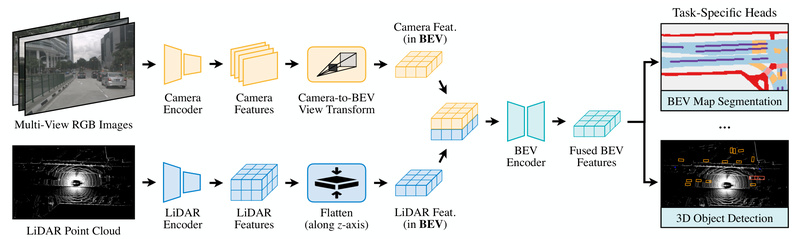
Building reliable perception systems for autonomous driving demands more than just collecting data from cameras and LiDARs—it requires intelligently fusing them in a way that preserves both geometric accuracy and semantic richness. Traditional fusion methods often project camera features directly onto sparse LiDAR points, discarding valuable visual context and limiting performance on semantic tasks like scene segmentation. BEVFusion solves this problem by rethinking sensor fusion from the ground up.
Developed by researchers at MIT and accepted at ICRA 2023, BEVFusion is a multi-task, multi-sensor fusion framework that unifies camera and LiDAR inputs into a shared bird’s-eye view (BEV) representation. This design preserves dense semantic information from cameras while retaining the precise geometric structure of LiDAR, enabling state-of-the-art performance across both 3D object detection and BEV map segmentation—without requiring major architectural changes between tasks.
Critically, BEVFusion isn’t just accurate—it’s efficient. Through an optimized BEV pooling operator, it reduces view transformation latency by over 40x compared to prior methods and cuts overall computation cost by 1.9x, making real-time deployment feasible on edge devices like NVIDIA Jetson Orin (achieving 25 FPS with TensorRT). With top rankings on nuScenes, Waymo, and Argoverse benchmarks, BEVFusion has proven its value not only in research but also in industry pipelines, including integration into NVIDIA DeepStream and MMDetection3D.
Why Traditional Fusion Falls Short
Before BEVFusion, many multi-sensor approaches relied on point-level fusion: enhancing each LiDAR point with corresponding camera features via projection. While intuitive, this method has a critical flaw—cameras capture dense semantic content across the entire field of view, but LiDAR point clouds are inherently sparse. When you project dense pixels onto sparse points, most of the visual information is lost.
This limitation is especially problematic for tasks like BEV map segmentation, where understanding drivable areas, lane markings, and road boundaries requires continuous semantic context—not just localized point annotations. BEVFusion sidesteps this issue entirely by lifting both modalities into a common BEV space first, then fusing them. This preserves the full semantic density of images while aligning them with LiDAR’s accurate 3D structure.
Core Advantages of BEVFusion
Task-Agnostic Architecture
One of BEVFusion’s most compelling features is its task-agnostic design. The same core fusion pipeline supports 3D object detection, BEV map segmentation, and potentially other BEV-based perception tasks—without redesigning the model. This modularity reduces engineering overhead and accelerates development cycles for teams building comprehensive autonomy stacks.
On nuScenes validation, BEVFusion achieves 68.52 mAP and 71.38 NDS for 3D detection and 62.95 mIoU for map segmentation—significantly outperforming both camera-only and LiDAR-only baselines, and even beating them in combination by 13.6% mIoU on segmentation.
Exceptional Efficiency
Efficiency isn’t an afterthought in BEVFusion—it’s central to its design. The team identified the view transformation step (lifting front-view camera features into BEV) as a major bottleneck. By introducing an optimized BEV pooling operator, they slashed latency by over 40x, enabling real-time inference.
This efficiency translates to practical deployment: NVIDIA’s TensorRT implementation runs at 25 frames per second on Jetson Orin, a key platform for embedded autonomous systems. Additionally, BEVFusion uses 1.9x less computation than competing fusion methods while delivering higher accuracy—ideal for resource-constrained environments.
Industry-Validated Performance
BEVFusion isn’t just a research prototype. It has consistently ranked #1 on major autonomous driving benchmarks:
- nuScenes 3D object detection (2022)
- Waymo 3D object detection (2022)
- Argoverse 3D object detection (2023)
Its adoption into NVIDIA DeepStream and MMDetection3D further validates its readiness for production use in perception pipelines for robotics, smart infrastructure, and autonomous vehicles.
Ideal Use Cases
BEVFusion shines in scenarios requiring robust, real-time perception from heterogeneous sensors:
- Autonomous vehicle perception stacks needing joint object detection and scene understanding.
- Robotic navigation in complex urban or indoor environments where semantic maps (e.g., drivable areas) and 3D obstacles must be inferred simultaneously.
- Smart city infrastructure, such as traffic monitoring systems that fuse roadside camera and LiDAR data to generate real-time BEV scene representations.
Its ability to handle both detection and segmentation with one unified model reduces system complexity—making it especially valuable for teams aiming to minimize model footprint without sacrificing performance.
Getting Started with BEVFusion
BEVFusion is built on MMDetection3D, a widely used 3D detection codebase, which lowers the barrier to entry for teams already familiar with the ecosystem. The project provides:
- Pretrained models for both detection and segmentation tasks.
- Clear training and evaluation scripts for nuScenes, with support for camera-only, LiDAR-only, and fused modalities.
- A Dockerfile for reproducible environment setup, including CUDA extension compilation.
- TensorRT deployment support, enabling edge deployment on NVIDIA platforms.
To evaluate a pretrained detection model, for example, you can run:
torchpack dist-run -np 8 python tools/test.py configs/nuscenes/det/.../convfuser.yaml pretrained/bevfusion-det.pth --eval bbox
Similarly, segmentation evaluation uses a one-line command with a different config and checkpoint. Training follows the same pattern, with optional initialization from pretrained LiDAR-only or camera-only models—enabling effective transfer learning.
Note: Due to BEVFusion’s forked version of MMDetection3D (prior to coordinate system updates), it’s recommended to regenerate nuScenes info files using the provided tools rather than reusing existing ones.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While BEVFusion offers significant advantages, users should consider the following:
- Hardware requirement: Optimal performance assumes access to both camera and LiDAR sensors. If only one modality is available, BEVFusion can still run (as shown in baselines), but its fusion benefit is lost.
- Dependency constraints: The codebase requires specific versions (e.g., Python ≥3.8, <3.9; PyTorch 1.9–1.10.2), which may complicate integration into newer environments.
- GPU dependency: Despite its efficiency gains, BEVFusion still requires GPU acceleration for training and real-time inference—unsuitable for CPU-only deployments.
Summary
BEVFusion redefines multi-sensor fusion for autonomous perception by unifying camera and LiDAR data in a shared bird’s-eye view representation. It overcomes the semantic loss of traditional point-level fusion, delivers state-of-the-art results across detection and segmentation, and does so with dramatically improved efficiency—enabling real-world deployment on edge devices. For engineering teams building next-generation autonomy systems, BEVFusion offers a proven, production-ready, and task-flexible foundation that reduces both computational cost and development complexity.