Training large-scale AI models—whether language models like LLaMA or video generators like Open-Sora—has become increasingly common, yet remains bottlenecked by hardware limitations. GPUs offer immense compute power, but their memory is finite. Without expert-level knowledge in distributed systems, most researchers and engineers struggle to scale models beyond a single device efficiently.
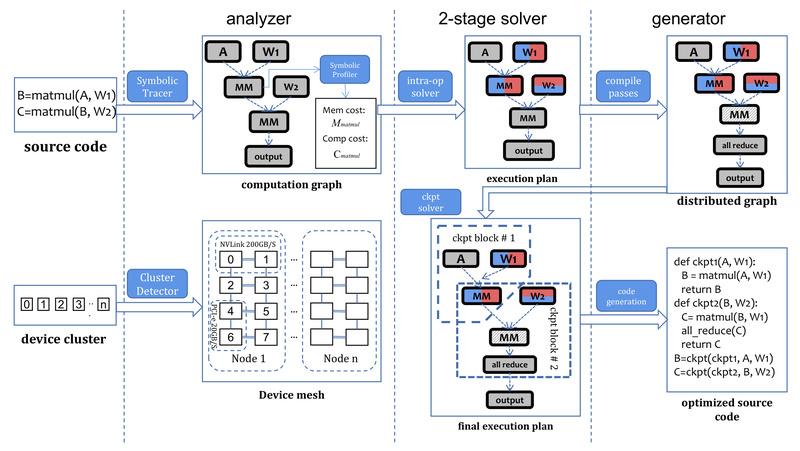
Enter Colossal-Auto, a core component of the Colossal-AI ecosystem. Colossal-Auto uniquely unifies the automation of model parallelism and activation checkpointing, two critical yet historically siloed optimization techniques. By jointly optimizing data, pipeline, and tensor parallelism alongside gradient checkpoint schedules, it enables faster, cheaper, and more accessible training of billion-parameter models—without requiring users to manually design or tune distributed execution plans.
What makes Colossal-Auto especially compelling is its minimal-code adoption model. Built on PyTorch, it lets you scale your existing model training scripts to multi-GPU clusters with only a configuration file change—no deep refactoring needed. This lowers the barrier for labs, startups, and individual developers to train or fine-tune state-of-the-art models on commodity or cloud hardware.
Why Manual Parallelization and Checkpointing Are Problematic
Traditionally, scaling models involves choosing among several parallelization strategies:
- Data Parallelism (DP): Replicates the model across devices, splitting batches.
- Tensor Parallelism (TP): Splits individual layers (e.g., matrix multiplications) across GPUs.
- Pipeline Parallelism (PP): Partitions the model depth-wise into stages.
Each has trade-offs in communication overhead, memory usage, and hardware utilization. On top of that, activation checkpointing—a technique that trades compute for memory by recomputing intermediate activations during backpropagation—adds another layer of complexity.
Prior systems either optimize parallelism or checkpointing, but not both together. Worse, they often rely on runtime profiling or scaled-down simulations to estimate memory and compute costs, which are slow and inaccurate. This leads to failed training runs, wasted cloud budgets, or suboptimal performance.
Colossal-Auto solves this by introducing a symbolic profiler that instantly computes memory and FLOP statistics for any PyTorch model—without executing it. This enables ahead-of-time joint optimization of both parallel execution and checkpointing plans, tailored precisely to your hardware.
Key Features That Address Real Pain Points
Unified Automation of Parallelism + Checkpointing
Colossal-Auto doesn’t just apply a single parallelism strategy. It evaluates combinations of Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO), 1D/2D/2.5D/3D Tensor Parallelism, Pipeline Parallelism, and Sequence Parallelism, then merges them with an optimal activation checkpointing schedule. This end-to-end automation eliminates guesswork and manual tuning.
Minimal Code Changes, Maximum Scalability
You don’t need to rewrite your model. Just wrap your training loop with Colossal-AI’s engine and provide a YAML/JSON config specifying your hardware. The system handles the rest—from operator placement to gradient synchronization.
Fast, Accurate Symbolic Profiling
Instead of running dummy passes or scaling inputs, Colossal-Auto uses symbolic execution to predict memory footprint and compute load in milliseconds. This prevents “out-of-memory” surprises and ensures your job starts correctly on the first attempt.
Ideal Use Cases: Who Should Use Colossal-Auto?
Colossal-Auto shines in scenarios where model size exceeds single-GPU memory or training costs must be minimized:
- Fine-tuning LLMs like LLaMA-2/3, GPT-2/3, or OPT on 8–16 GPU clusters without a dedicated infrastructure team.
- Training video generation models such as Open-Sora, where batch size and sequence length quickly exhaust GPU memory.
- Running billion-parameter models on a single consumer GPU (e.g., RTX 3080): Colossal-Auto enables up to 20× larger models via memory optimization.
- Cost-sensitive research labs or startups aiming to reduce cloud bills—Colossal-AI has demonstrated up to 50% lower hardware costs for Stable Diffusion training.
If you’re working with models in the 1B–300B+ parameter range and lack a full-time ML systems engineer, Colossal-Auto is designed for you.
Getting Started Is Surprisingly Simple
Installation is straightforward:
pip install colossalai
For advanced features like fused kernels:
BUILD_EXT=1 pip install colossalai
Once installed, you can enable distributed training by:
- Defining your model and training loop in standard PyTorch.
- Creating a parallelism configuration (e.g.,
zero2,tp2+pp4). - Launching your script through Colossal-AI’s launcher (
colossalai run).
The project provides ready-to-run examples for LLaMA, GPT-2, BERT, ViT, and more—so you can adapt a working template rather than start from scratch.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While powerful, Colossal-Auto has clear system requirements:
- Operating System: Linux only (no Windows or macOS support).
- PyTorch: Version ≥ 2.2 required.
- CUDA: ≥ 11.0.
- GPU: NVIDIA GPUs with compute capability ≥ 7.0 (e.g., V100, RTX 20-series, A100, H100, B200).
Additionally, fused optimizers and CUDA kernels—which boost performance—are not built by default and require the BUILD_EXT=1 flag during installation. Users on CUDA 10.2 must manually integrate the CUB library.
These constraints are typical for high-performance deep learning systems, but they’re important to verify before adoption.
Real-World Performance Gains
Benchmarks from the Colossal-AI team demonstrate tangible benefits:
- On 8× H200 GPUs, a 7B LLaMA model achieves 17.13 samples/second with ZeRO-2.
- Switching to 8× B200 GPUs with hybrid parallelism (
dp2+tp2+pp4) pushes throughput to 25.83 samples/second—a 50% increase. - For 70B models on 16 GPUs, throughput more than doubles (3.27 → 5.66 samples/sec) with the same parallelism strategy.
- On a single RTX 3080, GPT-2 training supports 120× larger model size compared to vanilla PyTorch.
- Stable Diffusion training sees 5.6× lower memory usage, enabling fine-tuning on consumer GPUs like the RTX 3060.
These aren’t theoretical gains—they translate directly into faster iterations, lower cloud costs, and broader hardware accessibility.
Summary
Colossal-Auto removes the biggest roadblocks to large-model training: the need for parallel computing expertise and the fear of memory overflows. By jointly automating parallelization and activation checkpointing—and backing it with fast symbolic profiling—it empowers any PyTorch user to scale models efficiently across GPUs. Whether you’re fine-tuning a 7B language model on a cloud instance or pushing the limits of a single workstation GPU, Colossal-Auto delivers speed, savings, and simplicity—without hidden complexity.
For teams serious about large-scale AI but lacking distributed systems bandwidth, Colossal-Auto isn’t just a tool—it’s a force multiplier.