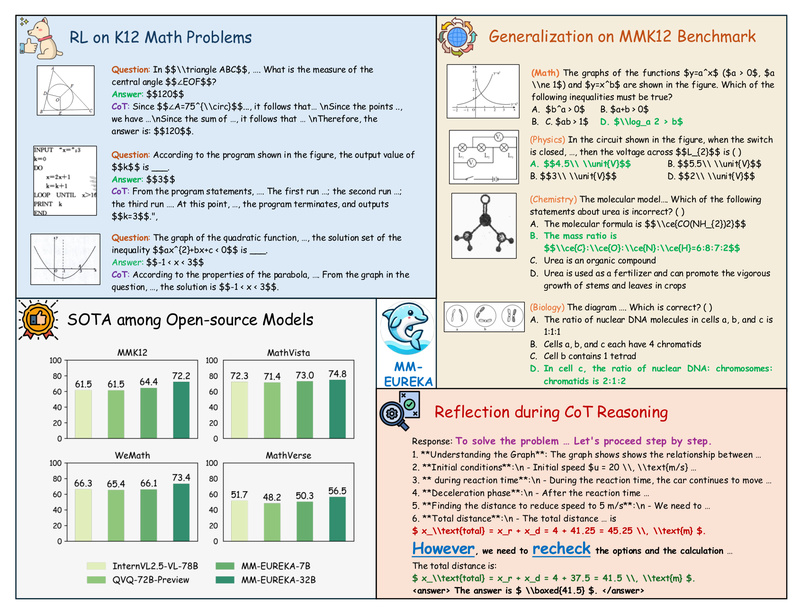
In the rapidly evolving field of multimodal AI, most models still struggle to combine visual understanding with precise, step-by-step logical reasoning—especially when it comes to K12-level science and math problems that involve diagrams, equations, or multi-step solutions. Enter MM-Eureka, an open-source, high-performance multimodal reasoning model that closes this gap by leveraging rule-based reinforcement learning to achieve state-of-the-art results on tasks requiring structured, verifiable reasoning over both images and text.
Developed by ModalMinds and built on the Qwen-VL architecture, MM-Eureka comes in two variants—7B and 32B parameters—and is trained on the newly introduced MMK12 dataset, a collection of over 15,000 high-quality, human-verified problems spanning math, physics, chemistry, and biology. Unlike many multimodal models that excel at image captioning or general visual QA but falter on analytical reasoning, MM-Eureka is explicitly designed for multidisciplinary STEM problem-solving, making it uniquely valuable for educational technology, research automation, and technical QA systems.
Why MM-Eureka Stands Out
Benchmark-Leading Performance on Reasoning Tasks
MM-Eureka doesn’t just perform well—it often outperforms much larger models. On the MathVista (testmini) benchmark, MM-Eureka-Qwen-7B scores 73.0, surpassing InternVL2.5-78B. The 32B version achieves 74.8, beating all open-source models and even top closed-source competitors like Claude 3.7 Sonnet and Qwen2.5-VL-72B on several key metrics. On the WeMath benchmark, it scores 73.4, and on the MMK12 evaluation set, it reaches 72.2—second only to OpenAI’s o1 and ahead of Gemini2-Flash.
This isn’t incremental progress—it’s a significant leap in open-source multimodal reasoning capability, particularly for structured, curriculum-aligned STEM problems.
Built on Proven Foundations with Strategic Innovations
MM-Eureka is not a from-scratch model. It builds on Qwen2.5-VL, a capable vision-language foundation, but introduces several algorithmic and data innovations that collectively enable stable, high-quality reinforcement learning:
- Rule-based rewards: Instead of relying on black-box human preferences or heuristic scoring, MM-Eureka uses programmable, interpretable rewards—such as format correctness, answer accuracy, and repetition penalties—that guide the model toward logically sound, step-by-step solutions.
- Online filtering: During training, low-accuracy model responses are dynamically filtered out using real-time accuracy rewards, improving data efficiency and training stability.
- Advanced RL algorithms: The project introduces and implements CPGD (Clipped Policy Gradient Optimization with Policy Drift), a novel reinforcement learning algorithm that enhances stability and performance over traditional methods like GRPO.
- Frozen ViT: The vision encoder is kept frozen during training, reducing instability and computational overhead while preserving strong visual feature extraction.
Fully Open and Reproducible
Unlike many high-performing models that release only inference weights or limited code, MM-Eureka open-sources everything: training code, evaluation scripts, the MMK12 dataset (including 2,000 multiple-choice questions for evaluation), and both 7B and 32B model checkpoints. This transparency enables researchers and engineers to reproduce results, adapt the pipeline, or fine-tune for their own domains—a rarity in cutting-edge multimodal AI.
Ideal Applications for Technical Decision-Makers
MM-Eureka is not a general-purpose chatbot or image tagger. It shines in specialized scenarios that demand accurate, explainable reasoning across modalities. Consider these use cases:
- AI-powered tutoring systems: Automate step-by-step feedback on student-submitted problems involving graphs, geometric figures, or chemical equations.
- Educational assessment platforms: Grade open-ended STEM questions where answers must be derived from visual prompts (e.g., “Calculate the current in this circuit diagram”).
- Technical documentation QA: Build internal tools that answer engineering or scientific queries referencing schematics, plots, or LaTeX-rendered equations.
- Research prototyping: Leverage MMK12 and the training pipeline to explore new rule-based RL approaches for multimodal reasoning without starting from scratch.
In each case, MM-Eureka’s ability to produce verifiable, intermediate reasoning steps—not just final answers—adds significant value over models that “hallucinate” plausible but incorrect solutions.
Getting Started: Practical Onboarding
Deploying or extending MM-Eureka is designed to be straightforward for teams with ML infrastructure experience:
- Installation: Clone the repository and install dependencies with
pip install -e .[vllm], which integrates vLLM for efficient inference and training. - Data: Use the provided MMK12 dataset or prepare custom data in the required JSONL format, where each sample includes a multimodal message (with image paths and text prompts) and a ground-truth answer string that can be parsed by the internal
math_verifymodule. - Training: Run pre-configured scripts for single-node or multi-node training (e.g.,
train_mm_eureka_qwen_7b_single_node.sh). The framework is built on OpenRLHF and supports distributed RL with Ray and vLLM. - Inference: Leverage the trained models for evaluation or integration into downstream applications using standard Hugging Face–compatible interfaces.
The pipeline is production-ready, well-documented, and built on community-supported backbones, lowering the barrier to adoption.
Important Limitations to Consider
While MM-Eureka excels in its niche, it’s essential to understand its boundaries before committing resources:
- Domain specialization: It’s optimized for K12 STEM reasoning, not general visual understanding, creative tasks, or open-ended conversation. Performance may degrade on non-academic or loosely structured problems.
- Compute requirements: Training the 32B model demands multi-GPU, distributed infrastructure and familiarity with RLHF-style workflows. Even inference benefits from high-end GPUs (e.g., A100 or H100).
- Expertise needed: Fine-tuning or modifying the reward rules requires understanding of reinforcement learning, multimodal architectures, and dataset curation—not a plug-and-play solution for non-technical teams.
- Language focus: Current models and data are English-centric, with limited support for multilingual or non-Western curricula.
Summary
MM-Eureka represents a major step forward in open, reproducible, and high-accuracy multimodal reasoning for technical and educational applications. By combining a strong vision-language foundation with rule-based reinforcement learning, online filtering, and a high-quality STEM dataset, it achieves performance that rivals or exceeds proprietary models—while remaining fully open.
For project leads, researchers, or engineering teams working on AI-driven education, technical QA, or structured multimodal reasoning, MM-Eureka offers a rare combination of state-of-the-art results, transparency, and adaptability. If your use case involves verifying logical steps across text and images—especially in math or science—this is a model worth serious evaluation.