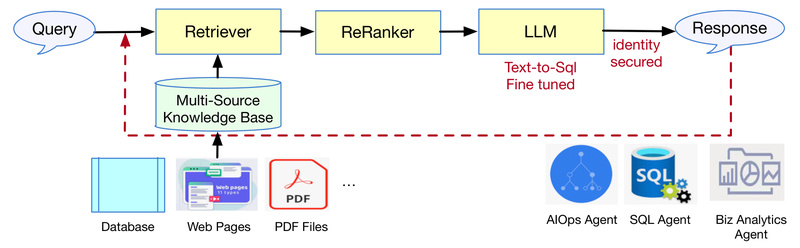
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are drowning in information—but starving for insights. Traditional database interfaces demand technical SQL knowledge, creating a barrier for business users, analysts, and even developers who just want quick answers from their data. Enter DB-GPT, an open-source, AI-native framework that bridges large language models (LLMs) with databases—enabling natural language interaction while keeping sensitive data private and on-premises.
Unlike generic cloud-based AI assistants that route your queries through external APIs, DB-GPT runs locally or in private environments. It empowers teams to ask questions like “Show me last quarter’s top-selling products by region” and get accurate SQL, visualizations, or narrative summaries—without ever exposing raw data to third parties. Built for both enterprise readiness and developer flexibility, DB-GPT combines cutting-edge LLM capabilities with robust data infrastructure.
Core Capabilities That Address Real Pain Points
Natural Language to SQL with High Accuracy
One of the most time-consuming tasks in data work is writing and debugging SQL. DB-GPT tackles this with its DB-GPT-Hub, a specialized Text-to-SQL engine fine-tuned on domain-specific datasets. It achieves an impressive 82.5% execution accuracy on the Spider benchmark, a widely used evaluation for complex cross-database queries. This means non-experts can generate reliable, multi-table SQL just by describing what they need in plain English.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for Context-Aware Answers
DB-GPT integrates a full-fledged RAG framework, allowing users to connect private knowledge bases—such as internal documentation, policy manuals, or customer support logs—to the LLM. When a user asks a question, DB-GPT retrieves relevant context from structured or unstructured data sources before generating a response. This ensures answers are grounded in your organization’s specific information, not generic internet knowledge.
Generative Business Intelligence (GBI)
Beyond query generation, DB-GPT supports Generative BI—automatically producing analytical reports, summaries, and insights from natural language prompts. Whether you’re connecting to a PostgreSQL database, a Snowflake data warehouse, or even an Excel file, DB-GPT can interpret your intent and deliver meaningful output, reducing the need for manual dashboard building.
Data-Driven Multi-Agent System
DB-GPT includes a multi-agent framework where specialized AI agents collaborate to solve complex data tasks. For example, one agent might validate a query, another fetches metadata, and a third generates a visualization—all orchestrated via AWEL (Agentic Workflow Expression Length), a declarative language for building agent workflows. This modular design supports automation while remaining transparent and debuggable.
Seamless Integration with Your Data Ecosystem
DB-GPT natively supports a wide range of data sources, including relational databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.), data warehouses, and flat files like CSV or Excel. Its Data Factory module helps clean, structure, and prepare data for LLM consumption, ensuring high-quality inputs that lead to accurate outputs.
For model flexibility, DB-GPT’s Service-oriented Multi-Model Framework (SMMF) supports dozens of open-source and commercial LLMs—including LLaMA, Qwen, DeepSeek, GLM, Baichuan, and more. You can swap models based on performance, cost, or privacy requirements without rewriting your application logic.
Privacy-First Architecture
Security isn’t an afterthought—it’s foundational. DB-GPT uses private LLMs fine-tuned on domain-specific corpora and avoids sending data to external servers. Techniques like proxy desensitization and local vector storage further protect sensitive information. This makes DB-GPT ideal for regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and government, where data residency and compliance are non-negotiable.
Getting Started Is Easier Than You Think
You don’t need a PhD in AI to begin. DB-GPT offers:
- Docker-based installation for one-command setup
- Pre-built application templates for common use cases
- AWEL workflows that let you visually or programmatically define agent pipelines
- Out-of-the-box support for natural language querying—just point DB-GPT to your database and start asking questions
As your needs grow, you can fine-tune models using the built-in automated Text-to-SQL fine-tuning framework, which supports LoRA, QLoRA, and P-Tuning—making model customization as streamlined as an assembly line.
Ideal Use Cases
- Internal data assistants for non-technical teams (e.g., marketing, HR)
- Secure, chat-based analytics dashboards that comply with data governance policies
- Legacy system modernization by adding natural language interfaces to old databases
- Rapid prototyping of AI-native data apps with minimal code, leveraging AWEL and agents
Important Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, DB-GPT isn’t magic. Its Text-to-SQL accuracy depends on schema clarity and data quality—ambiguous table names or poorly documented databases can reduce performance. Running large LLMs locally also demands sufficient GPU or CPU resources, though quantized models help mitigate this.
The multi-agent system, while promising, is still evolving—complex agent coordination may require careful design and testing. Finally, while installation is simplified via Docker, initial setup still assumes basic DevOps familiarity, especially for production deployments.
Summary
DB-GPT redefines how humans interact with data. By combining private LLMs, RAG, Generative BI, and a flexible agent architecture, it delivers a secure, accurate, and user-friendly interface for databases—without sacrificing control or privacy. Whether you’re a developer building the next-gen data app or an enterprise seeking compliant AI solutions, DB-GPT offers a practical, open-source path forward in the era of AI-native data interaction.