In the rapidly evolving landscape of large language models (LLMs), bigger isn’t always better—smarter is. Enter rStar2-Agent, a 14-billion-parameter reasoning model developed by Microsoft that redefines what’s possible with compact architectures. Despite its relatively modest size, rStar2-Agent achieves frontier-level performance in mathematical reasoning, even surpassing DeepSeek-R1—a model with 671 billion parameters—on rigorous benchmarks like AIME2024 and AIME2025. And it does so not by generating endless chains of thought, but by reasoning more deliberately, using tools like Python strategically, and learning from both successes and failures during problem-solving.
What makes rStar2-Agent especially compelling for researchers and engineers is its agentic reinforcement learning (RL) foundation, which enables it to plan, execute code, reflect on feedback, and iteratively refine its solutions—behaviors typically reserved for much larger or more resource-intensive systems. Crucially, all of this is achieved with only 64 MI300X GPUs and in just 510 RL training steps over one week, demonstrating unprecedented training efficiency.
For teams facing challenges like high inference costs, unreliable tool integration, or the computational burden of training massive models, rStar2-Agent offers a lean, powerful, and open-source alternative that’s ready for real-world deployment.
Why rStar2-Agent Stands Out: Solving Real-World Pain Points
Smarter Reasoning, Not Longer Outputs
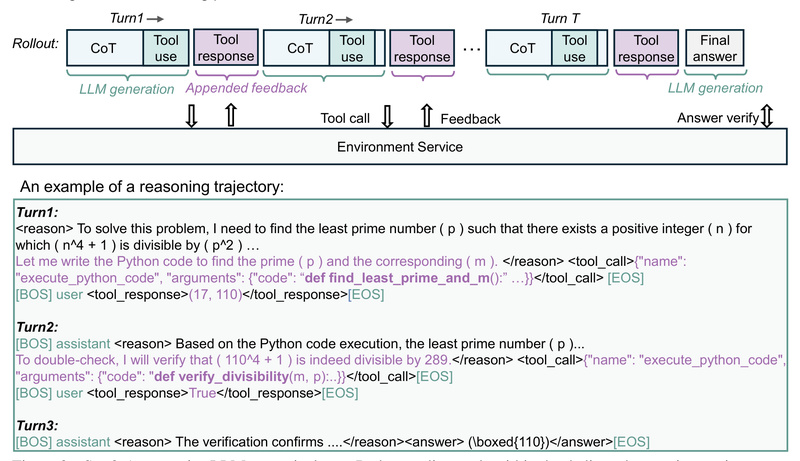
Traditional approaches to complex reasoning often rely on “long chain-of-thought” (CoT) prompting, where models generate verbose, step-by-step explanations in the hope that length correlates with accuracy. rStar2-Agent rejects this paradigm. Instead, it thinks before acting: it decides when to invoke a Python tool, interprets execution feedback, and autonomously corrects its path—producing shorter, more precise, and more reliable responses. This leads to better performance with lower token usage, reducing both latency and cost.
Three Innovations That Make Agentic RL Practical at Scale
rStar2-Agent’s breakthrough performance rests on three tightly integrated technical advances:
-
GRPO-RoC (Resample-on-Correct Reinforcement Learning)
Standard RL struggles in tool-augmented environments because code execution is noisy—correct logic can fail due to syntax errors, timeouts, or environment quirks. GRPO-RoC addresses this by resampling correct trajectories based on execution fidelity, not just final answers. It retains high-quality reasoning traces while preserving all failure cases for learning, enabling the model to distinguish between logical errors and tool-related noise. -
Efficient, High-Throughput RL Infrastructure
Agentic RL typically demands massive compute due to the cost of rolling out tool calls. rStar2-Agent’s infrastructure integrates a secure, scalable Python code execution environment (Code Judge) with Redis-backed task distribution, allowing thousands of parallel code evaluations. This slashes rollout costs and makes training feasible on just 64 GPUs—a fraction of what comparable systems require. -
Staged Training Recipe for Cognitive Maturation
Training starts with non-reasoning supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to establish basic instruction-following behavior. Then, it progresses through multi-stage RL phases, each with tighter response limits and increasingly difficult problems. This curriculum-style approach builds advanced reasoning capabilities incrementally, maximizing learning efficiency and minimizing wasted compute.
Ideal Use Cases: Where rStar2-Agent Delivers Maximum Value
rStar2-Agent excels in domains that demand precise, verifiable, and tool-augmented reasoning:
- Mathematical Problem Solving: Achieves 80.6% pass@1 on AIME2024 and 69.8% on AIME2025, rivaling models 50x larger. Ideal for competition math, STEM education tools, or automated tutoring systems.
- Scientific Reasoning: Capable of formulating hypotheses, running simulations via code, and interpreting results—useful in computational biology, physics, or chemistry workflows.
- Autonomous Tool Use: Can call, debug, and refine Python code in a closed loop, making it suitable for data analysis pipelines, automated debugging, or algorithm prototyping.
- Alignment-Sensitive Applications: Its concise, reflective reasoning reduces hallucination risks, supporting applications where correctness and auditability are critical.
If your project involves structured problem-solving with programmatic verification, rStar2-Agent is purpose-built for that challenge.
Getting Started: From Installation to Interactive Tool Use
The project provides a streamlined path for inference and evaluation—no need to train from scratch. Here’s how to run rStar2-Agent with tool calling:
-
Install Dependencies
Clone the repo and use the automatedinstall.shscript or follow manual steps to set upverl,code-judge, and the agent package. -
Deploy the Code Execution Environment Securely
- Start a Redis server for task coordination.
- Launch the Code Judge server and workers (in an isolated Docker container for safety, as arbitrary code execution poses security risks).
-
Serve the Model with vLLM
Use vLLM with--enable-auto-tool-choiceand--tool-call-parser hermesto support structured tool invocations. -
Run Interactive Inference
Execute:python examples/chat_with_tool_call.py --model /path/to/rstar2-agent --prompt "Solve: 2x + 3y = 7, x - y = 1" --max_tokens 8192
The model will generate a plan, call Python to solve the system, interpret the output, and return a verified answer—all in a single interaction.
Evaluation scripts for AIME2024/2025 and MATH500 are also included, allowing immediate benchmarking.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While rStar2-Agent is production-ready for inference and evaluation, users should note:
- Security First: The Code Judge executes arbitrary Python code. Never expose it to untrusted inputs or public networks. Always run in an isolated environment (e.g., Docker with resource limits).
- Training Framework Status: The open-sourced RL training pipeline is based on VERL v0.5 and has been validated for early-stage training (first 50 steps), but full end-to-end reproduction is still being finalized. Inference and evaluation, however, are fully supported.
- SFT Initialization Required: For best results, the base model (e.g., Qwen3-14B-Base) must undergo instruction-tuned SFT before RL. Skipping this step will degrade performance.
- Prompt Sensitivity: Like all agentic models, performance depends on clear task framing. Vague prompts may lead to suboptimal tool usage.
These considerations ensure users deploy the model responsibly and effectively.
Summary
rStar2-Agent proves that agentic intelligence doesn’t require massive scale—just smarter design. By combining reflective reasoning, robust tool integration, and an efficient RL training paradigm, it delivers state-of-the-art math performance in a 14B package, drastically cutting compute, cost, and response length. For researchers and engineers tackling complex, verifiable reasoning tasks—from Olympiad math to scientific automation—rStar2-Agent offers a compelling, open-source solution that’s both powerful and practical. With its code, training recipes, and evaluation tools publicly available, now is the ideal time to integrate agentic reasoning into your next project.