Deploying dozens—or even thousands—of fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) has traditionally been a costly and complex endeavor. Each adapter typically demands its own GPU memory footprint, leading to underutilized hardware, high operational overhead, and limited scalability. Enter S-LoRA: a high-performance serving system engineered specifically to manage thousands of concurrent Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) adapters on one or multiple GPUs with minimal overhead.
Built on the widely adopted “pretrain-then-finetune” paradigm, S-LoRA transforms LoRA from a fine-tuning technique into a scalable production-ready serving architecture. By intelligently managing GPU memory and optimizing computation across heterogeneous adapter configurations, S-LoRA delivers up to 4× higher throughput compared to existing solutions like HuggingFace PEFT and naive vLLM-based approaches—while supporting orders of magnitude more adapters simultaneously.
Why S-LoRA Matters for Real-World LLM Deployment
In many enterprise and research settings, teams fine-tune a single base LLM (e.g., Llama-7B) into hundreds or thousands of task- or user-specific variants using LoRA. However, serving these adapters efficiently is nontrivial. Standard frameworks either:
- Reload adapter weights between requests (causing high latency),
- Merge adapters into full models (wasting GPU memory), or
- Run separate inference processes (leading to poor resource utilization).
S-LoRA solves these problems by rethinking how adapter weights and attention KV caches are stored and scheduled during inference. Instead of keeping every adapter in GPU memory—a nonstarter at scale—S-LoRA stores all adapters in CPU main memory and dynamically loads only the needed ones into GPU memory on demand. This enables massive concurrency without proportional hardware costs.
Core Innovations That Enable High-Throughput, Low-Overhead Serving
Unified Paging: Eliminating GPU Memory Fragmentation
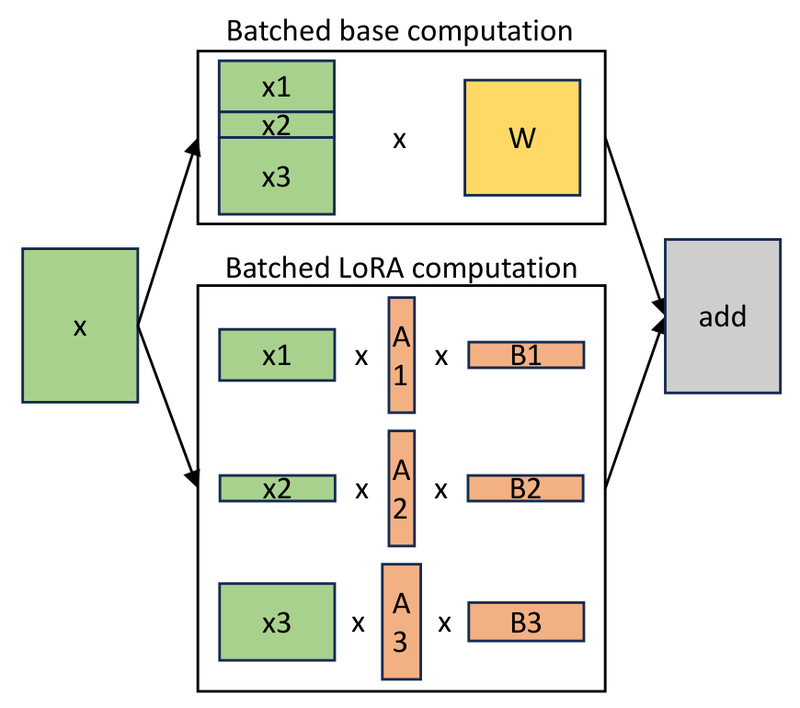
One of S-LoRA’s key innovations is Unified Paging, a unified memory management system that co-allocates space for both dynamic LoRA weights (which vary in rank) and variable-length KV cache tensors. Traditional systems treat these as separate memory pools, causing fragmentation and limiting batch size. Unified Paging merges them into a single, contiguous memory pool, dramatically improving memory utilization and enabling larger inference batches.
Heterogeneous Batching with Custom CUDA Kernels
LoRA adapters often have different ranks (e.g., rank 8, 16, 32, 64), making standard batched matrix multiplication inefficient due to padding or data copying. S-LoRA introduces highly optimized custom CUDA kernels that operate directly on non-contiguous memory layouts aligned with its Unified Paging design. This avoids unnecessary data movement and padding, allowing mixed-rank adapters to be processed in a single efficient batch—reducing latency and boosting throughput.
S-LoRA Tensor Parallelism (S-LoRA TP)
For multi-GPU deployments, S-LoRA implements a novel tensor parallelism strategy that minimizes communication overhead for LoRA-specific computations. Unlike naive approaches that replicate adapter logic across devices, S-LoRA TP fuses small LoRA tensor communications with those of the base model, ensuring near-linear scaling across GPUs without significant added latency.
When Should You Use S-LoRA?
S-LoRA shines in scenarios where many task-specific or user-specific adapters must be served dynamically and concurrently, such as:
- Personalized AI services: Imagine a customer support platform where each enterprise client has its own fine-tuned chatbot adapter—all served from the same infrastructure.
- Multi-tenant LLM platforms: Cloud providers offering fine-tuned model hosting can use S-LoRA to serve thousands of tenants on shared GPU clusters.
- Large-scale fine-tuning research: Teams running hyperparameter sweeps or adapter ablation studies can evaluate hundreds of LoRA variants in real time without redeploying models.
In all these cases, S-LoRA replaces the need for one-model-per-GPU deployments with a unified, efficient serving layer.
Getting Started with S-LoRA
S-LoRA is designed for production-style inference, not just experimentation. To get started:
-
Ensure hardware compatibility: You’ll need a CUDA 11.8–compatible GPU from the Ampere architecture or newer (e.g., A100). Note: Turing-class GPUs like the T4 are not supported due to lack of bfloat16 support.
-
Set up the environment:
conda create -n slora python=3.9 conda activate slora pip install torch==2.0.1 pip install -e .
Make sure
triton==2.1.0is installed. -
Launch a server (example with real Llama weights):
cd benchmarks python launch_server.py --num-adapter 100 --num-token 10000 --model-setting Real python run_exp.py --debug --model-setting Real
The system supports both real model weights and synthetic (dummy) adapters for benchmarking and development.
Current Limitations and Future Roadmap
While S-LoRA offers significant performance gains, users should be aware of its current constraints:
- GPU requirements: Only Ampere+ GPUs (e.g., A100) are supported; older architectures like T4 are excluded.
- Model support: As of now, S-LoRA primarily supports Llama-family models (7B, 13B, 30B, 70B). Broader model compatibility is planned.
- API maturity: The current interface is geared toward researchers and engineers comfortable with command-line deployment. A more user-friendly frontend is on the roadmap.
That said, the core system is production-ready for compatible setups, and the team continues to expand usability and model coverage.
Summary
S-LoRA redefines what’s possible in efficient, large-scale LoRA serving. By combining Unified Paging, heterogeneous batching, and optimized tensor parallelism, it enables organizations to deploy thousands of specialized LLMs on a fraction of the hardware traditionally required. For teams managing many fine-tuned models—whether for research, customer customization, or multi-tenant platforms—S-LoRA offers a compelling path to scalability, cost savings, and performance.
If your workflow involves serving numerous LoRA adapters and you’re operating on modern NVIDIA GPUs, S-LoRA is worth serious evaluation for your next-generation LLM infrastructure.