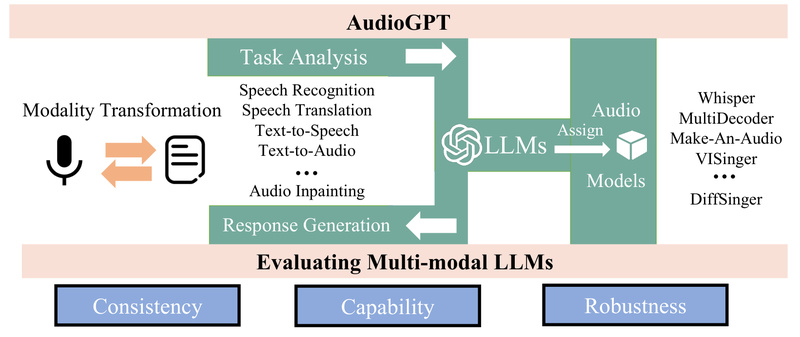
AudioGPT is a multimodal AI system that bridges the gap between large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and the rich world of audio. While LLMs excel at text-based reasoning, they lack native support for understanding or generating complex audio signals—such as human speech, singing, environmental sounds, or even synchronized talking faces. AudioGPT solves this by integrating foundation models specialized in audio tasks, enabling natural-language-driven control over a wide range of audio understanding and generation capabilities. This makes it uniquely suited for developers, researchers, and creators who want to build conversational agents that truly “hear” and “speak,” or automate rich audio content creation without deep signal processing expertise.
Why AudioGPT Stands Out
Unlike generic voice assistants that handle only narrow command sets, AudioGPT leverages the reasoning power of LLMs combined with state-of-the-art audio foundation models. It supports spoken dialogue through automatic speech recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech (TTS) interfaces, while also orchestrating specialized models for tasks like music synthesis, sound detection, and talking head animation—all through natural language prompts. This end-to-end multimodal design allows users to describe complex audio goals in plain English (e.g., “turn this script into a cheerful female voice with background rain sounds” or “generate a singing version of this poem in pop style”) and have the system coordinate the right models to fulfill the request.
Core Capabilities Across Audio Domains
AudioGPT organizes its functionality into four key domains, each powered by established or emerging foundation models:
Speech Processing
AudioGPT supports essential speech tasks including:
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) using models like VITS, FastSpeech, and SyntaSpeech—enabling expressive, high-quality voice synthesis.
- Speech Recognition via Whisper and Conformer, allowing accurate transcription of spoken input.
- Speech Enhancement and Separation using ConvTasNet and TF-GridNet to clean noisy recordings or isolate speakers.
- Style Transfer with GenerSpeech, which can adapt voice characteristics without retraining.
- Mono-to-Binaural Conversion using NeuralWarp for immersive 3D audio experiences.
Singing Synthesis
For musical applications, AudioGPT integrates models like DiffSinger and VISinger to convert text lyrics into realistic singing voices—complete with pitch, rhythm, and vocal timbre control. This opens possibilities for AI-assisted music prototyping or personalized vocal content.
General Audio Understanding & Generation
Beyond speech and singing, AudioGPT handles broader audio modalities:
- Text-to-Audio and Image-to-Audio generation using Make-An-Audio, enabling creation of sound effects from descriptions or visual cues.
- Audio Inpainting to reconstruct missing segments in audio recordings.
- Sound Detection and Target Sound Extraction using Audio-transformer, TSDNet, and LASSNet—ideal for surveillance, accessibility, or content tagging.
Talking Head Synthesis
Using GeneFace, AudioGPT can generate realistic facial animations synchronized with input speech, supporting applications in virtual avatars, telepresence, and digital humans.
Practical Applications for Developers and Researchers
AudioGPT isn’t just a research prototype—it addresses real-world pain points:
- Voice Assistant Enhancement: Move beyond keyword spotting to systems that understand audio context, reason about user intent, and generate multimodal responses.
- Media & Entertainment Automation: Rapidly generate voiceovers, background scores, or sound effects for games, films, or VR experiences using simple prompts.
- Accessibility Tools: Build systems that transcribe, summarize, and re-express audio content for users with hearing or cognitive differences.
- Multimodal Agent Prototyping: Create conversational agents that combine speech, sound, and visual feedback in unified interactions—ideal for human-computer interaction research.
Getting Started Is Designed for Accessibility
Despite its advanced capabilities, AudioGPT prioritizes usability. The system uses a modular architecture where each audio task is handled by a dedicated foundation model, all orchestrated via an LLM. Users interact through natural language, eliminating the need to manually chain models or write audio-specific code. Setup instructions are provided in the repository’s run.md, and the project builds on widely adopted frameworks like Hugging Face, ESPnet, and LangChain—ensuring compatibility with existing workflows. While some components are marked “Work-in-Progress” (e.g., speech translation, talking head synthesis), the core pipeline for speech recognition, TTS, and audio generation is functional and open-source.
Current Limitations to Consider
Prospective users should note that AudioGPT is still evolving:
- Several advanced features (e.g., speech translation, full talking head pipelines) are labeled “WIP” and may require additional setup or fine-tuning.
- Performance depends on the underlying foundation models, which vary in resource requirements and inference speed.
- Local deployment may require GPU resources and familiarity with Python-based deep learning environments.
That said, the project’s transparent status tracking and modular design allow users to adopt only the stable components relevant to their use case.
Summary
AudioGPT represents a significant step toward truly multimodal AI—where language models don’t just “talk about” audio but actively understand, manipulate, and create it. By unifying speech, music, sound, and visual speech synthesis under a single natural-language interface, it empowers developers and researchers to prototype, deploy, and innovate in audio AI without becoming experts in every subfield. For teams building next-generation voice interfaces, creative tools, or multimodal agents, AudioGPT offers a powerful, open-source foundation to accelerate development.