In today’s AI landscape, multimodal systems that understand both images and videos are increasingly essential—but most solutions force you to choose one modality or stitch together separate models. Chat-UniVi changes that. Developed by PKU-YuanGroup and recognized as a CVPR 2024 Highlight paper (top 3% of over 11,500 submissions), Chat-UniVi is a single, unified vision-language model that natively comprehends both static images and dynamic videos within the same architecture.
For technical decision-makers—whether you’re building customer support bots, e-learning platforms, content moderation tools, or internal enterprise applications—this unification eliminates the complexity, cost, and latency of maintaining dual pipelines. More importantly, it does so without sacrificing performance: Chat-UniVi consistently outperforms models designed exclusively for either images or videos, as validated across multiple benchmarks.
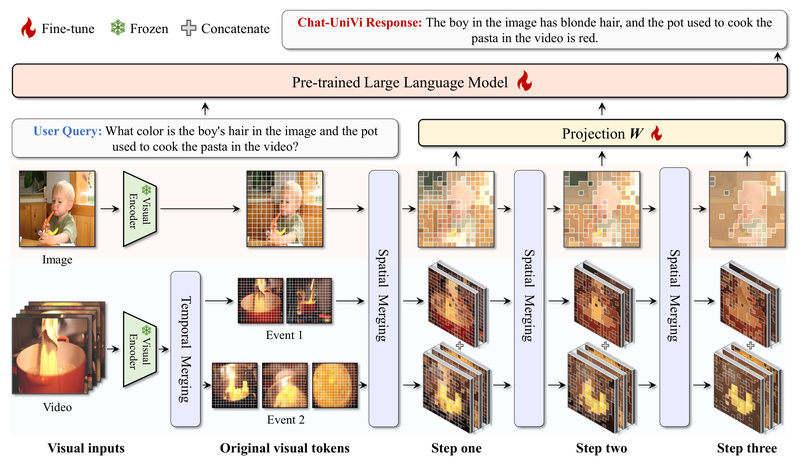
Built on a novel dynamic visual token strategy, Chat-UniVi captures both spatial details (for images) and temporal relationships (for videos) using a limited, efficient token budget. This makes it not only powerful but also practical for real-world deployment, even enabling full-parameter training of a 13B model on just 8 A100 GPUs in 3 days.
Unified Visual Representation: Fewer Tokens, Richer Understanding
Traditional multimodal models struggle with video because they treat each frame as an independent image, rapidly inflating token counts and diluting temporal coherence. Chat-UniVi solves this with a unified visual representation that dynamically allocates tokens based on content—whether it’s a single photograph or a minute-long clip.
This approach leverages multi-scale perception, allowing the model to simultaneously grasp high-level semantics (e.g., “a person is cooking”) and fine-grained visual details (e.g., “chopping onions on a wooden board”). Crucially, the same set of visual processing rules applies to both images and videos, ensuring consistent behavior across modalities.
The result? High-fidelity understanding without the computational bloat that plagues frame-by-frame video encoders. For teams managing infrastructure costs or latency-sensitive applications, this efficiency is a game-changer.
One Model, Seamless Multimodal Conversations
Chat-UniVi isn’t just capable of handling both images and videos—it’s trained jointly on a mixed dataset containing both. This means:
- You can ask questions about a photo, a video, or both in the same conversation.
- No need to switch models, reconfigure pipelines, or maintain separate inference endpoints.
- The system works out-of-the-box for mixed-media inputs, such as a support ticket containing a screenshot and a screen recording.
This is especially valuable in real-world scenarios where users naturally mix media types. Imagine an educational assistant that explains a diagram (image) and then walks through a lab demonstration (video)—all within a single, coherent dialogue.
Strong Performance Across Diverse Benchmarks
Unification doesn’t mean compromise. Chat-UniVi delivers state-of-the-art or competitive results across multiple evaluation suites:
- Image understanding: Scores 86.1 (relative to GPT-4) on LLaVA’s instruction-following benchmark with the 13B version—surpassing many image-only models.
- Video QA: Achieves top-tier results on MSRVTT-QA, MSVD-QA, TGIF-QA, and ActivityNet-QA, even outperforming earlier specialized systems like Video-ChatGPT.
- ScienceQA: Reaches 90.99% accuracy on the ScienceQA test set, demonstrating robust reasoning over scientific diagrams and contextual visuals.
- Hallucination control: Shows significantly lower object hallucination rates than LLaVA and Video-LLaVA on the POPE benchmark, enhancing reliability in safety-critical applications.
These results confirm that joint training on images and videos fosters complementary learning—each modality reinforces the other, leading to more grounded and accurate responses.
Easy Integration for Developers
Getting started with Chat-UniVi is straightforward. The project provides:
- Clear inference APIs for both image and video inputs in Python.
- Support for 7B and 13B model variants, enabling trade-offs between speed and capability.
- An online demo on Hugging Face for quick experimentation.
- Full training code and data preprocessing scripts (see
TRAIN_AND_VALIDATE.mdandDATA.md).
For inference, you only need standard PyTorch and a GPU. The codebase is built on the efficient LLaVA framework and includes utilities for video loading with variable-length support, eliminating outdated zero-padding that once hurt performance.
Running a video query is as simple as:
- Loading the model and tokenizer
- Preprocessing the video into frames
- Injecting dynamic visual tokens into the prompt
- Generating the response
The same pattern works for images—just swap the input modality.
Ideal Use Cases for Unified Understanding
Chat-UniVi shines in applications where mixed visual inputs are the norm:
- Social media monitoring: Analyze posts containing both memes (images) and short clips (videos) for sentiment or policy violations.
- E-learning platforms: Answer student questions about textbook figures and tutorial videos in one interface.
- Assistive technology: Describe real-world scenes from phone photos or recorded clips for visually impaired users.
- Enterprise documentation: Parse internal knowledge bases that combine screenshots, diagrams, and screen recordings.
In each case, maintaining separate models would add operational overhead. Chat-UniVi’s unified design streamlines both development and deployment.
Current Limitations and Practical Notes
While powerful, Chat-UniVi has realistic constraints to consider:
- Hardware: Inference requires a GPU; the 13B model benefits from ≥24GB VRAM.
- Video length: Very long videos are downsampled to a maximum of 100 frames (configurable), which may affect fine-grained temporal reasoning in hour-long footage.
- LLM base: Built on Vicuna, which inherits LLaMA’s licensing restrictions (non-commercial use without Meta’s approval).
- Language support: Primarily optimized for English; Chinese and other languages require external translation layers (as noted in the repo).
These are not dealbreakers—but they’re important for scoping your project’s feasibility.
Summary
Chat-UniVi redefines what’s possible in multimodal AI by unifying image and video understanding in a single, efficient, high-performing model. It eliminates the need for modality-specific systems, reduces infrastructure complexity, and delivers top-tier results across diverse benchmarks—all while being practical to deploy.
If your project involves processing visual content in any form, Chat-UniVi offers a compelling path forward. Explore the code, test the demo, and consider how a truly unified vision-language model could simplify your architecture and enhance your user experience.
Resources:
- GitHub: https://github.com/PKU-YuanGroup/Chat-UniVi
- Online Demo: Available on Hugging Face (link in repo)
- Documentation:
DATA.md,TRAIN_AND_VALIDATE.md,VISUALIZATION.md - Citation: Jin et al., arXiv:2311.08046