Building voice-enabled applications today often means stitching together separate models for speech recognition, sound classification, audio captioning, and spoken response generation. This fragmented approach introduces complexity, inconsistency, and high engineering overhead—especially when trying to deliver a seamless, real-time user experience. Kimi-Audio changes this paradigm.
Kimi-Audio is an open-source audio foundation model that unifies a wide spectrum of audio tasks—ranging from automatic speech recognition (ASR) and emotion detection to end-to-end spoken conversation—into a single, deployable system. Developed by Moonshot AI and built on top of the Qwen 2.5-7B language model, Kimi-Audio delivers state-of-the-art performance across major audio benchmarks while offering straightforward APIs for developers and researchers. Whether you’re building a voice assistant, an audio analytics pipeline, or a multimodal agent, Kimi-Audio reduces technical debt by replacing multiple specialized models with one general-purpose audio intelligence engine.
One Model, Many Audio Tasks
Unlike traditional systems that require task-specific models, Kimi-Audio handles diverse audio modalities out of the box:
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): Transcribe speech in multiple languages with high accuracy.
- Audio Question Answering (AQA): Answer questions based on spoken or environmental audio.
- Audio Captioning (AAC): Generate descriptive text summaries of audio clips.
- Sound and Scene Classification: Identify sound events (e.g., dog barking, car honking) or acoustic scenes (e.g., café, forest).
- Speech Emotion Recognition: Infer emotional states from vocal prosody.
- End-to-End Speech Conversation: Engage in spoken dialogue with coherent audio and text responses.
This universality eliminates the need to maintain separate inference pipelines, data preprocessing logic, and model update cycles for each task—dramatically simplifying development and deployment.
State-of-the-Art Performance Across Real-World Benchmarks
Kimi-Audio consistently outperforms existing models—including Qwen2-Audio, GLM-4-Voice, and Step-Audio-Chat—across a comprehensive suite of audio evaluation tasks:
- On LibriSpeech test-clean, it achieves a record-low 1.28% WER (Word Error Rate), surpassing all known open models.
- On AISHELL-1, it reaches 0.60% WER, setting a new benchmark for Mandarin ASR.
- In audio understanding, it leads on MMAU (73.27% on sound), Nonspeech7k (93.93%), and CochlScene (80.99% on dev)—demonstrating strong non-speech comprehension.
- For spoken dialogue, it scores highest in speed control (4.30) and emotion control (4.27) among open models, approaching GPT-4o’s conversational quality.
- On VoiceBench, it achieves top results in reasoning (63.12%), trivia (62.17%), and instruction-following (IFEval: 61.10%).
These results are not just academic—they translate directly into more reliable transcription, richer audio insights, and more natural voice interactions in real applications.
Engineered for Production Use
Beyond raw performance, Kimi-Audio is designed for real-world deployment:
- 12.5Hz Audio Tokenizer: Balances fidelity and computational efficiency by compressing raw audio into both discrete semantic tokens and continuous acoustic features.
- Chunk-Wise Streaming Detokenizer: Based on flow matching, it enables low-latency audio generation—critical for interactive voice agents.
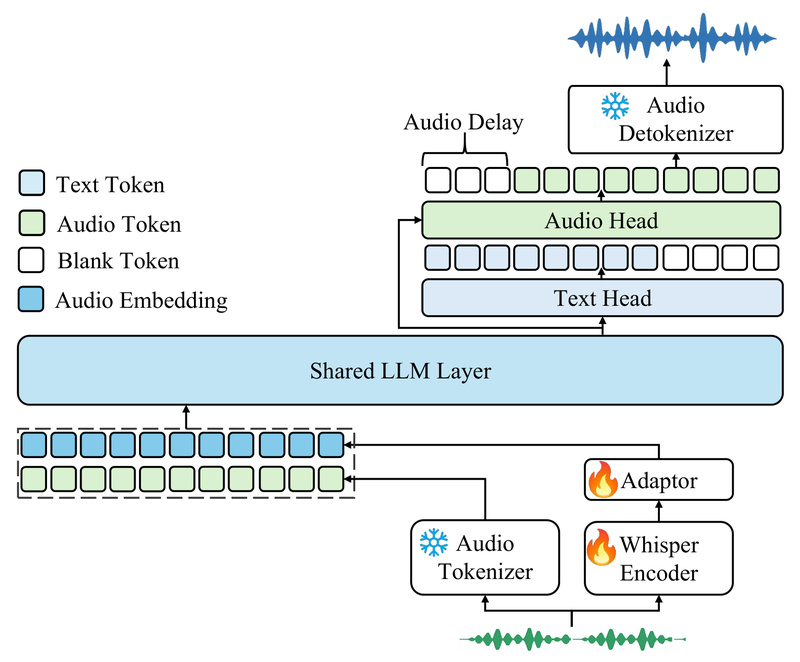
- Dual-Head LLM Architecture: Shares a transformer backbone but uses parallel heads to generate text tokens and audio tokens simultaneously, supporting mixed-modal responses.
- 24kHz Mono Audio Output: Generated speech is high-quality and compatible with standard telephony and voice assistant requirements.
These features make Kimi-Audio suitable for latency-sensitive applications like real-time customer service bots, voice-controlled devices, or live transcription services.
Getting Started in Minutes
Kimi-Audio is easy to integrate, even for teams without deep audio expertise. Installation is as simple as:
pip install torch pip install git+https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-Audio.git
With just a few lines of Python, you can run ASR or spoken dialogue:
from kimia_infer.api.kimia import KimiAudio
model = KimiAudio(model_path="moonshotai/Kimi-Audio-7B-Instruct", load_detokenizer=True)
# Audio-to-text transcription
messages = [{"role": "user", "message_type": "audio", "content": "input.wav"}]
_, text = model.generate(messages, output_type="text")
# Spoken response generation
wav, text = model.generate(messages, output_type="both")
Pre-trained and instruction-tuned checkpoints (e.g., Kimi-Audio-7B-Instruct) are available on Hugging Face, and the repository includes examples for single-turn and multi-turn conversations.
Validate Performance with the Open-Source Evaluation Toolkit
Adopting a new foundation model requires confidence in its capabilities. Kimi-Audio ships with Kimi-Audio-Evalkit, a comprehensive benchmarking suite that:
- Standardizes evaluation across ASR, audio understanding, AQA, and spoken dialogue.
- Integrates LLM-based judges to assess response quality in conversational tasks.
- Enables fair, reproducible comparisons with other audio models using shared inference recipes.
This toolkit empowers technical teams to validate Kimi-Audio against their own requirements before full-scale integration—reducing adoption risk.
Current Limitations and Practical Considerations
While powerful, Kimi-Audio has a few constraints to consider:
- Training Data Bias: The majority of pre-training data is in Chinese, though strong results on Fleurs (English WER: 4.44%) show solid multilingual ASR capability. For non-Chinese applications, performance may vary depending on domain and language.
- Audio Output Format: Generated speech is 24kHz mono—sufficient for most voice applications but not high-fidelity music or stereo audio.
- Fine-Grained Control: While it supports basic emotion and speed control in speech, advanced voice customization (e.g., speaker identity cloning, precise accent modulation) is not yet a core feature.
These limitations are typical for general-purpose audio foundation models, and the open-source nature of Kimi-Audio invites community contributions to extend its capabilities.
Summary
Kimi-Audio represents a significant step toward truly unified audio intelligence. By consolidating speech recognition, sound understanding, and spoken dialogue into a single, open-source, and high-performing model, it solves critical pain points in building multimodal voice applications: fragmented tooling, inconsistent performance, and complex deployment. With its production-ready architecture, easy-to-use APIs, and transparent evaluation toolkit, Kimi-Audio is an ideal choice for engineering teams, researchers, and product builders looking to accelerate development of next-generation audio AI systems—without sacrificing quality or control.