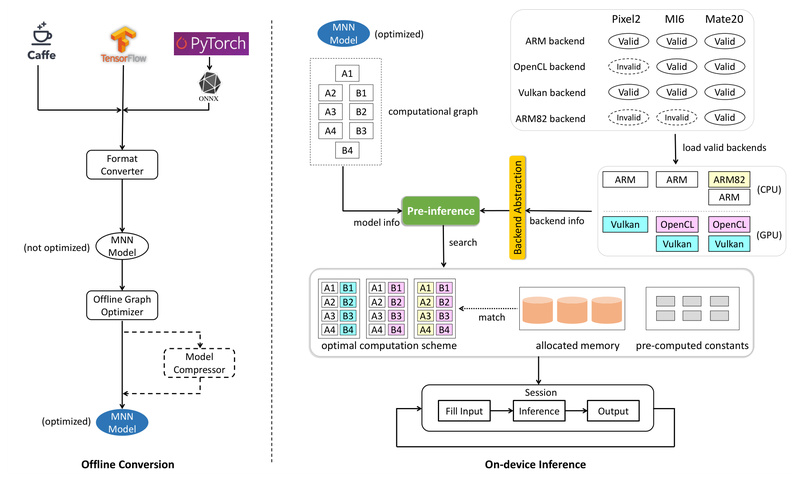
Mobile Neural Network (MNN) is an open-source, lightweight deep learning inference engine developed by Alibaba Group to bring powerful AI capabilities directly to mobile phones, embedded devices, and edge platforms—without relying on the cloud. Designed from the ground up for real-world deployment constraints, MNN addresses three critical pain points that developers and product teams face when integrating AI into on-device applications: model compatibility across frameworks, hardware diversity across devices, and strict limitations on memory, power, and binary size.
Unlike general-purpose frameworks that prioritize training or cloud inference, MNN focuses exclusively on efficient, low-latency, offline execution. It’s already in production across more than 30 Alibaba apps—including Taobao, DingTalk, Youku, and Xianyu—powering features like live video filters, image-based product search, voice assistants, and real-time recommendation systems in over 70 distinct use cases. If you’re building an application that needs to run AI locally—whether it’s a multimodal LLM chatbot, an image generator, or an IoT sensor analyzer—MNC delivers industry-leading performance with minimal footprint.
Why MNN Stands Out for On-Device AI
Ultra-Lightweight Footprint, Minimal Integration Overhead
One of MNN’s biggest advantages is its remarkably small binary size, which directly reduces app bloat—a major concern for mobile developers. On Android (armv7a with c++_shared), the core shared library is only about 800KB. On iOS, the static library for armv7+arm64 is roughly 12MB, and linking it into an app typically increases the executable size by just 2MB. For even tighter constraints, enabling the MNN_BUILD_MINI option can shrink the package by ~25%, albeit with fixed input shapes.
This compactness doesn’t come at the cost of versatility. MNN supports a wide range of neural network architectures—including CNNs, RNNs, Transformers, and GANs—and accepts models exported from TensorFlow, TensorFlow Lite, Caffe, ONNX, and TorchScript. With support for over 150–170 operators per framework, it covers the vast majority of real-world model topologies, including those with multiple inputs/outputs, dynamic shapes, and control flow.
Hardware-Aware Performance Optimization
MNN doesn’t just run models—it runs them fast. The engine includes deeply optimized kernels written in assembly for ARM and x86 CPUs, leveraging instruction sets like AVX2, AVX512, ARMv8.2 FP16, and dot-product (SDOT/VNNI) to accelerate core operations like convolution. For example, Winograd algorithms are extensively used to speed up common symmetric convolutions (3×3, 5×5, etc.), and FP16 on ARMv8.2 can deliver up to 2x speedup.
Beyond CPU, MNN supports GPU acceleration via Metal (iOS), OpenCL/Vulkan (Android/Linux), and CUDA (NVIDIA). On mobile GPUs, FP16 and Int8 inference are fully supported and well-optimized, enabling faster multimodal processing. While NPU support (via CoreML, NNAPI, HIAI, etc.) is available, it’s generally less mature than CPU/GPU paths—so for maximum reliability and performance, CPU and GPU backends are recommended.
Built for Real-World Multimodal and LLM Applications
Recent updates highlight MNN’s evolution beyond traditional vision models. The MNN-LLM and MNN-Diffusion subprojects demonstrate its capability to run large language models (like Qwen3, Llama, Baichuan) and stable diffusion models entirely offline on consumer devices. Official Android and iOS apps already showcase these features—enabling local text-to-text, image-to-text, audio-to-text, and text-to-image generation, even with models as large as Qwen2.5-7B or Qwen3-VL.
This makes MNN uniquely suited for privacy-sensitive, low-latency, or connectivity-constrained scenarios—such as a voice assistant that works in airplane mode, a camera app that adds AI filters without internet, or an industrial IoT device that analyzes sensor data in real time.
Getting Started: A Practical Workflow for Developers
Adopting MNN is streamlined through a set of well-documented tools:
- MNN-Converter: Translates models from TensorFlow, ONNX, PyTorch, and other formats into MNN’s optimized runtime format, applying graph-level optimizations automatically.
- MNN-Compress: Applies quantization (FP16, Int8) to reduce model size by 50–70% while maintaining accuracy—critical for mobile deployment.
- MNN Python API: Enables rapid prototyping, inference, image processing, and even on-device training without writing C++.
- MNN-CV: A lightweight (~100KB) alternative to OpenCV for basic image operations, fully integrated with MNN tensors.
- MNN Workbench: A desktop GUI tool that offers one-click model deployment, visualization, and pretrained model management.
This toolchain lowers the barrier to entry for ML engineers who want to deploy models without deep systems programming knowledge. You can convert, compress, test, and deploy—all within familiar Python or C++ environments.
Ideal Use Cases for MNN
MNN excels in scenarios where offline execution, low latency, and resource efficiency are non-negotiable:
- Mobile AI apps: Offline chatbots (e.g., MNN Chat App with Qwen3), real-time camera filters, visual search, and voice interfaces.
- Embedded and IoT systems: Smart cameras, wearables, or industrial sensors with limited memory and no cloud connectivity.
- Multimodal local AI: Applications combining text, image, and audio—like the MNN TaoAvatar app, which runs LLM, ASR, TTS, and animation models entirely on-device.
- Privacy-first AI: Any use case where user data must never leave the device (e.g., health monitoring, personal assistants).
Limitations and Considerations
While MNN is highly capable, it’s important to set realistic expectations:
- Training is supported but not the focus—MNN is first and foremost an inference engine.
- Precision and hardware support varies: For example, BF16 is only available on ARMv8.6, and NPU backends (CoreML, NNAPI, etc.) are functional but not as thoroughly optimized as CPU/GPU. Always consult the official support table before committing to a specific hardware-precision combination.
- Community support is active but primarily Chinese-speaking. English users are welcome, but documentation and forum discussions may require translation or patience.
That said, comprehensive benchmarks (available in the /benchmark directory and the OSDI’22 Walle paper) consistently show MNN outperforming TensorFlow Lite, PyTorch Mobile, and TVM in on-device inference speed and memory efficiency.
Summary
MNN is not just another deep learning framework—it’s a purpose-built solution for bringing state-of-the-art AI directly to end-user devices. By combining ultra-small binaries, broad model format support, hardware-specific optimizations, and real-world validation at Alibaba scale, it removes the biggest roadblocks to on-device AI deployment. Whether you’re building a consumer mobile app, an enterprise IoT solution, or experimenting with local LLMs, MNN gives you the tools to run powerful models offline—fast, privately, and efficiently.
With its Apache 2.0 license and active open-source development, MNN is ready for integration today. Explore the code at github.com/alibaba/MNN and see how it can accelerate your next edge AI project.