Overview
Training large language models (LLMs) to reliably use external tools over multiple conversation turns is a persistent challenge in agentic AI. While LLMs excel at reasoning, they often falter when interacting with real-world APIs, databases, or custom functions—especially when those tools vary in interface, latency, or reliability. Traditional reinforcement learning (RL) post-training frameworks for tool use are typically slow, tightly coupled with environment logic, and require deep RL expertise to adapt.
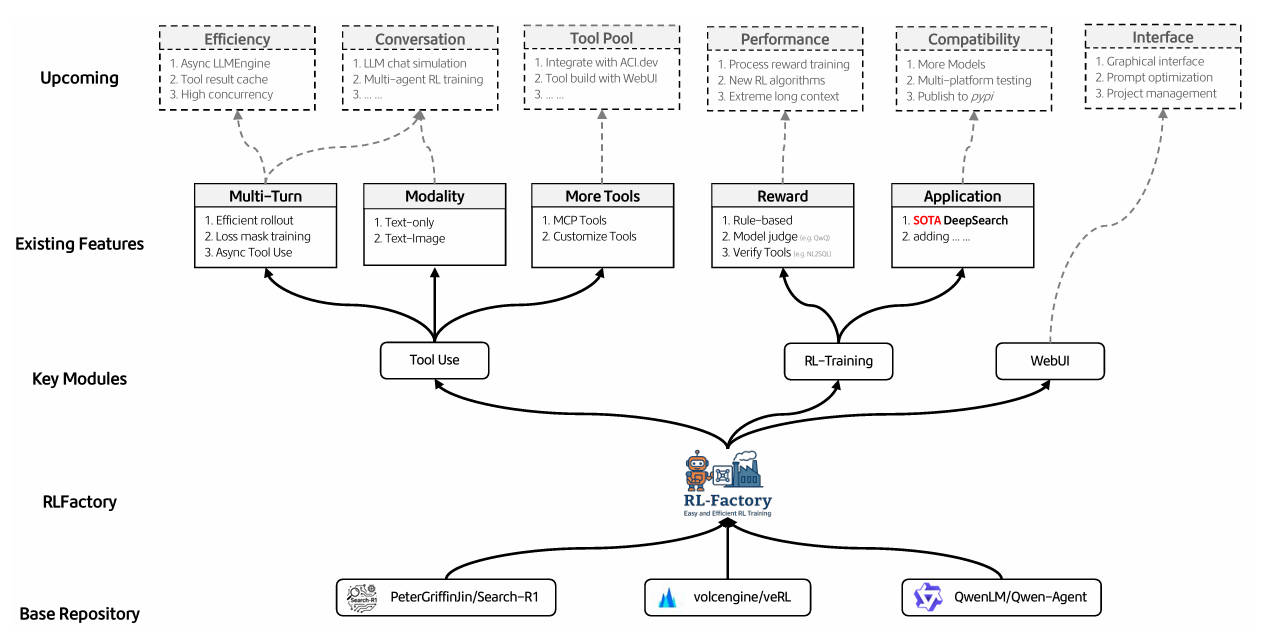
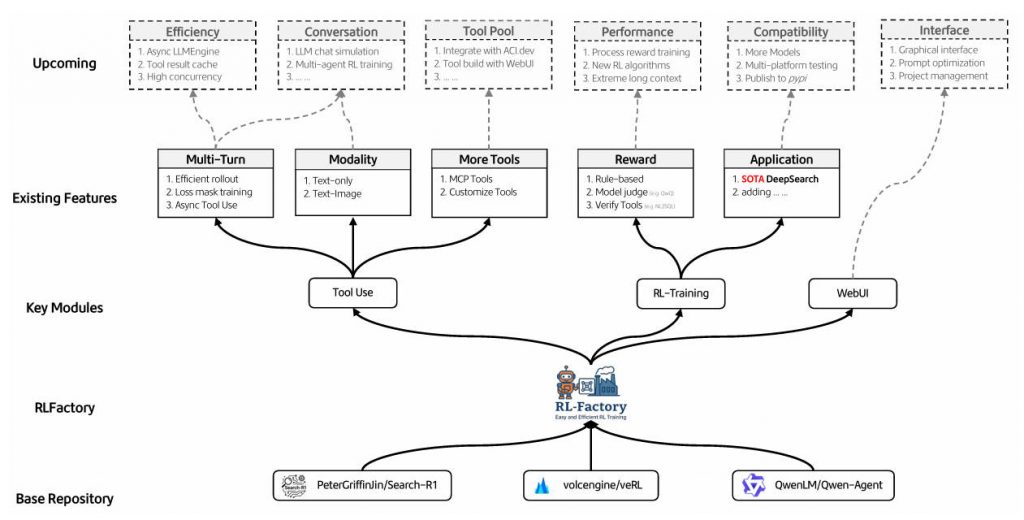
Enter RLFactory: a plug-and-play RL post-training framework built specifically for multi-turn LLM tool use. It removes the friction of environment setup, accelerates training through asynchronous tool calling, and lets you define rewards using rules, models, or tool feedback—all while decoupling the RL engine from your tool logic. If you’re building agents that search, book flights, analyze data, or orchestrate APIs across multiple steps, RLFactory is designed to get you from idea to trained agent faster and with less code.
Why Multi-Turn Tool Use Needs a New Approach
Most LLM agents today are trained using supervised fine-tuning (SFT), which teaches them to mimic tool-call patterns from static datasets. But real-world tool interactions are dynamic: APIs fail, responses change, and multi-step reasoning requires feedback loops. RL is better suited for this, but standard RL pipelines for LLMs struggle with:
- Environment coupling: RL code and tool logic are often tangled, making it hard to swap tools or reward strategies.
- Slow rollouts: Sequential tool calls during training create bottlenecks, especially when tools involve network I/O.
- Reward rigidity: Many frameworks only support simple rule-based rewards, missing nuanced signals like model-judged correctness or tool-side validation.
RLFactory directly addresses these pain points with a clean architecture built for agentic learning—not just language modeling.
Core Strengths of RLFactory
Decoupled Environment Design
RLFactory separates the tool environment from the RL training engine. To train an agent, you only need to provide:
- A tool configuration file (supporting MCP-compatible tools or custom functions)
- A reward function that can be rule-based, model-judged (e.g., using a large reward model like QwQ-32B), or even verified by the tool itself
This decoupling means you can iterate on reward logic or tool behavior without touching the RL infrastructure—ideal for teams focused on agent behavior rather than distributed training systems.
Async Tool Calling for 2× Faster Training
RLFactory implements an asyncio-based asynchronous caller that processes multiple tool invocations in parallel during rollouts. This alone reduces training time by 1.5–2× compared to synchronous alternatives (e.g., the original Search-R1 framework). When combined with distributed reward model inference, the speedup becomes even more pronounced—enabling rapid iteration cycles even on large models.
In benchmarks on the Natural Questions (NQ) dataset using the DeepSearch task:
- RLFactory + Qwen3-4B achieves a test score of 0.458 in 5.3 hours (8× A100)
- This outperforms Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct-GRPO (0.451) trained with similar methods but taking 9.25 hours
Flexible, Multi-Source Reward Layer
Not all correct tool use looks the same. RLFactory’s reward layer supports:
- Rule-based rewards: e.g., “Did the agent call the search tool with a non-empty query?”
- Model-judged rewards: Deploy a large reward model (LRM) to assess answer quality or reasoning validity
- Tool-verified rewards: Let the tool itself confirm success (e.g., “Did the API return valid data?”)
This flexibility ensures your agent learns from signals that match your real-world success criteria—not just proxy metrics.
Native Qwen3 Support with Strong Zero-Shot Tool Use
Qwen3 models demonstrate exceptional out-of-the-box tool-calling ability, even without supervised fine-tuning. RLFactory leverages this by providing native support for Qwen3-4B and Qwen3-8B, allowing immediate RL post-training. Benchmarks show Qwen3 consistently outperforms Qwen2.5 in tool-use accuracy, making it a compelling base for agentic applications.
Practical Use Cases
RLFactory excels in scenarios requiring multi-turn, tool-augmented reasoning, such as:
- Search Agents: Reproduce the DeepSearch setup with one-click training using Qwen3 and a search tool config.
- Travel Planners: Chain flight, hotel, and weather APIs across multiple turns to build itineraries.
- Data Analysts: Let LLMs query databases, run code, and visualize results iteratively.
- Android Automation: Version 0.2 adds Android OS environment support, enabling phone-based agent training.
Crucially, all these use cases start from the same minimal template: define your tools, define your reward, run a script.
Getting Started Is Deliberately Simple
The user workflow is intentionally lightweight:
- Install dependencies (Python ≥3.10, CUDA ≥12.0, vLLM ≥0.8.3)
- Provide a tool config (YAML or JSON) and a reward function (Python)
- Run
bash main_grpo.sh(with paths to your base model and reward model) - Evaluate with
bash main_eval.sh
No need to modify RL loops, rollout workers, or policy networks. RLFactory handles the infrastructure—so you focus on what your agent should do, not how to train it.
The framework also includes a full reproduction example for Search-R1 in docs/rl_factory/main_tutorial.md, making it easy to validate setup before building your own agent.
Current Limitations and Roadmap
While powerful, RLFactory has some constraints to consider:
- Model support: Officially tested and optimized for Qwen3 models. Support for Llama, Deepseek, and others is planned (tracked in GitHub issues #5).
- Feature maturity: The WebUI, multimodal agent training, and Android environment are under active development in v0.2.
- Hardware requirements: Requires modern GPUs (A100 or equivalent) and CUDA 12.0+ due to dependencies like vLLM and FlashAttention.
That said, the core framework is stable, well-documented, and already delivers measurable efficiency and performance gains over prior approaches.
Summary
RLFactory lowers the barrier to training capable, multi-turn tool-using LLM agents. By decoupling environment logic from RL infrastructure, enabling asynchronous tool calls, and supporting flexible reward signals, it solves real-world bottlenecks in agentic learning. With strong out-of-the-box performance on Qwen3 and a minimal-code workflow, it’s an ideal choice for researchers and engineers who want to build and iterate on LLM agents—fast, without becoming RL experts.