If your team is building AI applications that need to see, reason, and act—like desktop assistants that interpret screenshots, UI automation tools, or systems that analyze complex reports with charts and images—you’ve likely hit a wall with existing vision-language models (VLMs). Many open-source VLMs excel at simple captioning but falter when asked to solve STEM problems, navigate GUIs, or understand 50-page technical documents.
Enter GLM-V, an open-source family of multimodal models—including GLM-4.6V, GLM-4.5V, and GLM-4.1V-Thinking—designed specifically to bridge the gap between basic perception and versatile, real-world reasoning. Unlike models that treat images as afterthoughts, GLM-V treats vision as a first-class input for complex decision-making, powered by scalable reinforcement learning and optimized for practical deployment.
Developed by the ZAI team and open-sourced on GitHub, GLM-V isn’t just another benchmark-chaser. It’s built to be usable, actionable, and extensible—with features like native function calling, precise visual grounding, and support for 128K-token context windows. For technical decision-makers evaluating multimodal AI stacks, GLM-V offers a rare combination: state-of-the-art performance, transparent architecture, and ready-to-use tooling—all without vendor lock-in.
Why GLM-V Stands Out
State-of-the-Art Performance, Even in Compact Sizes
GLM-V’s models consistently outperform competitors—often dramatically—despite using far fewer parameters. For instance:
- GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking (a 9-billion-parameter model) beats Qwen2.5-VL-72B (a 72B model) on 29 out of 42 public benchmarks, including coding, STEM reasoning, and GUI interaction.
- GLM-4.5V achieves near-universal SOTA among open-source VLMs of comparable scale across diverse tasks: video understanding, document parsing, and spatial reasoning.
- GLM-4.6V pushes further, matching or exceeding closed-source models like Gemini-2.5-Flash on agent-oriented tasks.
This performance isn’t accidental. It stems from a reasoning-centric training framework that combines large-scale pre-training with Reinforcement Learning with Curriculum Sampling (RLCS)—a technique that progressively exposes the model to harder reasoning tasks, sharpening its ability to plan, reflect, and execute.
Native Multimodal Function Calling (GLM-4.6V)
One of GLM-V’s most practical innovations is native multimodal function calling, introduced in GLM-4.6V. Unlike traditional approaches that force visual data through text-only tool interfaces, GLM-4.6V can:
- Pass screenshots, document pages, or charts directly as inputs to tools (e.g., a code interpreter or web search).
- Interpret visual tool outputs (like rendered HTML or plotted graphs) and weave them back into its reasoning chain.
This closes the loop from perception → understanding → action, making it uniquely suited for multimodal agents in real business workflows—such as automating customer support bots that diagnose UI issues from user screenshots.
Real-World Reasoning Capabilities
GLM-V excels where many VLMs fail: structured, multi-step reasoning over visual content. Key capabilities include:
Precise Visual Grounding
Given a natural language query like “Locate all fire extinguishers in this factory image,” GLM-4.5V outputs normalized bounding boxes (e.g., [x1,y1,x2,y2]) enclosed in special tokens (<|begin_of_box|>...<|end_of_box|>). This enables downstream applications like robotic navigation or safety compliance checks.
GUI Agent Support
GLM-V can interpret desktop, mobile, or web UIs from screenshots and generate actionable plans—e.g., “Click the ‘Submit’ button” or “Extract the total from this invoice.” The project includes ready-made prompt templates and a desktop assistant app that captures screen content and routes it to the model via API.
Long Multimodal Document Understanding
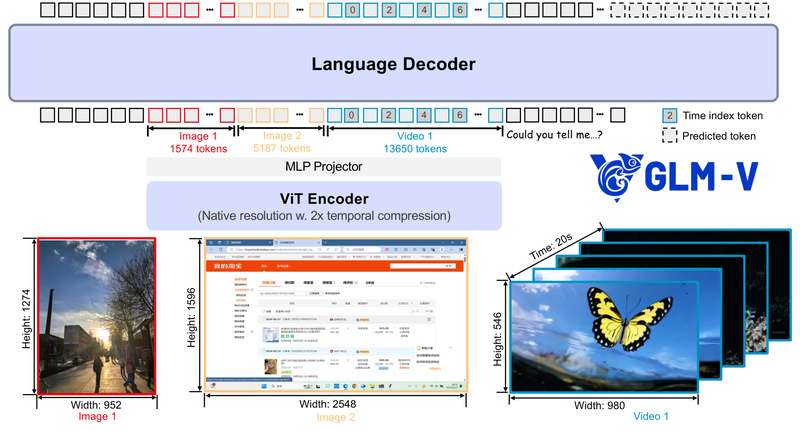
With support for 128K tokens (in GLM-4.6V), GLM-V processes entire technical manuals, financial reports, or research papers—including embedded images, tables, and diagrams—as a single input. It understands layout, cross-references figures, and answers complex questions without requiring OCR or manual preprocessing.
Flexible Reasoning Control
Users can toggle “Thinking Mode” (available in GLM-4.5V and GLM-4.1V-Thinking) to balance speed vs. depth. For simple queries, disable thinking for fast responses; for complex tasks, enable it to trigger chain-of-thought reasoning. This mirrors the behavior of GLM-4’s language-only variant, ensuring consistency across modalities.
Ideal Use Cases for Technical Teams
Automating UI Workflows with Visual Agents
Teams building RPA (Robotic Process Automation) or test automation tools can use GLM-V to create agents that:
- Watch screen recordings and diagnose UI bugs.
- Convert Figma mockups or screenshots into production-ready HTML/CSS (via the UI2Code^N extension).
- Navigate legacy applications with no API by interpreting their visual state.
Intelligent Document Processing
For enterprises drowning in PDFs, scanned forms, and presentation decks, GLM-V offers a unified pipeline to:
- Extract structured data from invoices, contracts, or lab reports—preserving visual context like chart trends or handwritten notes.
- Summarize multi-page documents while referencing specific figures or tables.
Video and Multimodal Analytics
GLM-V handles long video inputs, segmenting events and answering temporal questions (“When did the warning light turn on?”). This is valuable for security monitoring, sports analytics, or industrial quality control.
Rapid Prototyping with Open-Source Tooling
The GLM-V repo includes:
- A desktop assistant app (for Windows/macOS) that connects to the model API and supports images, videos, PDFs, and PPTs.
- Gradio and CLI demos for quick evaluation.
- Fine-tuning recipes via LLaMA-Factory, with explicit support for visual reasoning traces (using
<think>...</think>tags during training).
Getting Started: Deployment and Evaluation
GLM-V supports multiple inference backends, making it adaptable to your stack:
Quick Evaluation
- Use
trans_infer_gradio.pyto launch a web UI that accepts multimodal inputs. - Try the pre-built desktop assistant (available for download) to test real-time screen interpretation.
Production Deployment
- vLLM: Optimized for high-throughput serving with multimodal support. Enable thinking mode and tool calling via flags like
--tool-call-parser glm45. - SGLang: Ideal for video-heavy workloads; increase
SGLANG_VLM_CACHE_SIZE_MBfor better performance. - Both backends support thinking budget control, limiting reasoning length to manage latency.
Fine-Tuning for Custom Tasks
Using LLaMA-Factory, you can fine-tune GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking with datasets that include:
- Paired image-text examples.
- Explicit reasoning traces (wrapped in
<think>tags), which guide the model’s internal process without appearing in chat history.
Known Limitations and Trade-Offs
While GLM-V excels in multimodal reasoning, it has intentional trade-offs:
- Pure text QA is weaker—the team prioritized visual tasks; text-only performance will improve in future updates.
- Overthinking or repetition can occur on ambiguous prompts, especially with thinking mode enabled. Mitigations (like reasoning truncation) are available in evaluation scripts.
- Fine-grained visual perception (e.g., counting small objects, identifying specific faces) remains challenging—a common issue across current VLMs.
These limitations are transparently documented, and the team actively addresses them in updates (e.g., reducing repetitive outputs in GLM-4.5V vs. earlier versions).
Summary
GLM-V represents a significant leap for open-source vision-language models—not by chasing scale alone, but by engineering for real-world utility. With SOTA performance in compact sizes, native multimodal tool integration, and support for complex agents and document understanding, it directly addresses pain points faced by teams building practical AI systems.
If your project requires more than image captioning—if it demands reasoning, action, and contextual depth—GLM-V offers a transparent, performant, and community-supported foundation. With models, code, and deployment recipes all open-sourced, it’s never been easier to evaluate, customize, and deploy multimodal intelligence in your own workflows.