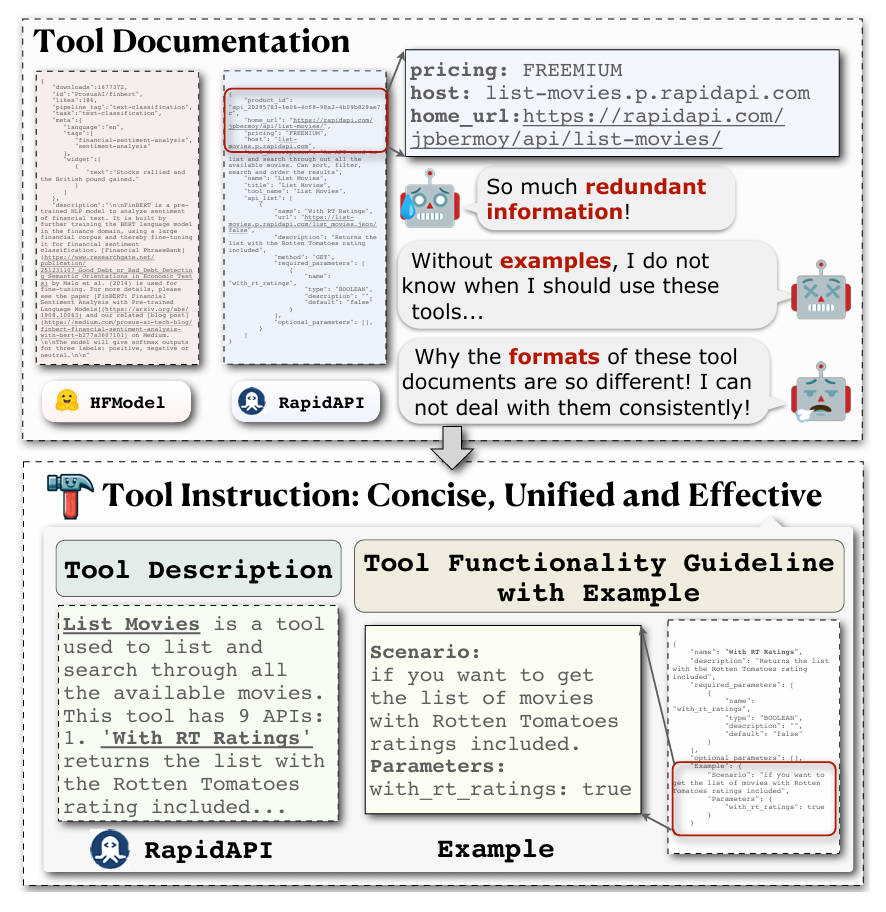
Building capable AI agents that interact with real-world tools—like APIs, software libraries, or external services—is a core challenge in deploying large language models (LLMs) beyond chat. A major bottleneck? The chaotic state of tool documentation. Documentation across different tools is often verbose, inconsistent, incomplete, or scattered across formats, making it hard for LLMs to reliably understand and use them.
Enter EASYTOOL, a framework developed by Microsoft as part of the JARVIS project. EASYTOOL tackles this problem head-on by transforming diverse, lengthy, and unstructured tool documentation into concise, standardized tool instructions that LLM-based agents can easily parse and execute. Rather than forcing models to sift through redundant paragraphs or guess missing parameters, EASYTOOL distills only the essential information—functionality, inputs, outputs, and usage constraints—into a clean, unified interface.
This isn’t just about neatness. By simplifying how tools are described, EASYTOOL directly enhances agent performance while cutting down on computational cost—a win for both developers and end users.
Why Tool Documentation Is a Hidden Bottleneck for LLM Agents
LLM-based agents often rely on tool-augmented reasoning to complete complex tasks: booking flights, analyzing financial data, generating images, or automating workflows. To do this, they must “read” tool documentation to decide which function to call and how to format its arguments.
In practice, however, tool documentation varies wildly:
- Some APIs provide exhaustive Swagger specs; others offer only GitHub README snippets.
- Parameter names might be inconsistent (e.g.,
img_pathvs.image_url). - Critical constraints—like rate limits or required authentication—are buried in footnotes.
When fed directly into an LLM, this noise leads to higher token consumption, misinterpretation of tool capabilities, and frequent execution failures. Worse, redundant text inflates inference costs and slows down agent decision-making.
EASYTOOL solves this by acting as a preprocessing layer: it ingests raw documentation from multiple sources and outputs a minimal, structured instruction that captures only what the LLM needs to know to use the tool correctly.
Core Benefits: Efficiency Meets Reliability
EASYTOOL delivers two major advantages, validated through extensive experiments across diverse real-world tasks:
1. Drastically Reduced Token Usage
By compressing verbose documentation into essential instructions, EASYTOOL significantly lowers the number of tokens an LLM must process during tool selection and invocation. This translates into lower latency, reduced API costs, and scalability when agents need to manage dozens or hundreds of tools.
2. Improved Tool-Usage Accuracy
With standardized, unambiguous instructions, LLM agents make fewer mistakes in argument formatting, tool selection, and dependency handling. This leads to higher task success rates, especially in multi-step workflows where one tool’s output feeds into another’s input.
In essence, EASYTOOL doesn’t just make tool usage easier—it makes it more reliable.
Ideal Use Cases for EASYTOOL
EASYTOOL shines in scenarios where LLM agents must integrate with heterogeneous tool ecosystems, such as:
- Task automation platforms (e.g., Microsoft’s JARVIS or HuggingGPT-style systems), where agents dynamically select from hundreds of models and APIs.
- Enterprise AI assistants that interact with internal and third-party services—each with its own documentation style.
- Research benchmarks like TaskBench, which evaluate how well LLMs can plan and execute complex, multi-tool tasks.
If your agent needs to juggle tools from Hugging Face, REST APIs, CLI utilities, or Python libraries—all documented differently—EASYTOOL provides the glue that turns chaos into coherence.
How to Get Started with EASYTOOL
Using EASYTOOL follows a straightforward pipeline:
- Input: Provide raw tool documentation from any source (e.g., API docs, GitHub READMEs, OpenAPI specs).
- Process: EASYTOOL parses and extracts core functional information—what the tool does, its inputs/outputs, and key constraints.
- Output: A concise, standardized tool instruction is generated in a consistent format.
- Deploy: Feed these instructions to your LLM agent during planning and execution phases.
The full implementation, including code and evaluation datasets, is available in the JARVIS GitHub repository (https://github.com/microsoft/JARVIS/), released under the EASYTOOL module. While EASYTOOL itself focuses on instruction standardization, it’s designed to plug into larger agent frameworks like JARVIS, which handle task planning, model selection, and execution orchestration.
Note that running the full JARVIS system requires configuring access to an LLM (e.g., via OpenAI) and optionally deploying local models, as detailed in the repository’s setup guide. However, the core idea of EASYTOOL—clean, minimal tool instructions—can inspire similar preprocessing steps even in custom agent architectures.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
It’s important to recognize that EASYTOOL is not a standalone tool but a component within an agent ecosystem. Its effectiveness depends on:
- The quality and completeness of the original documentation. If critical details are missing from source docs, EASYTOOL can’t magically infer them.
- Proper integration with an agent framework that can consume standardized instructions and execute tool calls.
- Access to an LLM backend and (optionally) local model infrastructure, as per the JARVIS system requirements.
EASYTOOL simplifies instruction—but it doesn’t replace the need for robust tool execution infrastructure, error handling, or security considerations around API access.
Summary
EASYTOOL addresses a critical yet often overlooked challenge in LLM agent development: the inefficiency and unreliability caused by inconsistent tool documentation. By distilling complex, noisy tool specs into concise, unified instructions, it enables agents to use tools more accurately, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
For developers and researchers building next-generation AI agents—especially those integrating diverse external tools—EASYTOOL offers a practical, proven way to reduce friction and boost performance. With its code and datasets publicly available, it’s ready to enhance your agent pipeline today.