting or even Chain-of-Thought (CoT)—ARQs introduce intermediate, focused questions that force the model to re-evaluate essential constraints, rules, or goals before proceeding.
This approach is especially valuable in scenarios where instruction fidelity matters more than creative freedom. For example, in a customer support chatbot that must strictly follow privacy policies or product availability rules across multiple dialogue turns, ARQs ensure that the model doesn’t “forget” these constraints mid-conversation.
Key Strengths Backed by Empirical Results
The effectiveness of ARQs isn’t just theoretical—it’s rigorously tested. In the original paper, ARQs were evaluated within Parlant, a framework built for reliable, customer-facing AI agents. Across 87 real-world test scenarios, ARQs achieved a 90.2% success rate, outperforming both:
- Chain-of-Thought reasoning (86.1%)
- Direct response generation without structured reasoning (81.5%)
More importantly, ARQs showed exceptional performance in addressing persistent LLM failure modes:
- Guideline re-application: Ensuring instructions are reapplied correctly after context shifts.
- Hallucination prevention: Reducing fabricated or unsupported responses by anchoring reasoning to verified constraints.
Additionally, well-designed ARQs can be more computationally efficient than free-form reasoning. By limiting unnecessary digressions and focusing the model’s attention on essential decision steps, ARQs reduce token waste and streamline inference—without sacrificing accuracy.
Ideal Use Cases
ARQs are not a one-size-fits-all solution, but they excel in specific contexts:
- Customer support agents that must adhere to brand voice, product rules, and compliance guidelines.
- Regulated domains like finance or healthcare, where deviations from protocol carry legal or safety risks.
- Tool-augmented LLMs that need to correctly invoke APIs (e.g., checking drink availability) while respecting business logic.
In short, if your application demands consistent, rule-bound behavior over multiple dialogue turns, ARQs provide a structured, reliable framework to enforce it.
How to Use ARQs in Practice
Implementing ARQs involves designing a reasoning blueprint—a sequence of targeted queries that align with your domain’s critical decision points. For instance, before allowing an LLM to recommend a product, an ARQ might ask:
“Based on the user’s location and current inventory, which drinks are actually available?”
The Parlant team has made this easier by publishing real prompt examples in the GitHub repository under supplementary_materials/prompts/. These include side-by-side comparisons of ARQ, CoT, and baseline (no reasoning) prompts for a test scenario involving a single tool call (get_available_drinks).
To validate ARQ performance in your own setup:
- Install Parlant and switch to the
arqs-a-systematic-method...branch. - Run the full test suite using
pytest --no-cache. - Analyze results via the provided
analyze_resultsscripts, which generate success-rate tables fromparlant_test_results.jsonl.
This transparent, reproducible workflow allows developers and researchers to verify ARQ effectiveness in their specific context before full integration.
Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, ARQs aren’t plug-and-play. Their success depends on thoughtful design of reasoning blueprints that accurately reflect your domain’s operational logic. They work best within structured agent frameworks like Parlant and may add overhead in highly dynamic or open-ended tasks where strict instruction adherence isn’t required.
Moreover, ARQs prioritize instruction fidelity over creativity—making them less suitable for brainstorming or generative storytelling. But in business-critical applications where reliability is non-negotiable, this trade-off is not just acceptable—it’s essential.
Summary
Attentive Reasoning Queries offer a principled, empirically validated method to enhance instruction-following in LLMs—particularly in multi-turn, rule-bound environments. By systematically reinstating critical guidelines through targeted intermediate queries, ARQs reduce hallucinations, prevent instruction drift, and deliver higher success rates than conventional approaches.
For teams building customer-facing agents, compliance-driven assistants, or any LLM application where consistency trumps improvisation, ARQs provide a robust, efficient, and transparent path to more reliable AI behavior. With open-source examples and a reproducible evaluation pipeline, adopting ARQs is both practical and low-risk.