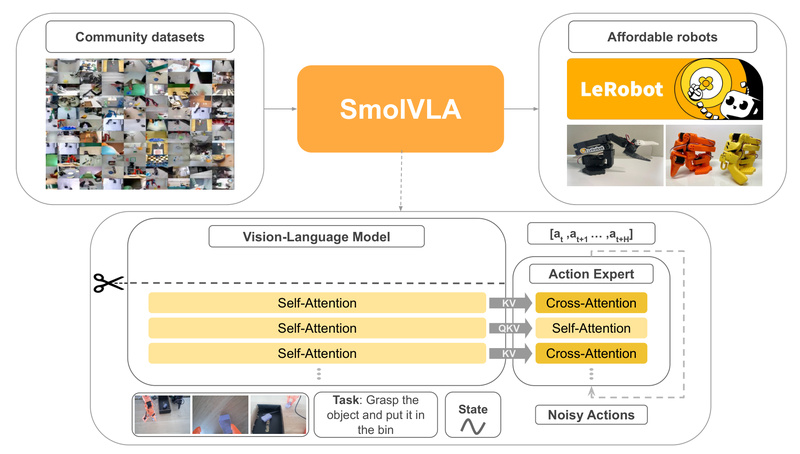
SmolVLA is a compact yet capable Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model designed to bring state-of-the-art robot control within reach of researchers, educators, and hobbyists—without the need for expensive hardware or billion-parameter architectures. Built as part of the LeRobot toolkit by Hugging Face, SmolVLA demonstrates that small models can deliver competitive performance in real-world robotic manipulation when trained efficiently on community-sourced data.
Unlike many existing VLAs that demand massive compute resources and proprietary datasets, SmolVLA is intentionally lightweight: it can be trained on a single consumer GPU and deployed even on a CPU, making robotics experimentation dramatically more accessible. Its design aligns with a growing trend in AI—doing more with less—while maintaining responsiveness through an innovative asynchronous inference stack that decouples perception from action execution.
This article walks you through what makes SmolVLA stand out, where it excels, how it solves real-world bottlenecks, and how you can start using it today—whether you’re simulating a robot on your laptop or building a physical SO-101 arm in your garage.
What Makes SmolVLA Different?
Efficiency Without Sacrificing Capability
SmolVLA challenges the assumption that robotic intelligence requires enormous models. Despite being up to 10x smaller than leading VLAs, it achieves comparable performance on a range of simulated and real-world robotic tasks. This efficiency stems from thoughtful architecture choices and a focus on practical deployability rather than theoretical scale.
Built for Real Hardware Constraints
SmolVLA was explicitly designed to run on affordable hardware:
- Trainable on a single GPU (e.g., RTX 3090 or similar)
- Deployable on consumer-grade GPUs or even CPUs
- Optimized for low-latency control via asynchronous inference, enabling higher action update rates by generating actions in chunks while the robot executes previous ones
This stands in stark contrast to other VLAs that require multi-GPU setups or cloud inference—barriers that exclude many academic labs and individual developers.
Community-Driven Data Philosophy
Rather than relying solely on large-scale academic or industrial datasets, SmolVLA leverages community-collected demonstrations from low-cost robotic platforms like the SO-101 (costing around €114 per arm) and HopeJR humanoid hands. This not only reduces data acquisition costs but also ensures the model learns from real, diverse, and accessible hardware—making it more practical for everyday use.
Where SmolVLA Shines: Ideal Use Cases
Academic Research & Rapid Prototyping
For researchers testing new imitation learning or vision-language-action paradigms, SmolVLA offers a fast iteration loop. You can:
- Reproduce state-of-the-art results using provided configs (e.g.,
lerobot-train --config_path=lerobot/diffusion_pusht) - Swap in custom datasets or policies without waiting days for training to complete
- Validate ideas on simulation environments (ALOHA, PushT, SimXArm) before moving to real hardware
Educational Robotics & Student Projects
SmolVLA’s low barrier to entry makes it ideal for university labs or coding bootcamps. Students can:
- Train a working robot policy in minutes on a laptop
- Visualize training data using
lerobot-dataset-viz - Explore real robotic manipulation without institutional budgets
Hobbyist & Maker Robotics
If you’re building your own SO-101 arm or HopeJR hand, SmolVLA integrates seamlessly with LeRobot’s ecosystem. The framework provides:
- Pretrained models on Hugging Face (e.g.,
lerobot/aloha_static_coffee) - Clear tutorials for assembly and control
- Support for mobile extensions like the LeKiwi robot on wheels
Solving Real Pain Points in Robotics AI
Breaking the “Big Model” Bottleneck
Traditional VLAs often require:
- Billions of parameters
- Expensive datasets (e.g., from multi-thousand-dollar robot fleets)
- Cloud-scale inference infrastructure
SmolVLA directly addresses these pain points by proving that compact models trained on affordable data can still generalize well across tasks—enabling teams without venture funding or GPU clusters to participate meaningfully in robotics innovation.
Bridging Simulation and Reality
LeRobot includes both simulation environments and real-world datasets, all formatted consistently via the LeRobotDataset class. This unified interface means you can:
- Develop and debug in simulation
- Seamlessly switch to real hardware using the same code
- Leverage temporal-aware sampling (
delta_timestamps) to model dynamics accurately
Democratizing Robot Learning
By open-sourcing all code, models, and datasets, the LeRobot team ensures that SmolVLA isn’t just a research artifact—it’s a reusable tool. Anyone can download, finetune, and deploy it, fostering a collaborative ecosystem around affordable robotics.
Getting Started with SmolVLA
Installation
You can install LeRobot (which includes SmolVLA support) via PyPI:
pip install lerobot
Or from source for development:
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot.git cd lerobot pip install -e .
Loading and Using Pretrained Models
Pretrained SmolVLA-compatible policies are available on Hugging Face under the lerobot organization. For example:
from lerobot import load_pretrained_policy
policy = load_pretrained_policy("lerobot/your_smolvla_model")
You can also visualize datasets:
lerobot-dataset-viz --repo-id lerobot/pusht --episode-index 0
Training Your Own SmolVLA
To train from scratch or finetune:
- Prepare your dataset in
LeRobotDatasetformat - Use a config file (e.g., from
lerobot/configs/) - Run:
lerobot-train --config_path=your_config.yaml
All trained models can be uploaded to Hugging Face for sharing using standard huggingface-cli commands.
Limitations and Considerations
While SmolVLA excels in accessibility and efficiency, it’s important to set realistic expectations:
- Task Scope: Currently focused on dexterous manipulation tasks (e.g., pick-and-place, pouring, hand control) with supported arms like SO-101 and HopeJR. It is not designed for navigation, locomotion, or highly abstract reasoning.
- Learning Paradigm: Relies on imitation learning from demonstrations, so performance depends on the quality and coverage of the training data. It does not incorporate online reinforcement learning by default.
- Model Capacity: In extremely complex, multi-stage tasks requiring long-horizon reasoning, larger VLAs may still outperform SmolVLA—though often at prohibitive cost.
For most practical manipulation scenarios on affordable hardware, however, SmolVLA strikes an exceptional balance between performance, cost, and usability.
Summary
SmolVLA redefines what’s possible in accessible robotics AI. By combining a small model footprint, single-GPU trainability, CPU deployability, and strong performance on real-world tasks, it empowers a new generation of developers to build, train, and deploy vision-language-action systems without massive resources. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or maker, SmolVLA—through the LeRobot framework—offers a clear, open, and practical path into the future of embodied AI.
All code, models, and datasets are freely available at github.com/huggingface/lerobot and huggingface.co/lerobot.