Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become a go-to architecture for grounding large language models (LLMs) in external knowledge. Yet, even the most advanced RAG systems struggle when faced with tasks that require connecting facts across multiple documents, reasoning over evolving knowledge bases, or efficiently incorporating new information without costly retraining. These limitations become especially pronounced in enterprise, legal, medical, or research settings—where knowledge is relational, dynamic, and multi-layered.
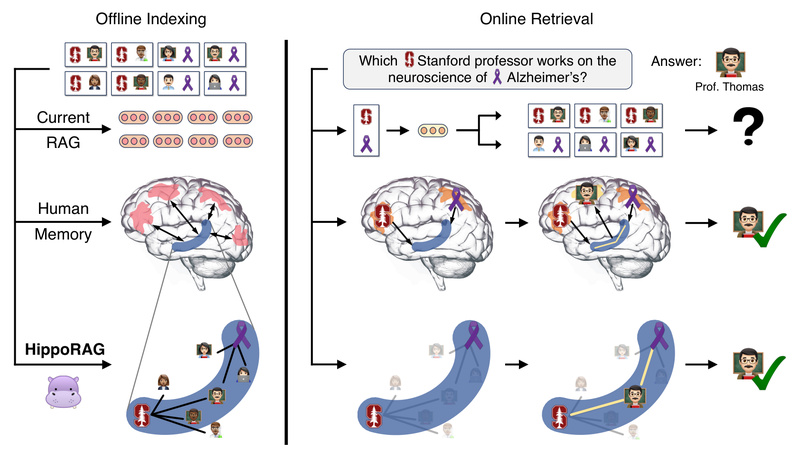
Enter HippoRAG, a novel retrieval framework that rethinks RAG not as a simple lookup mechanism, but as a long-term memory system inspired by how the human brain integrates and retrieves knowledge. Drawing from the hippocampal indexing theory of memory, HippoRAG combines LLMs, knowledge graphs, and the Personalized PageRank algorithm to enable deep, associative reasoning—while remaining fast, cost-effective, and scalable.
Unlike traditional RAG approaches that treat documents as isolated units, HippoRAG explicitly models relationships between entities and facts. This allows it to answer complex, multi-hop questions in a single retrieval step—matching or outperforming iterative methods like IRCoT at a fraction of the cost and latency.
Why Traditional RAG Isn’t Enough
Standard RAG pipelines retrieve documents based on lexical or semantic similarity between a query and individual passages. This works well for simple, single-fact questions (“Who is George Rankin?”), but fails when answers require reasoning across multiple supporting facts. For example:
“What county is Erik Hort’s birthplace a part of?”
Answering this requires linking “Erik Hort → Montebello → Rockland County”—a chain that spans at least two documents. Traditional RAG often misses such connections because it lacks an explicit model of relationships. Worse, iterative retrieval strategies (e.g., IRCoT) that attempt to bridge these gaps do so at high computational cost, requiring multiple LLM calls and increased latency.
Additionally, most RAG systems are static: adding new documents doesn’t update the system’s understanding of how that knowledge connects to existing facts. This leads to fragmented memory and poor continual learning—forcing teams to reindex entire corpora or even retrain components.
For technical decision-makers building knowledge-intensive applications, these gaps translate into inaccurate answers, slow response times, and unsustainable operational costs as data scales.
How HippoRAG Mimics Human Long-Term Memory
HippoRAG addresses these challenges by emulating two key brain structures: the neocortex (for storing factual knowledge) and the hippocampus (for indexing and retrieving relational memories).
Here’s how it works:
- Information Extraction: Using an LLM, HippoRAG extracts structured triples (subject–relation–object) from input documents—e.g., (Erik Hort, born in, Montebello).
- Knowledge Graph Construction: These triples form a lightweight, entity-centric knowledge graph that captures semantic relationships across the entire corpus.
- Personalized PageRank (PPR): At query time, HippoRAG identifies relevant entities in the question, then uses PPR to propagate relevance through the graph—effectively “activating” all related facts in one shot.
- Retrieval & Generation: The top-ranked passages (linked via the graph) are passed to the LLM for final answer generation.
This process enables associative retrieval: instead of matching a query to isolated passages, HippoRAG retrieves a coherent subgraph of interconnected knowledge. The result is deeper reasoning with far fewer LLM calls.
Key Strengths for Practitioners
HippoRAG delivers measurable advantages that matter in real-world deployments:
- Up to 20% higher accuracy on multi-hop QA benchmarks (e.g., MuSiQue, HotpotQA, 2Wiki) compared to state-of-the-art RAG methods.
- Single-step retrieval that matches or exceeds the performance of iterative approaches like IRCoT—without their overhead.
- 6–13x faster inference and 10–30x lower cost than iterative alternatives, thanks to eliminating multiple LLM rounds.
- Efficient offline indexing: Despite using a knowledge graph, HippoRAG’s indexing is significantly lighter than graph-based RAG systems like GraphRAG, RAPTOR, or LightRAG—making it practical for large-scale or resource-constrained environments.
These benefits are not theoretical: HippoRAG consistently outperforms competitors across three critical dimensions—factual memory, sense-making (e.g., narrative comprehension in NarrativeQA), and associativity—as shown in peer-reviewed NeurIPS 2024 and ICML 2025 papers.
Ideal Use Cases
HippoRAG is particularly valuable when your application involves:
- Evolving knowledge bases: Continually updated documentation, research repositories, or regulatory databases where new facts must connect to existing ones.
- Complex question answering: Multi-hop queries common in legal discovery, technical support, or biomedical research.
- Narrative or contextual understanding: Tasks requiring synthesis across long documents—e.g., summarizing case law, clinical notes, or technical manuals.
- Associative reasoning: Questions that depend on implicit chains of information, like the “Erik Hort” example above.
It’s less suited for simple keyword-based lookups where standard dense retrieval suffices—but excels wherever relationships matter.
Getting Started: Simple Integration
HippoRAG is designed for easy adoption. Installation is a one-liner:
pip install hipporag
Then, in just a few lines of Python, you can index documents and run retrieval-augmented QA:
from hipporag import HippoRAG docs = ["Erik Hort's birthplace is Montebello.","Montebello is a part of Rockland County." ] hipporag = HippoRAG(save_dir='outputs',llm_model_name='gpt-4o-mini',embedding_model_name='nvidia/NV-Embed-v2' ) hipporag.index(docs=docs) result = hipporag.rag_qa(queries=["What county is Erik Hort's birthplace a part of?"])
HippoRAG supports both cloud APIs (OpenAI, Azure, or any OpenAI-compatible endpoint) and local LLMs via vLLM (e.g., Llama 3.3 70B), giving teams flexibility for cloud, hybrid, or on-prem deployments.
For production, you can even use vLLM’s offline batch mode to accelerate indexing by over 3x—ideal for large corpora.
Current Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, HippoRAG has a few constraints to keep in mind:
- Embedding model support is currently limited to NV-Embed, GritLM, and Contriever.
- The knowledge graph is built offline during indexing—real-time incremental updates are possible but require re-running the information extraction step.
- No built-in vector database integration (e.g., Pinecone, Weaviate) is available yet, though this is on the roadmap (see GitHub TODO).
- Best performance is achieved when queries benefit from relational reasoning; for simple retrieval tasks, standard RAG may suffice.
These trade-offs reflect HippoRAG’s focus on relational intelligence over raw speed or plug-and-play simplicity—a deliberate design choice for knowledge-intensive applications.
How It Stacks Up: Real Gains, Real Efficiency
In head-to-head comparisons, HippoRAG doesn’t just edge out competitors—it redefines what’s possible in non-parametric continual learning for LLMs. On benchmarks like MuSiQue (multi-hop QA) and NarrativeQA (complex context understanding), it surpasses all existing RAG methods, including graph-based and iterative approaches.
Critically, it achieves this without sacrificing latency or cost. Where other systems add layers of complexity, HippoRAG simplifies the pipeline: one retrieval step, one LLM call, one coherent answer.
For teams already using RAG who are hitting walls with accuracy or scalability, HippoRAG offers a pragmatic upgrade path—bringing true long-term memory to LLMs, without the overhead of retraining or massive infrastructure changes.
Summary
HippoRAG transforms RAG from a document-fetching tool into a neurobiologically inspired memory system capable of deep, relational reasoning over dynamic knowledge. By leveraging knowledge graphs and Personalized PageRank, it enables LLMs to connect facts across documents in a single, efficient step—delivering superior accuracy, lower cost, and faster responses than iterative alternatives.
Whether you’re building an enterprise knowledge assistant, a research navigator, or a legal QA system, HippoRAG provides a compelling foundation for applications where understanding how facts relate is as important as the facts themselves.
With simple integration, support for both cloud and local models, and strong empirical results, it’s a framework worth evaluating for any knowledge-intensive LLM project.