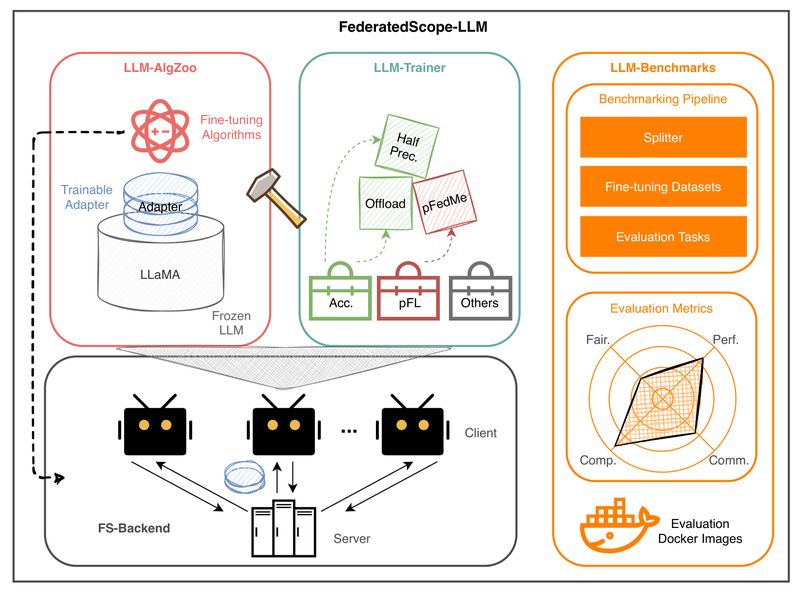
In today’s data-sensitive world, organizations increasingly want to harness the power of large language models (LLMs) while complying with strict privacy regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or internal data governance policies. FederatedScope-LLM (FS-LLM) is an open-source package built specifically to enable collaborative fine-tuning of LLMs across multiple parties—without ever sharing raw data. Developed by Alibaba’s FederatedScope team, FS-LLM provides a practical, efficient, and extensible solution for federated learning (FL) scenarios involving modern foundation models.
Whether you’re a researcher exploring privacy-preserving NLP, a healthcare institution training a medical assistant, or an enterprise customizing a customer service chatbot across regions, FS-LLM lowers the barrier to deploying LLMs in real-world, decentralized environments.
Why Federated Fine-Tuning of LLMs Matters
Large language models excel at general knowledge but often require task-specific fine-tuning to perform well in specialized domains. However, fine-tuning typically demands access to large, high-quality datasets—many of which contain sensitive information that cannot be centralized due to legal, ethical, or competitive constraints.
Federated learning offers a compelling alternative: each participant (or “client”) keeps their data local and only shares model updates—not the data itself. But applying this approach to LLMs introduces new challenges:
- Massive model sizes lead to high communication and memory costs.
- Proprietary or closed-source models (e.g., from API-only providers) can’t be fully accessed or modified.
- Lack of standardized pipelines for data splitting, training, and evaluation in federated LLM settings.
FederatedScope-LLM directly addresses these pain points with a purpose-built toolkit designed for real-world constraints.
Core Capabilities That Set FS-LLM Apart
End-to-End Benchmarking Pipeline
FS-LLM automates the entire federated fine-tuning workflow:
- Data preprocessing: Built-in support for instruction-tuning datasets like Alpaca, Dolly-15k, GSM8K, and CodeSearchNet, with flexible splitters (IID, LDA, or metadata-based) to simulate realistic client partitions.
- Federated training execution: Runs in standalone (simulation) or distributed mode with minimal configuration.
- Performance evaluation: Includes ready-to-use evaluation scripts for domain-specific benchmarks (e.g., MMLU for general knowledge, GSM8K for math reasoning, HELM for holistic assessment).
This pipeline ensures reproducibility and accelerates experimentation—critical for both academic research and industrial deployment.
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) Out of the Box
To keep communication and compute costs low, FS-LLM integrates popular PEFT methods via the Hugging Face PEFT library. Only small adapter modules are trained and exchanged between clients, not the full model. Supported techniques include:
- LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation)
- Prefix Tuning
- P-Tuning
- Prompt Tuning
Each method can be enabled with a few lines in a YAML config file, making it easy to compare approaches or adapt to resource-constrained devices.
Resource Efficiency for Real-World Constraints
FS-LLM includes multiple strategies to reduce memory and compute demands:
- Model sharing: Clients share a single base model instance in memory (
federate.share_local_model=True), drastically cutting CPU usage in simulation. - FP16 training: Halves memory footprint via half-precision (
train.is_enable_half=True). - DeepSpeed integration: Enables full-parameter fine-tuning of 7B-parameter models on 4×V100 GPUs.
- Adapter offloading: Moves trained adapters to CPU after training to free GPU memory.
These features make it feasible to experiment with larger models even on modest hardware.
Fine-Tuning Closed-Source LLMs with Offsite Tuning
One of FS-LLM’s most innovative features is support for federated fine-tuning of closed-source models—where neither the full model architecture nor the training data leaves the client.
Using offsite tuning, clients train a lightweight “emulator” (e.g., a distilled or layer-dropped version of the original model) locally. Only the emulator and adapters are updated, while the original black-box model remains untouched. Evaluation can then be performed on either:
- The emulator (for fast, proxy performance estimates), or
- The full model + fine-tuned adapter (for final validation, if API access permits).
This capability opens federated learning to commercial LLM APIs, expanding its applicability beyond open weights.
Getting Started Is Straightforward
FS-LLM prioritizes usability. After installing with pip install -e .[llm], you can launch a federated fine-tuning job with a single command:
python federatedscope/main.py --cfg federatedscope/llm/baseline/testcase.yaml
The configuration file defines everything: model type (e.g., gpt2 or llama-7b-hf), dataset (alpaca@llm), PEFT method (e.g., LoRA), number of clients, and training hyperparameters.
Custom datasets are also supported—just provide a JSON or JSONL file with instruction, input, and output fields, and FS-LLM handles the rest.
Ideal Use Cases
FS-LLM shines in scenarios where:
- Data silos exist across organizations (e.g., hospitals, banks, or government agencies) that cannot share records but benefit from a shared, improved model.
- Regulatory compliance prohibits data centralization, yet domain-specific LLM customization is needed.
- Resource-limited clients (e.g., edge devices or small teams) must fine-tune LLMs without massive infrastructure.
For example, multiple clinics could collaboratively improve a diagnostic assistant using local patient notes, each retaining full data control, while the global model converges to higher accuracy through federated updates.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While powerful, FS-LLM has current constraints users should consider:
- GPU memory requirements remain significant for large models, though mitigated by PEFT and efficiency features.
- Tokenizer compatibility issues may arise with certain Hugging Face models (e.g.,
LLaMATokenizervs.LlamaTokenizer), requiring manual fixes. - Offsite tuning for closed-source models is still an emerging capability—evaluation workflows assume either emulator access or API-based inference.
- The framework assumes users have basic familiarity with federated learning concepts and YAML-based configuration.
That said, the project is actively maintained, well-documented, and includes extensive examples to ease onboarding.
Summary
FederatedScope-LLM bridges a critical gap in the AI ecosystem: it enables privacy-preserving, collaborative fine-tuning of large language models at scale. By combining automated pipelines, parameter-efficient methods, and support for both open and closed models, it empowers teams to innovate without compromising data sovereignty. For project leads, researchers, and engineers working in regulated or decentralized environments, FS-LLM offers a robust, practical foundation for the next generation of secure, collaborative AI.