Overview
For technical decision makers evaluating multimodal AI, choosing between closed-source APIs and open alternatives often means trading off control, cost, and capability. InternLM-XComposer changes that equation. Built as a vision-language large model (VLLM) with a focus on both deep comprehension and creative composition, it delivers performance competitive with GPT-4V and Gemini Pro—despite running on a lightweight 7B-parameter language backbone. What truly sets it apart is its ability to intelligently weave images into coherent, context-aware narratives, understand ultra-high-resolution visuals and long-form videos, and even generate functional webpages from simple instructions. All of this is available under a permissive license that allows free commercial use, making it a rare blend of power, openness, and practicality.
Advanced Text-Image Composition That Feels Human
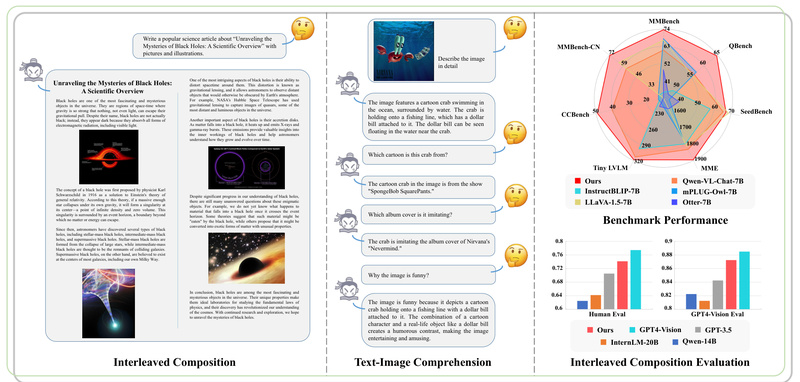
One of InternLM-XComposer’s defining strengths is its capacity for free-form text-image composition. Unlike models that merely caption images or answer questions, it can generate full-length articles where images are inserted precisely where they enhance the narrative—without manual intervention. Provide a prompt like “Write a blog about French pastries,” and it returns a structured, engaging post complete with logically placed visual suggestions or actual embedded images. This isn’t just templated output; the model uses Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to ensure contextual relevance and editorial quality. For teams building content automation pipelines—think marketing, education, or technical documentation—this capability dramatically reduces the loop between ideation and publication.
High-Resolution and Video Understanding Without Compromise
InternLM-XComposer-2.5 introduces a native 560×560 vision encoder and dynamic resolution handling, enabling it to process images of any aspect ratio up to 4K. More impressively, it treats long videos as dense composites of tens or even hundreds of frames, allowing fine-grained analysis that captures subtle visual details. In practice, this means you can ask it to describe a sports highlight clip and get accurate player codes, or analyze a documentary segment and extract contextual facts. Benchmarks confirm its edge: it outperforms or matches leading open and closed models on video tasks like MVBench, MLVU, and MMBench-Video. This makes it ideal for applications in media analysis, surveillance summarization, or interactive educational tools where visual fidelity matters.
Turn Visual Inputs into Functional Web Experiences
Beyond understanding and writing, InternLM-XComposer can generate working HTML, CSS, and JavaScript from diverse inputs. Give it a text instruction (“Create a website for a research lab with a blue nav bar and project images”), upload a resume in Markdown, or even provide a screenshot of a UI mockup—and it will output clean, responsive code. This “screenshot-to-webpage” and “instruction-to-webpage” functionality is particularly valuable for rapid prototyping, low-code development, or automating frontend generation in design-to-deployment workflows. Teams in product design, internal tooling, or digital agencies can leverage this to accelerate iteration cycles without deep frontend expertise.
Real-World Integration Made Practical
Getting started is straightforward. The model is available via Hugging Face Transformers with clear examples for video Q&A, multi-image dialogue, article writing, and webpage generation. For resource-constrained environments, 4-bit quantized versions via LMDeploy cut memory usage significantly—enabling inference on as few as two RTX 4090 GPUs. Fine-tuning is supported through ModelScope Swift, and quick demos can be launched with Gradio. While it does require CUDA 11.4+ and flash-attention2 for high-resolution tasks, these are standard in most modern AI stacks, and the project provides detailed installation and deployment guides.
Limitations to Consider
InternLM-XComposer is powerful but not magic. Its full 7B model demands substantial GPU memory, though quantization mitigates this. The long-context capabilities (supporting up to 96K tokens via RoPE extrapolation) require careful configuration. And while it excels across 28 benchmarks—including CCBench for Chinese cultural knowledge and OCR-heavy tasks like DocVQA—it may still lag behind proprietary systems in niche, highly subjective domains. Importantly, its strengths shine brightest when inputs are clear and tasks align with its training data: factual QA, structured composition, and visual reasoning.
Why It Stands Out in a Crowded Field
Compared to alternatives, InternLM-XComposer offers a uniquely balanced proposition. It’s fully open, commercially usable, and continuously updated—with recent spin-offs like XComposer2.5-Reward (a multimodal reward model) and OmniLive (for streaming video/audio interaction). For teams tired of API rate limits, opaque pricing, or black-box behavior, this model provides transparency, customization, and state-of-the-art performance in one package. If your project demands both creative output and analytical depth across text and visuals—without vendor lock-in—InternLM-XComposer is a compelling choice.
Summary
InternLM-XComposer bridges the gap between research-grade multimodal AI and real-world application needs. By mastering both comprehension and composition—from generating magazine-style articles with embedded visuals to converting UI mockups into live code—it empowers developers, researchers, and product teams to build richer, more interactive experiences. Its strong benchmark results, open licensing, and practical tooling make it not just an academic curiosity, but a viable engine for production systems. For anyone evaluating vision-language models in 2025, it deserves serious consideration.