For teams deploying large language models (LLMs) in production—whether for chatbots, reasoning APIs, or batch processing—latency and inference cost are persistent bottlenecks. Standard autoregressive decoding is inherently slow: each token depends on the previous one, forcing sequential computation that scales linearly with output length. While speculative decoding offers a promising path to parallelism, many approaches trade speed for fidelity or require complex integration.
Enter EAGLE-3, the latest evolution of the EAGLE (Extrapolation Algorithm for Greater Language-model Efficiency) framework. EAGLE-3 delivers up to 6.5× faster inference over vanilla decoding while provably preserving the exact same output distribution as the original model. This means you get dramatically reduced latency and GPU usage—without compromising on accuracy, fluency, or reliability.
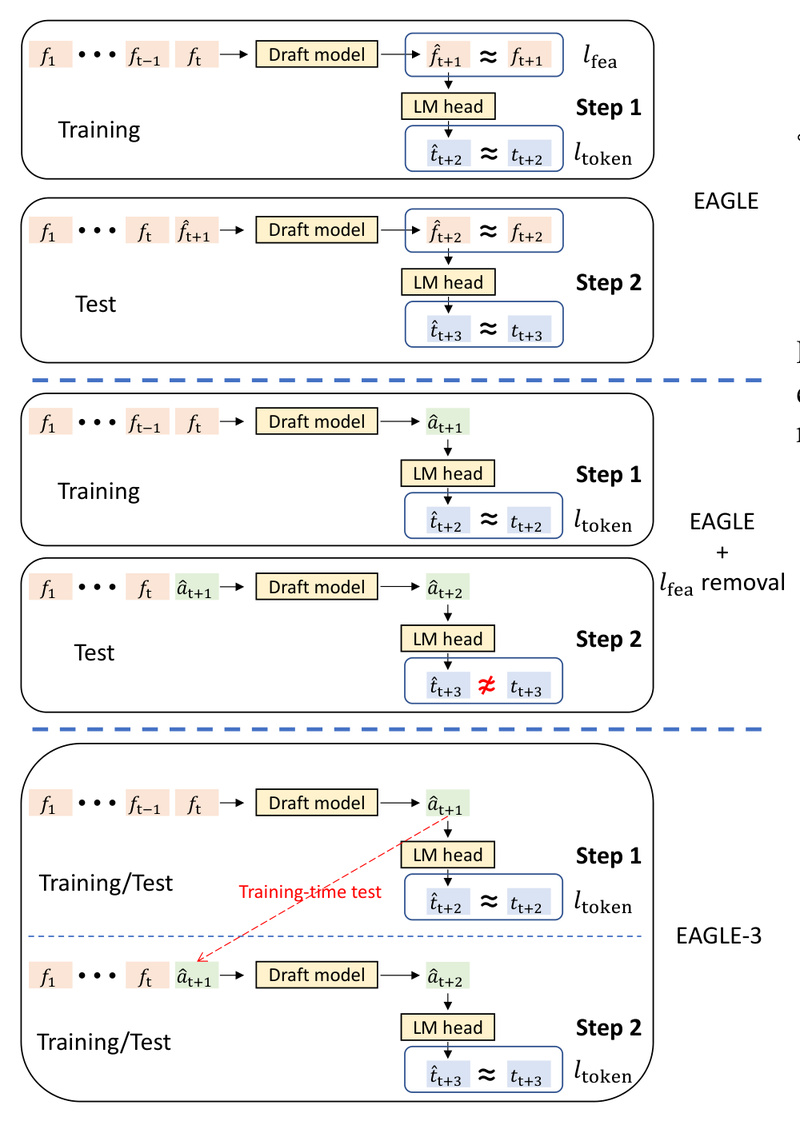
Developed by SafeAILab and accepted to NeurIPS 2025, EAGLE-3 represents a major leap in practical LLM acceleration. Unlike earlier versions that relied on feature-level extrapolation, EAGLE-3 abandons feature prediction entirely in favor of direct token prediction, fused with multi-layer semantic representations from the base model. This architectural shift unlocks full compatibility with data scaling and enables consistent speedups across diverse model families.
Why EAGLE-3 Stands Out
Among the Fastest Speculative Methods—Certified
Independent evaluations have certified EAGLE as the fastest speculative decoding method available. EAGLE-3 builds on this lead:
- 5.6× faster than vanilla decoding on Vicuna-13B
- 1.4× faster than EAGLE-2
- 1.38× higher throughput at batch size 64 in the SGLang framework
These gains aren’t theoretical—they’re measured on real hardware (e.g., 2× RTX 3090 GPUs) and hold across both chat-oriented and reasoning-intensive workloads.
Works Out of the Box with Leading LLMs
EAGLE-3 supports a broad and growing roster of state-of-the-art models, including:
- LLaMA-3.1/3.3/4 (8B to 70B+ parameters)
- Qwen3 (4B to 235B MoE variants)
- Vicuna, DeepSeek-R1, MiniCPM4, and OLMoE
Pre-trained EAGLE-3 draft models are publicly available on Hugging Face for immediate use—no custom training required unless you’re working with non-English data or unsupported architectures.
Seamless Integration with Major Inference Stacks
You don’t need to rewrite your deployment pipeline. EAGLE is natively integrated into leading LLM serving frameworks, including:
- vLLM
- SGLang
- TensorRT-LLM
- MLC-LLM
- DeepSpeed
- Intel Extension for Transformers
- AMD ROCm and NVIDIA NeMo
This plug-and-play compatibility means you can enable EAGLE-3 acceleration with minimal code changes.
Affordable to Train and Test
Training a draft model for EAGLE-3 is accessible even to teams without access to large GPU clusters. The entire process can be completed in 1–2 days on 8× RTX 3090 GPUs. For even easier adoption, the authors recommend SpecForge—a tool that enables out-of-the-box EAGLE-3 training with SGLang.
Ideal Use Cases
EAGLE-3 shines in scenarios where speed, cost, and output consistency are non-negotiable:
- High-throughput chat services: Reduce per-request latency and increase user capacity without retraining your base model.
- Low-latency reasoning APIs: Accelerate chain-of-thought or agent-based workflows where every millisecond counts.
- Batch inference in research: Speed up evaluation on benchmarks like MT-Bench or custom datasets.
- Cost-sensitive deployments: Cut GPU hours (and cloud bills) by up to 85% while maintaining identical model behavior.
Critically, EAGLE-3 requires no modification to your base LLM. It operates as a lightweight "draft head" that proposes candidate tokens, which are then verified by the original model—ensuring mathematical equivalence to standard decoding.
Getting Started in Minutes
Adopting EAGLE-3 is straightforward:
- Select a pre-trained draft model matching your base LLM (e.g.,
yuhuili/EAGLE3-LLaMA3.1-Instruct-8Bformeta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct). - Load both models using the
EaModelinterface:from eagle.model.ea_model import EaModel model = EaModel.from_pretrained(base_model_path="meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct",ea_model_path="yuhuili/EAGLE3-LLaMA3.1-Instruct-8B",torch_dtype=torch.float16,device_map="auto",use_eagle3=True,total_token=-1 # Enables dynamic draft length (EAGLE-2+) )
- Generate text using
eagenerate(), which mirrors Hugging Face’sgenerate()API:output_ids = model.eagenerate(input_ids, temperature=0.7, max_new_tokens=256)
Both code-based and web UI inference options are provided. For custom models (e.g., non-LLaMA architectures), minor modifications to the base model’s KV-cache logic—documented in the repo—enable EAGLE compatibility.
Important Limitations and Considerations
While EAGLE-3 is powerful, keep these points in mind:
- Model-specific draft heads: You need a draft model trained for your exact base LLM variant. Not all community models are supported out of the box.
- Language constraints: For example, the official Qwen2 draft models are trained on English-only data (ShareGPT). Chinese or multilingual use requires custom training.
- Hardware and precision: Qwen2-based models require bf16 precision to avoid numerical overflow; fp16 is sufficient for most others.
- Versioning: The main branch defaults to EAGLE-3. To use EAGLE-1, switch to the
v1branch and setuse_eagle3=False.
Performance gains also scale with model size and hardware—larger models on faster GPUs see the highest absolute speedups.
Summary
EAGLE-3 redefines what’s possible in LLM inference acceleration. By replacing fragile feature extrapolation with robust, multi-layer token prediction—and validating candidates through the original model—it achieves unprecedented speedups without altering output quality. With broad model support, seamless framework integration, and accessible training, EAGLE-3 is a practical, production-ready solution for any team looking to reduce latency, cut costs, and scale LLM deployments—without compromise.