Large language models (LLMs) are no longer just tools for answering questions—they power agents, structured data pipelines, multi-turn conversations, and multimodal reasoning systems. But as these applications grow more complex, traditional inference engines struggle with latency, memory inefficiency, and rigid output control.
Enter SGLang: a high-performance serving framework built specifically for executing structured, multi-step, and multimodal LLM programs efficiently. Developed by the team behind LMSYS and adopted by leading tech companies and research institutions worldwide, SGLang combines a developer-friendly programming interface with a highly optimized runtime—delivering up to 6.4x higher throughput than state-of-the-art systems on real-world tasks like JSON generation, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), logical reasoning, and agent control.
Whether you’re deploying Llama, DeepSeek, GPT, or LLaVA models on NVIDIA, AMD, TPU, or CPU hardware, SGLang simplifies production-grade LLM serving without forcing you to become a systems expert.
Why SGLang Solves Real Engineering Bottlenecks
Prefix Reuse with RadixAttention
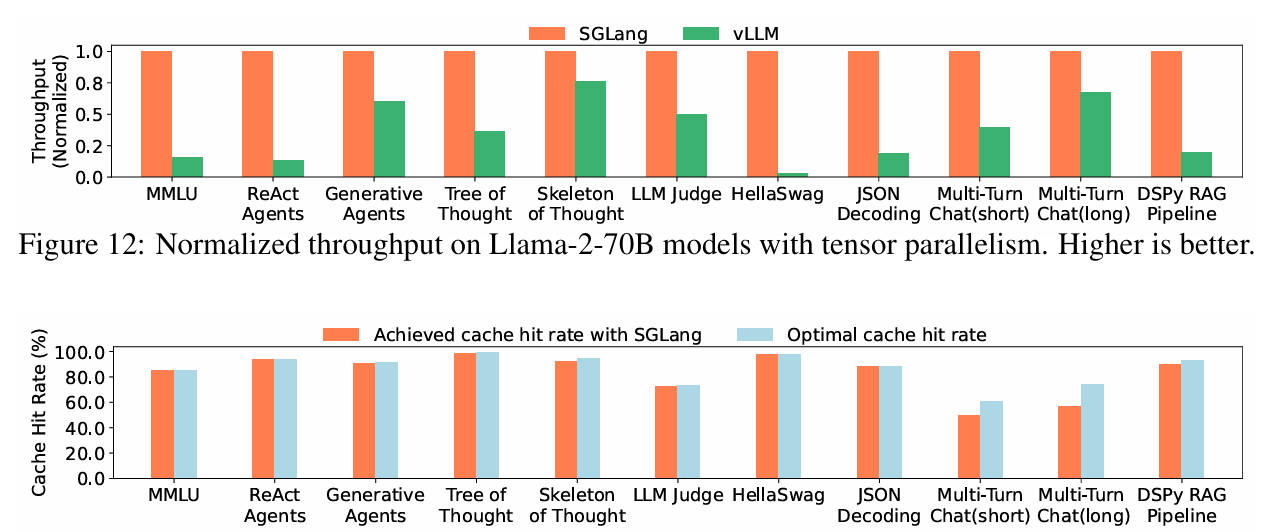
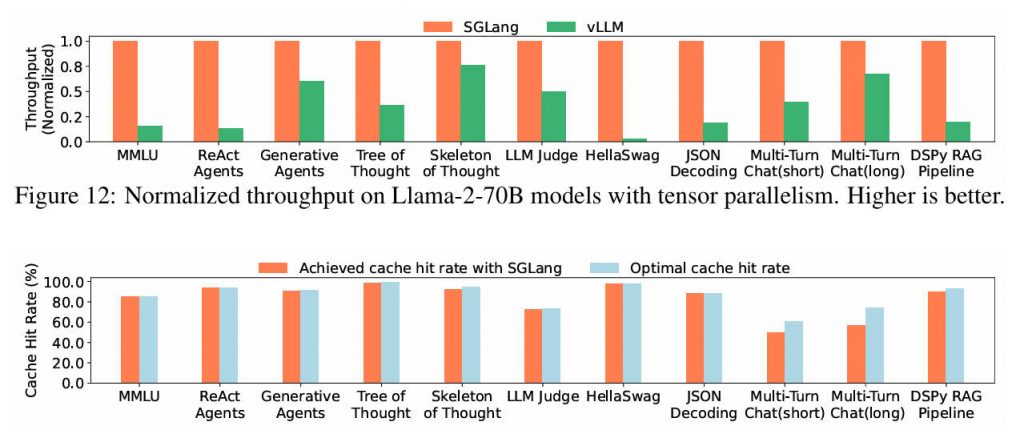
Repeated prompts or shared context across requests—common in chatbots, agents, and batched inference—waste GPU memory and compute if handled naively. SGLang’s RadixAttention reuses key-value (KV) caches for shared prefixes across requests, dramatically reducing redundant computation. Benchmarks show up to 5x faster inference on tasks with overlapping prompts, such as few-shot learning or multi-turn dialogues.
Structured Output at Speed
Enforcing JSON, XML, or custom schemas during decoding is notoriously slow in standard frameworks. SGLang compiles output constraints into compressed finite state machines (FSMs) that guide token generation in real time—without backtracking or post-hoc validation. This enables 3x faster JSON decoding while guaranteeing syntactic correctness, a critical requirement for APIs, data extraction, and agent tool calling.
Zero-Overhead Scheduling and Prefill-Decode Disaggregation
Traditional LLM servers couple prefill (prompt processing) and decode (token generation) on the same GPU, creating resource contention. SGLang separates these stages (prefill-decode disaggregation) and pairs them with a zero-overhead CPU scheduler and cache-aware load balancer, maximizing hardware utilization. In large-scale deployments (e.g., 96 H100 GPUs), this approach delivers 3.8x faster prefill and 4.8x higher decode throughput.
Built for Parallelism and Scalability
SGLang natively supports tensor, pipeline, expert, and data parallelism, including advanced configurations like large-scale expert parallelism for sparse models (e.g., DeepSeek-V3.2). Combined with continuous batching, chunked prefill, and paged attention, it scales seamlessly from a single GPU to rack-level clusters like NVIDIA GB200 NVL72.
Who Benefits Most from SGLang?
- ML Engineers building production LLM services who need low latency, high throughput, and reliable structured outputs.
- Product Teams creating agent-based applications, RAG pipelines, or multi-turn assistants that require chaining LLM calls with control flow.
- Startups and Researchers who want to prototype complex LLM workflows quickly using an intuitive frontend language—without sacrificing performance.
- Infrastructure Teams managing heterogeneous hardware (NVIDIA, AMD, TPU, CPU) who need a unified, vendor-agnostic serving stack.
SGLang’s frontend lets you write programs like:
@sgl.function
def multi_step_agent(s, query):
s += f"User: {query}\nAgent:"
thought = sgl.gen("thought", max_tokens=100)
if "search" in thought:
result = external_search(thought)
s += f"\nSearch result: {result}\nFinal answer:"
return sgl.gen("answer", max_tokens=50)
else:
return sgl.gen("direct_answer", max_tokens=50)
This blends generation, control logic, and external tool use—all executed efficiently by the SGLang runtime.
Seamless Integration and Broad Compatibility
SGLang works out of the box with:
- Models: Llama, Qwen, DeepSeek, GPT, Gemma, Mistral, GLM, LLaVA-OneVision (multi-image/video), embedding models (e5-mistral, gte), and reward models.
- Hardware: NVIDIA (H100, A100, GB200), AMD (MI300X, MI355), Intel CPUs, Google TPUs (via SGLang-Jax), and Ascend NPUs.
- Ecosystems: Hugging Face Transformers, OpenAI-compatible APIs, and quantization formats (AWQ, GPTQ, FP8, INT4).
Day-zero support for new models—like DeepSeek-V3.2 with sparse attention or OpenAI’s open-source GPT variants—ensures you’re never blocked by framework limitations.
Getting Started Is Straightforward
Installation is as simple as:
pip install sglang
Then launch a server:
python -m sglang.launch_server --model meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct
And use it via OpenAI-compatible endpoints or the native SGLang frontend. Tutorials cover everything from basic generation to multimodal inputs and structured JSON output—making adoption frictionless for teams already familiar with standard LLM tooling.
Limitations to Consider
While SGLang dramatically lowers the barrier to efficient LLM serving, users should note:
- Basic understanding of LLM inference concepts (e.g., batching, KV cache) helps when tuning performance.
- New hardware backends (e.g., TPU/Jax) are actively developed but may have fewer optimizations than mature NVIDIA support.
- Highly custom runtime modifications still require systems-level work, though SGLang’s modular design encourages extension.
For most production use cases—especially those involving structured outputs, multi-step logic, or multimodal inputs—SGLang provides a robust, high-performance baseline out of the box.
Summary
SGLang isn’t just another LLM inference engine—it’s a complete system for programming and executing complex LLM applications efficiently. By unifying an expressive frontend with a runtime optimized for prefix reuse, structured decoding, and hardware-aware parallelism, it solves real pain points in latency, throughput, and output reliability.
With support across major models, hardware platforms, and cloud providers—and adoption across 400,000+ GPUs globally—SGLang has become the de facto standard for teams shipping serious LLM applications. If you’re building agents, RAG systems, JSON APIs, or multimodal assistants, SGLang is worth evaluating today.