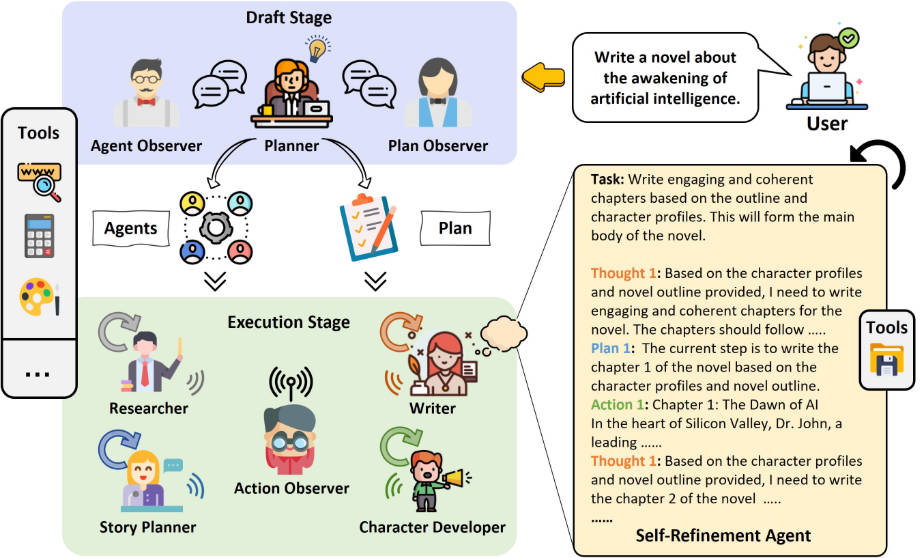
Building intelligent systems that can handle open-ended, multi-step problems has long been a challenge in AI development. Traditional multi-agent frameworks often rely on static, pre-defined roles—limiting their adaptability when tasks evolve or require diverse expertise. AutoAgents changes this paradigm. Released by Link-AGI and accepted at IJCAI 2024, AutoAgents is an open-source framework that dynamically generates specialized AI agents on the fly, tailored precisely to the task at hand. Instead of forcing generic agents into every problem, AutoAgents creates a collaborative team of experts—each with a distinct role, skill set, and purpose—and coordinates their work toward a shared goal.
This capability makes AutoAgents uniquely suited for real-world applications where flexibility, collaboration, and reflective reasoning matter more than rigid, one-size-fits-all automation.
How AutoAgents Works: Adaptive Agent Generation in Action
At the core of AutoAgents is a simple but powerful insight: complex tasks require diverse perspectives. The framework operationalizes this through a four-part architecture:
The Planner: Architect of the AI Team
When given a high-level goal—such as “Verify whether LK-99 is a room-temperature superconductor”—AutoAgents’ Planner first analyzes the problem and determines what kinds of expertise are needed. It then defines an execution plan composed of sequential or parallel steps, assigning at least one specialized agent to each step. This eliminates the need for manual agent design and ensures the team structure aligns with task demands.
Auto-Generated Expert Agents
Based on the Planner’s blueprint, Agents are generated with specific attributes: a name, domain expertise, assigned tools (e.g., web search), and LLM instructions optimized for their role. For example, verifying scientific claims might spawn a Researcher, a Fact-Checker, and a Scientific Critic—each operating with contextual awareness of their responsibilities.
The Observer: Built-In Quality Control
Unlike most multi-agent systems that execute plans blindly, AutoAgents includes an Observer role that continuously evaluates the reasonableness of both the plan and agent responses. It reflects on potential gaps, inconsistencies, or inefficiencies and triggers refinements—introducing a layer of self-correction that dramatically improves output coherence and accuracy.
Tool Integration for Real-World Grounding
AutoAgents currently supports search tools (via SerpAPI, Serper, or Google Custom Search) to pull real-time information, ensuring agents aren’t limited to static knowledge. While broader tool support is planned, this integration already enables agents to validate claims, gather evidence, and stay up to date—critical for tasks like rumor verification or technical research.
Real-World Applications That Benefit from Adaptive Collaboration
AutoAgents shines in scenarios that are too complex for single-agent systems but too dynamic for hand-crafted multi-agent teams. Demonstrated use cases include:
- Rumor Verification: Automatically assembling a team to assess the credibility of viral claims by cross-referencing sources, analyzing evidence, and producing a reasoned conclusion.
- Interactive Game Development: Building a playable version of “Gluttonous Snake” where agents handle game logic, user interaction, and visual rendering—showcasing creative problem decomposition.
- Scientific Inquiry: Answering nuanced research questions (e.g., about novel materials like LK-99) by coordinating domain specialists who gather, interpret, and synthesize technical literature.
These examples highlight AutoAgents’ strength: breaking down ill-defined problems into structured, collaborative workflows—without requiring developers to pre-specify every role or interaction.
Getting Started Is Simple for Developers and Researchers
AutoAgents prioritizes usability. Setup requires only three steps:
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/Link-AGI/AutoAgents cd AutoAgents python setup.py install
- Configure API keys via environment variables (no YAML files needed):
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-..." export SERPAPI_API_KEY="your-serpapi-key"
- Run via command line or as a WebSocket service:
python main.py --mode commandline --idea "Is LK-99 really a room-temperature superconductor?"
Or launch a service for integration with custom frontends:
python main.py --mode service --host 127.0.0.1 --port 9000
Optional configurations—like switching to gpt-4o-mini, using Azure OpenAI, or routing traffic through a proxy—are supported via additional environment variables or CLI flags, making the framework adaptable to diverse deployment environments.
Limitations to Consider
While powerful, AutoAgents has practical constraints worth noting:
- LLM Dependency: Agent quality and reasoning depth depend heavily on the underlying language model (e.g., GPT-4). Using weaker models may reduce performance.
- Tool Scope: Currently limited to search-based tools; integration with code execution, databases, or APIs beyond web search isn’t yet supported.
- Latency and Cost: Dynamic agent generation and multi-turn collaboration can increase token usage and response time compared to single-agent approaches.
These limitations are typical of early-stage multi-agent frameworks, but the AutoAgents team is actively expanding capabilities—especially through community contributions.
Summary
AutoAgents addresses a critical gap in AI automation: the need for flexible, self-organizing teams of specialized agents that adapt to task complexity rather than forcing tasks into fixed agent templates. By combining dynamic role generation, collaborative planning, and reflective oversight, it enables more robust, accurate, and context-aware problem solving. For developers, researchers, and product teams tackling multi-faceted challenges—from scientific analysis to content verification—AutoAgents offers a low-barrier, high-impact entry point into next-generation multi-agent AI. With its MIT license, active development, and IJCAI-24 validation, it’s a framework worth exploring for anyone building intelligent, collaborative systems.