Reinforcement learning (RL) is rapidly becoming the engine behind next-generation agentic AI—powering everything from math-reasoning language models to vision-guided robotic agents. Yet despite its promise, many teams hit a wall when trying to scale RL training: existing frameworks often suffer from rigid architecture, poor hardware utilization, and complex manual tuning. Enter RLinf, an open-source, high-performance RL infrastructure purpose-built for the post-training phase of foundation models.
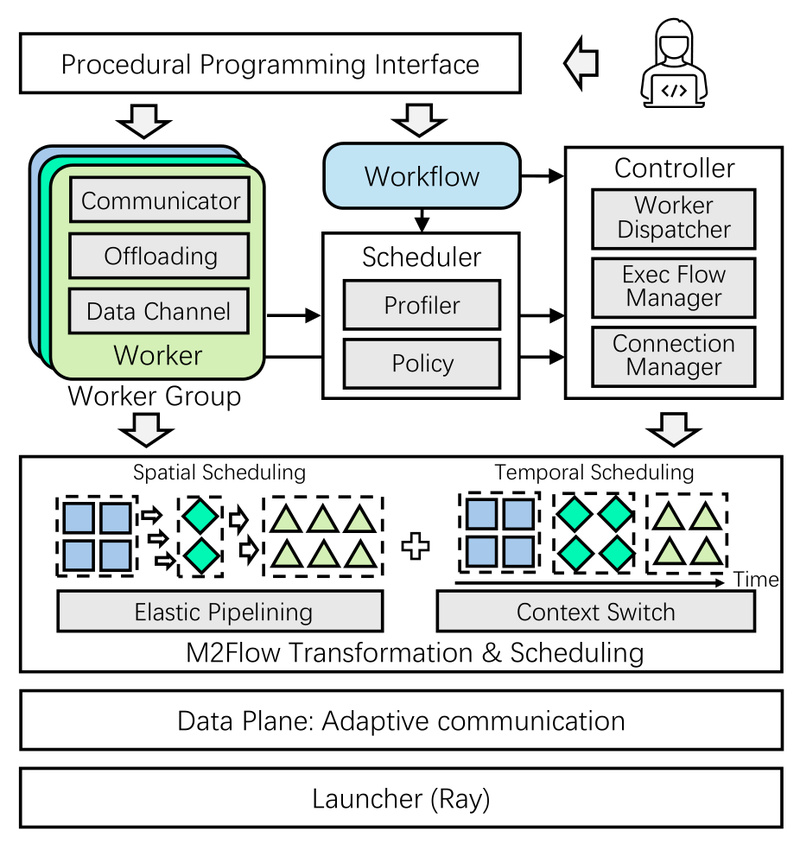
RLinf directly addresses these pain points by introducing a novel system design paradigm called Macro-to-Micro Flow Transformation (M2Flow). This innovation decouples high-level workflow logic from low-level execution, enabling automatic optimization across both time and space dimensions. The result? Faster training, higher throughput, and unprecedented flexibility—without sacrificing ease of use.
Whether you’re fine-tuning a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model for robot manipulation or training a math-reasoning agent with PPO, RLinf gives you the tools to scale efficiently while keeping your pipeline simple.
What Makes RLinf Different?
The M2Flow Paradigm: From Logical Design to Optimized Execution
At the core of RLinf is M2Flow—a system-level insight that separates what you want to do (macro-level logical flow) from how it’s executed (micro-level physical flow). Traditional RL systems often tie these two together, forcing users to manually balance communication, computation, and resource allocation.
RLinf automates this process. It analyzes your high-level workflow and dynamically recomposes it into an optimized sequence of micro-execution steps. This transformation is powered by two key mechanisms:
- Context switching: Allows workers to switch between tasks without idle time.
- Elastic pipelining: Enables fine-grained overlap of computation and communication.
Combined with profiling-guided scheduling, M2Flow ensures that your training runs at peak efficiency—automatically adapting to changes in workload or hardware availability.
Flexible Execution Modes for Every Scale
RLinf offers three execution modes, letting you choose the right balance of performance and simplicity:
- Collocated mode: All components (actor, learner, optimizer) share the same GPU pool—ideal for prototyping or small-scale experiments.
- Disaggregated mode: Separates components across devices for maximum pipelining and throughput—suited for large clusters.
- Hybrid mode: A customizable mix of both, offering fine-grained control without manual orchestration.
Thanks to RLinf’s auto-scheduling policy, you don’t need to decide upfront. The system observes your workload and selects the optimal mode—dynamically adjusting if conditions change.
Built for Real-World RL Tasks
RLinf isn’t just fast—it’s practical. It ships with native support for:
- Embodied intelligence: Full compatibility with ManiSkill3 and LIBERO benchmarks. Pre-integrated with OpenVLA, OpenVLA-OFT, π₀, and π₀.₅ models.
- Reasoning intelligence: Ready-to-run examples for mathematical reasoning using PPO, GRPO, DAPO, and more on datasets like AIME and GPQA-diamond.
In evaluations, RLinf consistently outperforms existing systems:
- 81.93% average success rate on ManiSkill tasks with OpenVLA-PPO (vs. 39.10% for base model).
- 40.84 average score on math reasoning with a 1.5B model—leading across AIME 24, AIME 25, and GPQA-diamond.
- 1.1x–2.13x end-to-end throughput speedup compared to state-of-the-art RL frameworks.
Who Should Use RLinf?
For Robotics and Embodied AI Teams
If you’re training VLA models for robotic manipulation, RLinf removes the infrastructure bottleneck. It supports standardized simulators like ManiSkill3 and LIBERO out of the box, and enables the first RL fine-tuning of the π₀ and π₀.₅ model families. With built-in flow-matching action experts and seamless checkpointing, you can iterate faster and deploy more capable agents.
For Reasoning and Language Agent Developers
RLinf makes it straightforward to apply RL to large language models for complex reasoning. Just plug in your model via Hugging Face or Megatron, select an algorithm (PPO, GRPO, etc.), and launch training. The system handles the rest—scaling, communication, and scheduling—so you can focus on algorithm design and task formulation.
For Teams Balancing Prototyping and Production
RLinf bridges the gap between experimentation and scale:
- Use FSDP + Hugging Face for rapid prototyping with new models.
- Switch to Megatron + SGLang when you’re ready for large-scale, multi-node training.
Both backends are fully supported, and you can transition between them with minimal code changes.
Getting Started Is Simpler Than You Think
You don’t need a PhD in distributed systems to use RLinf. The project provides:
- Pre-built examples: Train a VLA on ManiSkill3 or a math agent on AIME in minutes.
- Unified APIs: One interface for both embodied and reasoning tasks.
- Built-in algorithm support: PPO, GRPO, DAPO, Reinforce++, and more—no need to implement from scratch.
- LoRA integration: Efficient fine-tuning without full-parameter updates.
Installation is standard (pip install rlinf), and documentation covers everything from single-GPU runs to multi-node deployments. Even better: you don’t need to rewrite your entire pipeline. RLinf works with your existing environments and models—just wrap them in its standardized RL interface.
Current Limitations and the Road Ahead
RLinf is powerful today—but still evolving. Be aware of the following boundaries:
- Simulation-first: Currently optimized for simulators like ManiSkill3 and LIBERO; real-world robotic deployment isn’t natively supported yet.
- Hardware constraints: No built-in support for heterogeneous GPUs or Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models—though both are on the roadmap.
- Environment standardization: For embodied tasks, you’ll need to use supported simulators or implement a compatible interface.
That said, the roadmap is ambitious and community-driven:
- Multi-agent training
- Vision-Language Model (VLM) support
- Integration with Meta-World, GENESIS, and RoboTwin
- World model and real-world RL capabilities
This active development signals RLinf’s commitment to becoming the backbone of scalable, agentic AI.
Summary
RLinf solves the critical scalability and flexibility challenges that plague modern reinforcement learning workflows. By introducing the M2Flow paradigm, offering adaptive execution modes, and supporting both reasoning and embodied tasks out of the box, it empowers teams to train smarter, faster, and at scale—without drowning in infrastructure complexity.
If you’re building agentic systems that learn through interaction—whether in math, robotics, or beyond—RLinf provides a robust, future-ready foundation. With strong benchmark results, intuitive design, and active development, it’s not just another RL framework. It’s the infrastructure for the next era of intelligent agents.