For teams building or fine-tuning large language models (LLMs), one of the biggest bottlenecks is the scarcity of high-quality, diverse instruction data. Human-written instruction-following examples are expensive to collect, limited in creativity, and often fail to cover the long tail of real-world tasks. Enter Self-Instruct—a practical, nearly annotation-free framework that enables pretrained language models to teach themselves how to follow instructions by generating and curating their own training data.
Originally introduced in the paper “Self-Instruct: Aligning Language Models with Self-Generated Instructions”, this method bootstraps instructional data directly from a language model’s own outputs. Starting with just a small seed set of manually written instructions, Self-Instruct iteratively expands this pool by prompting the model to create new instructions, input-output examples, and then filtering out low-quality or redundant entries. The result? A scalable, synthetic instruction dataset that dramatically improves zero-shot generalization—without relying on private user data or extensive human labeling.
If you’re a project or technical decision-maker looking to enhance your model’s instruction-following ability under tight budget or data constraints, Self-Instruct offers a compelling alternative to traditional supervised fine-tuning.
Why Self-Instruct Matters for Real-World Projects
Reducing Reliance on Scarce Human Annotations
Most state-of-the-art instruction-tuned models—like InstructGPT—depend heavily on large volumes of human-generated demonstrations and feedback. These resources are not only costly but often proprietary. Self-Instruct sidesteps this by using the model itself as a data engine. This is especially valuable for startups, academic labs, or open-source initiatives that lack access to massive human annotation pipelines.
Closing the Performance Gap with Minimal Effort
When applied to vanilla GPT-3, Self-Instruct achieved a 33% absolute improvement on the Super-NaturalInstructions benchmark. Remarkably, this brings its performance nearly on par with InstructGPT-001—a model trained using private user interactions and extensive human annotations. In human evaluations on novel, expert-designed tasks, Self-Instruct-tuned GPT-3 significantly outperformed models fine-tuned on existing public instruction datasets, trailing InstructGPT-001 by only 5%.
This demonstrates that high instruction-following fidelity doesn’t always require massive human effort—it can emerge from smart, self-driven data synthesis.
A Public, Reusable Synthetic Dataset
The project releases a ready-to-use dataset containing 52,000 instructions and 82,000 input-output instances, all generated through the Self-Instruct pipeline. This data is formatted for direct fine-tuning with GPT-3 and serves as a valuable public resource for training or benchmarking instruction-tuned models. For researchers and practitioners, this eliminates the need to build such a dataset from scratch.
Ideal Use Cases for Technical Decision-Makers
Self-Instruct shines in scenarios where:
- Budgets for data labeling are limited, but you still need to improve your model’s general instruction-following capability.
- You’re working with open or proprietary LLMs and want to enhance their zero-shot performance on unseen tasks without access to user interaction logs.
- You aim to rapidly prototype instruction-tuned variants of existing models for domain-specific applications (e.g., customer support, content generation, or internal tooling).
- Your team values reproducibility and open science, and seeks methods that don’t depend on non-public, human-in-the-loop data.
It’s particularly well-suited for research teams exploring efficient alignment techniques or product teams building AI features with lean data resources.
Getting Started with Self-Instruct
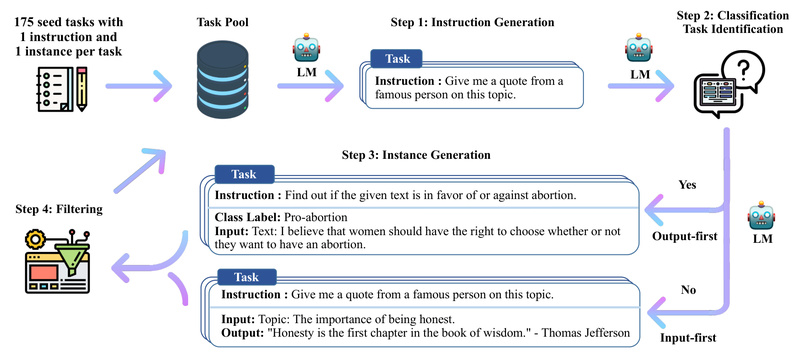
The Self-Instruct pipeline is designed to be modular and transparent. Here’s how it works in practice:
- Start with a seed set of 175 human-written instructions (provided in the repository).
- Generate new instructions: Use the model (currently tested with GPT-3 via OpenAI API) to produce diverse instruction prompts based on the seed.
- Classify task types: Determine whether each new instruction corresponds to a classification task—a key step for generating appropriate outputs.
- Create input-output instances: For each instruction, generate realistic example pairs.
- Filter and curate: Remove low-quality, redundant, or invalid generations using heuristic and similarity-based filters.
- Fine-tune your model: Use the final dataset (available in
data/finetuning/self_instruct_221203) to instruction-tune your target LLM.
The repository provides ready-to-run scripts for each stage:
generate_instructions.shis_clf_or_not.shgenerate_instances.shprepare_for_finetuning.sh
You can either use the pre-generated 82K-instance dataset or run the full pipeline yourself with your own seed tasks or models.
Important Limitations and Cautions
While powerful, Self-Instruct comes with important caveats:
- Model dependency: The current implementation is tailored for GPT-3 via the OpenAI API. Adapting it to other models (e.g., LLaMA, Mistral) requires modifying the prompting and generation logic.
- Data quality issues: The paper’s analysis estimates that ~46% of generated samples may contain errors, inconsistencies, or biases. Users are strongly encouraged to apply additional filtering or post-processing before fine-tuning.
- Active development status: The codebase is still evolving. Version stability isn’t guaranteed, so exercise caution when integrating into production pipelines.
These limitations don’t diminish Self-Instruct’s innovation—they simply underscore the need for thoughtful validation when using synthetic data.
Summary
Self-Instruct offers a pragmatic, scalable path to instruction-tuning without heavy reliance on human annotations. By leveraging a model’s own generative capabilities to bootstrap high-quality training data, it enables teams with limited resources to build competitive, instruction-following LLMs. With its public dataset, clear pipeline, and demonstrated performance gains, Self-Instruct is a valuable tool for anyone exploring efficient alignment strategies in natural language processing.
Whether you’re fine-tuning a foundation model for a new application or researching next-generation alignment methods, Self-Instruct provides both a methodology and a starting point—proving that sometimes, the best teacher is the model itself.