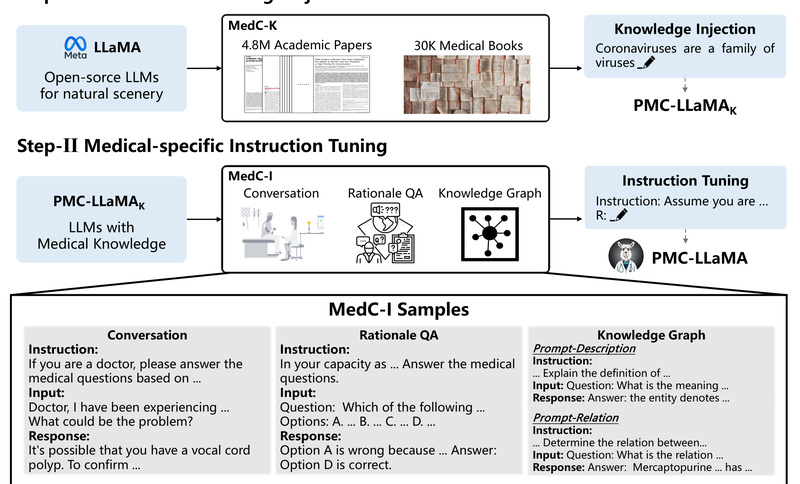
PMC-LLaMA is an open-source large language model explicitly engineered for the medical domain. Unlike general-purpose LLMs—such as LLaMA-2 or even ChatGPT—that often falter when faced with complex clinical reasoning or factual medical knowledge, PMC-LLaMA was built from the ground up to understand, reason, and respond with high precision in healthcare contexts. It achieves this through a two-stage training process: first, extensive pretraining on a massive corpus of biomedical literature, and second, fine-tuning on a high-quality instruction dataset that mimics real-world medical queries and dialogues.
For engineers, researchers, and product teams working in digital health, clinical AI, or biomedical informatics, PMC-LLaMA offers a rare combination: strong performance on medical benchmarks, open access to models and code, and a design tailored for integration into technical workflows. Most notably, its 13-billion-parameter version has been shown to surpass ChatGPT on key medical question-answering benchmarks like USMLE and PubMedQA—despite being significantly smaller in scale.
Why Domain Specialization Matters in Medical AI
General-purpose language models are trained on broad internet-scale data, which dilutes their ability to handle domain-specific tasks requiring factual rigor. In medicine, even minor inaccuracies can have serious consequences—making “hallucination” or vague responses unacceptable. PMC-LLaMA addresses this by injecting deep medical knowledge directly into the model architecture through curated, high-quality domain data.
The project’s creators didn’t just add a few medical examples on top of an existing LLM. Instead, they:
- Pretrained the base LLaMA model on 4.8 million PubMed Central (PMC) academic papers and 30,000 medical textbooks, ensuring deep exposure to authoritative clinical knowledge.
- Created a 202-million-token instruction-tuning dataset covering medical question answering, reasoning rationales, and multi-turn clinical dialogues—enabling the model to follow structured prompts reliably.
This systematic approach ensures that PMC-LLaMA doesn’t just “sound” medical—it actually knows medicine at a level that aligns with professional standards.
Proven Performance on Real Medical Benchmarks
PMC-LLaMA’s effectiveness isn’t theoretical—it’s been validated against widely accepted medical QA benchmarks:
| Model | USMLE | MedMCQA | PubMedQA |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT (175B) | 57.0 | 44.7 | 63.9 |
| LLaMA-2 (13B) | 42.7 | 37.4 | 68.0 |
| PMC-LLaMA (13B) | 56.4 | 56.0 | 77.9 |
These results show that PMC-LLaMA outperforms both general LLMs and other medical fine-tuned models (like Med-Alpaca) across multiple datasets. Importantly, it achieves ChatGPT-level or better performance on USMLE and PubMedQA despite having less than 10% of ChatGPT’s parameter count—making it far more efficient for deployment in resource-constrained environments.
Ideal Use Cases for Technical Teams
PMC-LLaMA excels in applications where factual correctness, structured output, and domain fidelity are non-negotiable. Consider these scenarios:
Clinical Decision Support Prototypes
While not a certified diagnostic tool, PMC-LLaMA can power internal prototypes that help clinicians explore differential diagnoses, interpret lab results, or review treatment guidelines—especially when integrated with verified knowledge bases.
Medical Q&A Systems
For telehealth platforms, patient education apps, or hospital intranets, PMC-LLaMA can generate accurate, concise answers to common clinical questions, reducing the burden on human staff and improving response consistency.
Automated Medical Report Summarization or Drafting
When paired with validated retrieval systems, PMC-LLaMA can assist in drafting radiology impressions, discharge summaries, or research abstracts based on structured inputs—thanks to its ability to produce coherent, citation-aware narratives.
Medical Education and Training Tools
Its strong performance on USMLE-style questions makes it a valuable asset for building adaptive learning platforms that simulate board exam conditions or provide explanations for complex clinical scenarios.
Getting Started: Simple Integration for Engineers
PMC-LLaMA is designed for rapid evaluation and integration. The 13B model is publicly available on Hugging Face and can be loaded in just a few lines of Python:
import transformers
tokenizer = transformers.LlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained('axiong/PMC_LLaMA_13B')
model = transformers.LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained('axiong/PMC_LLaMA_13B')
model.cuda() # Run on GPU for faster inference
A standard prompt template structures inputs as instruction-context-response triples—a pattern that aligns well with many real-world medical queries. Example prompts include patient cases with multiple-choice options, enabling the model to select and justify the best clinical answer.
Environment & Hardware Requirements
- PyTorch 1.13+, transformers 4.28.1, and sentencepiece are required.
- The 13B model typically requires ≥24GB GPU memory for full-precision inference (quantization or model parallelism can reduce this).
- No internet access is needed at inference time—ideal for secure or offline clinical environments.
Limitations and Responsible Deployment
Despite its strengths, PMC-LLaMA is not a plug-and-play solution for regulated clinical use. Key constraints include:
- LLaMA License Dependency: Since it’s built on Meta’s LLaMA, users must comply with LLaMA’s licensing terms, which restrict commercial use without approval.
- No Real-Time or Personalized Data: The model reflects knowledge up to its training cutoff and cannot access real-time guidelines, patient records, or individual health data.
- Not a Medical Device: PMC-LLaMA should never be used as a standalone diagnostic or treatment recommendation system without human oversight and regulatory validation.
For regulated settings, treat PMC-LLaMA as a research-grade foundation—excellent for prototyping, knowledge augmentation, and internal tooling, but not for direct patient-facing decisions without rigorous validation.
Summary
PMC-LLaMA represents a significant step toward practical, open-source AI in medicine. By combining massive-scale biomedical pretraining with high-quality instruction tuning, it delivers accuracy that rivals or exceeds much larger proprietary models—while remaining accessible to researchers and developers. For technical teams building health-focused applications, it offers a powerful, transparent, and benchmark-validated starting point to explore the next generation of medical language AI.