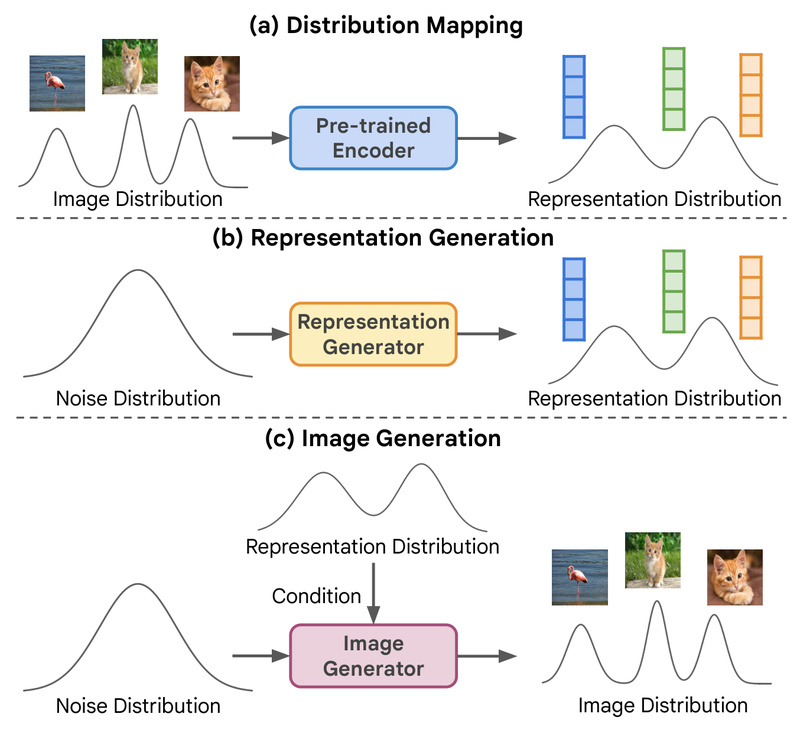
For years, unconditional image generation—creating realistic images without relying on human-provided class labels—has lagged significantly behind its class-conditional counterpart in terms of quality and coherence. This performance gap discouraged many from pursuing label-free generative approaches, despite the enormous potential of learning from vast unlabeled datasets.
Enter RCG (Representation-Conditioned Generation): a breakthrough self-supervised framework that finally bridges this gap. By leveraging semantic representations from a pre-trained self-supervised encoder (like MoCo v3 ViT), RCG conditions a diffusion-based image generator without ever using labels. The result? State-of-the-art unconditional generation performance that rivals or even matches top class-conditional models—achieving a remarkable FID of 2.15 on ImageNet 256×256, a 64% improvement over prior best unconditional methods.
For practitioners working with unlabeled data, limited annotation resources, or seeking scalable generative pipelines, RCG offers a compelling solution that unlocks high-quality synthesis without supervision.
How RCG Works: Self-Supervision Meets Generative Modeling
At its core, RCG decouples the generative process into two stages, both operating in the representation space rather than raw pixels or labels:
-
Representation Diffusion Model (RDM):
Instead of modeling pixel-level noise, RCG trains a diffusion model to generate semantic representations—specifically, features extracted by a self-supervised vision encoder such as MoCo v3 ViT-B or ViT-L. These representations capture meaningful structure and semantics without any class labels. -
Pixel Generator (e.g., MAGE, DiT, ADM, or LDM):
A second-stage generator (like MAGE or DiT) is trained to reconstruct full-resolution images conditioned on the synthetic representations produced by the RDM. Because these representations encode rich semantic content, the generator produces highly coherent, diverse, and realistic images—even though no labels were ever used.
This two-stage design enables RCG to sidestep the ambiguity of raw pixel-level unconditional generation while retaining full autonomy from human annotations.
Key Strengths That Set RCG Apart
1. Closes the Unconditional–Conditional Performance Gap
Prior to RCG, the best unconditional FID on ImageNet 256×256 was around 5.91. RCG slashes this to 2.15—a level previously seen only in class-conditional models. This leap makes unconditional generation viable for real-world applications that demand high fidelity.
2. Fully Self-Supervised and Label-Free
RCG requires no human-labeled data at any stage. It relies solely on self-supervised pre-training (e.g., MoCo v3) and unlabeled ImageNet-scale datasets. This is ideal for domains where labeling is expensive, subjective, or simply unavailable.
3. Flexible Generator Backends
RCG is not tied to a single architecture. The project provides official support and pre-trained checkpoints for multiple pixel generators:
- MAGE (Masked generative modeling)
- DiT (Diffusion Transformers)
- ADM (Classifier-free diffusion with adaptive normalization)
- LDM (Latent Diffusion Models)
This modularity allows teams to integrate RCG into their preferred generative stack.
Ideal Use Cases for Practitioners and Teams
Generating Synthetic Data from Unlabeled Corpora
If your organization has petabytes of unlabeled images (e.g., satellite imagery, medical scans, or user-generated content), RCG enables you to build powerful generative models without costly annotation pipelines.
Data Augmentation Without Annotation Bias
In domains like scientific imaging or industrial inspection, where class boundaries are ambiguous or evolving, RCG provides a robust way to synthesize realistic variations without imposing artificial labels that may misrepresent the data distribution.
Creative and Simulation Applications
For applications in gaming, VR, or digital art—where diversity and realism matter more than strict class adherence—RCG’s high-fidelity unconditional outputs offer a scalable, label-free foundation for content creation.
Research on Fundamental Generative Learning
RCG revives interest in unconditional generation as a standalone problem, demonstrating that self-supervision can provide the “missing signal” that labels once supplied. This opens new avenues for studying representation learning and generative modeling in harmony.
Getting Started with RCG: Practical Workflow
The RCG repository provides a complete toolkit for training and evaluation:
- Prepare Data: Use the standard ImageNet dataset (unlabeled training set suffices).
- Set Up Environment: Install dependencies via the provided
environment.yaml. - Download Pre-trained Components:
- MoCo v3 ViT-B or ViT-L encoder
- VQGAN tokenizer (for LDM/MAGE)
- Train the RDM: Use the provided config (e.g.,
mocov3vitb_simplemlp_l12_w1536.yaml) to train the representation diffusion model on 4+ GPUs. - Train the Pixel Generator: Condition MAGE, DiT, or ADM on RDM-generated representations. Pre-trained checkpoints are available for immediate inference or fine-tuning.
- Evaluate with Standard Metrics: The repo includes scripts for FID and Inception Score using
torch-fidelity, with statistics aligned to the ADM evaluation suite.
For quick validation, you can skip training entirely and use the provided pre-trained MAGE-L or DiT checkpoints to generate images out of the box.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While RCG delivers unprecedented quality in unconditional generation, it’s important to consider real-world constraints:
- High Compute Requirements: Full training of RCG with DiT or ADM typically requires 64–128 V100 GPUs, making it impractical for small labs or individual developers without cloud-scale resources.
- Dependency on Pre-trained Encoders: RCG relies on strong self-supervised encoders like MoCo v3. Performance may degrade if applied to domains where such encoders haven’t been pre-trained.
- Inference Is Efficient, Training Is Not: Once trained, RCG generators can run inference on a single GPU. However, the initial training cost remains substantial.
That said, the availability of pre-trained models significantly lowers the barrier to use RCG, even if you can’t afford to retrain it from scratch.
Summary
RCG redefines what’s possible in unconditional image generation. By conditioning diffusion models on self-supervised representations rather than human labels, it achieves class-conditional-level quality without any annotation—a major leap forward for scalable, privacy-preserving, and domain-agnostic generative AI.
If your work involves large unlabeled datasets, synthetic data needs, or a desire to move beyond label-dependent pipelines, RCG offers a technically sound, empirically validated path forward. With flexible architecture support and publicly available checkpoints, it’s ready for adoption in research and production alike—provided you have access to sufficient compute for training or are willing to leverage existing models for inference and fine-tuning.