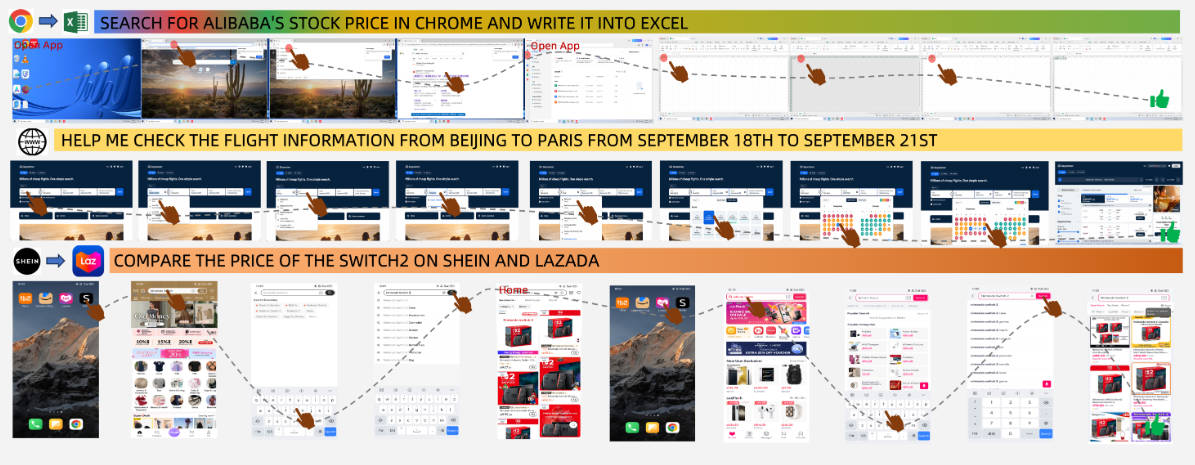
Imagine giving a natural language instruction like “Book a round-trip flight from Beijing to Paris on Skyscanner for September 18–21” and having an AI agent autonomously navigate your browser, fill out forms, and complete the task—without writing a single line of platform-specific code. That’s the promise of Mobile-Agent-v3, an open-source, general-purpose GUI automation framework developed by Tongyi Lab at Alibaba Group.
Built on top of GUI-Owl, a foundational vision-language model (VLM) trained specifically for graphical user interface interaction, Mobile-Agent-v3 enables end-to-end control of real-world mobile and desktop applications through high-level instructions. Unlike traditional automation tools that rely on brittle XPath selectors, hardcoded coordinates, or platform-specific scripting languages, Mobile-Agent-v3 perceives the screen like a human, reasons about its goal, plans actions step-by-step, and adapts to unexpected UI changes—making it robust, flexible, and truly cross-platform.
For engineering teams, QA specialists, product developers, and researchers tired of fragile automation pipelines that break with every UI update, Mobile-Agent-v3 offers a fundamentally new approach: generalist agents that understand what they’re doing, not just replaying recorded clicks.
State-of-the-Art Performance on Real GUI Benchmarks
Mobile-Agent-v3 isn’t just a conceptual prototype—it’s a rigorously evaluated system that delivers the best-known results among all open-source GUI agents as of 2025. On AndroidWorld, a challenging benchmark for mobile automation, it achieves a score of 73.3, significantly outperforming its predecessor and other open models. On OSWorld, which tests complex desktop interactions across Windows, macOS, and Ubuntu, it reaches 37.7, setting a new open-source standard despite the inherent difficulty of desktop environments.
These numbers aren’t abstract—they reflect real capabilities in tasks such as:
- Navigating multi-step app flows (e.g., searching for travel guides on Xiaohongshu and saving a note)
- Performing cross-application workflows (e.g., copying data from one app to another)
- Handling dynamic UI elements like pop-ups, ads, and loading states
- Executing precise operations like inserting “Word Art” with custom text into a PowerPoint slide
In essence, Mobile-Agent-v3 bridges the gap between research-grade AI and industrial-strength automation.
Core Innovations That Address Real Engineering Pain Points
Dynamic Task Decomposition & Reasoning
Rather than executing rigid, pre-recorded scripts, Mobile-Agent-v3 breaks down complex instructions into subtasks, reasons about the current screen state, and decides the next best action. This enables it to handle open-ended requests like “Create a new PPT and add Alibaba as Word Art”—a task requiring multiple distinct operations across toolbars, menus, and text editors.
Robustness to UI Disruptions
One of the biggest frustrations in GUI automation is scripts failing when an unexpected alert, advertisement, or system dialog appears. Mobile-Agent-v3 includes built-in exception handling and reflection mechanisms that allow it to detect anomalies, pause, reassess the situation, and recover—without crashing or requiring manual intervention.
Memory and Cross-Application Awareness
For multi-step tasks that span apps or sessions (e.g., “Find hotel options on App A, compare prices on App B, then book via App C”), Mobile-Agent-v3 maintains key information in memory and leverages its planning module to coordinate actions across contexts—something traditional automation tools simply cannot do.
Unified Perception-to-Action Pipeline
At the heart of the system is GUI-Owl, a multimodal foundational model that unifies perception (understanding what’s on screen), grounding (locating actionable elements), reasoning (what to do next), and execution (generating precise actions like taps or clicks) in a single neural policy. This eliminates the need for separate modules for OCR, object detection, and action mapping—reducing complexity and error propagation.
Practical Use Cases for Teams and Developers
Mobile-Agent-v3 shines in scenarios where flexibility, reliability, and cross-platform support matter more than speed or ultra-low latency:
- QA Automation: Test mobile and desktop apps across OS versions without maintaining dozens of brittle test scripts.
- Customer Support Bots: Automate routine user tasks (e.g., flight bookings, account updates) by operating real apps on behalf of users.
- Enterprise Demo Agents: Create interactive product demos that actually use the software instead of showing static slides.
- Accessibility Tools: Build assistive agents for users with disabilities who need help navigating complex interfaces.
- Research & Development: Rapidly prototype agent-based UI interaction systems using open, reproducible components.
Notably, it excels when tasks involve unstructured, visual interfaces—precisely where API-based automation fails.
Getting Started Without Heavy Infrastructure
You don’t need a GPU cluster or a device farm to try Mobile-Agent-v3. The team provides:
- Free online demos via ModelScope and Bailian, powered by Wuying Cloud Desktop and virtual mobile devices—no local setup required.
- Open-source code for GUI-Owl and the Mobile-Agent-v3 framework on GitHub, including checkpoints for both the 7B and 32B model variants.
- Support for four major platforms: Android, Windows, macOS, and Ubuntu—out of the box.
This dramatically lowers the barrier to evaluation. Within minutes, you can input a natural language command and watch the agent operate a real device—remotely and securely.
Current Limitations and Considerations
While groundbreaking, Mobile-Agent-v3 isn’t a silver bullet:
- Performance on complex desktop environments (reflected in the 37.7 OSWorld score) still lags behind mobile, as desktop UIs are more heterogeneous and less standardized.
- It relies on visual input, so interfaces with non-standard rendering (e.g., custom game UIs or heavily animated elements) may confuse the perception module.
- The hosted demos require internet access and may have usage limits; self-hosting demands significant compute resources for the 32B model.
These constraints are important for realistic deployment planning—but they don’t diminish the framework’s value for a wide range of practical automation challenges.
Summary
Mobile-Agent-v3 represents a paradigm shift in GUI automation: from brittle, rule-based scripts to generalist AI agents that see, reason, and act across platforms. By combining a powerful foundational model (GUI-Owl) with a multi-agent architecture that supports planning, memory, and error recovery, it solves real-world pain points that have long plagued automation engineers. With strong benchmark results, open-source availability, and easy-to-access demos, it’s now possible for teams to evaluate and integrate human-like GUI agents into their workflows—without reinventing the wheel.
For anyone building or managing software that interacts with graphical interfaces, Mobile-Agent-v3 isn’t just an academic curiosity—it’s a practical tool ready for real use.