Deploying large language models (LLMs) like LLaMA, Mistral, or Vicuna often demands multiple high-end GPUs, complex inference pipelines, and substantial cloud costs—primarily due to memory bottlenecks, not computation. For technical decision-makers managing AI infrastructure, this creates a difficult trade-off: use smaller models with lower quality, or accept high operational overhead.
SqueezeLLM changes this equation. It’s a post-training quantization framework that enables 3-bit and 4-bit LLM deployment with near-FP16 accuracy—while reducing memory footprint enough to run models like LLaMA-7B in under 6 GB of VRAM. Unlike naive quantization approaches that degrade model quality, SqueezeLLM preserves performance through two key innovations: sensitivity-aware bit allocation and Dense-and-Sparse weight decomposition. The result? Faster inference, lower hardware costs, and no compromise on benchmark scores like MMLU or perplexity.
How SqueezeLLM Solves the Real Bottleneck in LLM Inference
Contrary to common assumptions, the primary constraint in single-batch LLM inference isn’t compute power—it’s memory bandwidth. Moving weights from GPU memory to compute units becomes the limiting factor, especially as model sizes grow. Quantization reduces weight size, but uniform low-bit quantization often damages performance by treating all weights equally.
SqueezeLLM tackles this with a smarter strategy. Instead of applying the same bitwidth across all parameters, it:
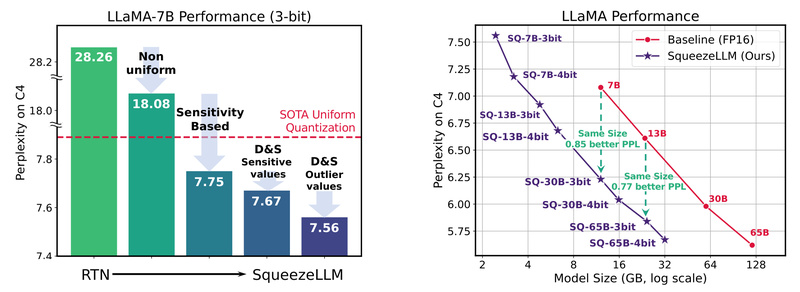
- Analyzes weight sensitivity using second-order information to identify which layers or weight groups are most critical to model quality.
- Assigns higher precision selectively to sensitive regions while aggressively quantizing less important ones—enabling non-uniform, optimized bit allocation.
This alone improves accuracy over prior quantization methods. But SqueezeLLM goes further.
Dense-and-Sparse Decomposition: Keep Outliers, Compress the Rest
Not all weights are created equal. A small fraction—often outliers or structurally important values—have outsized impact on model behavior. SqueezeLLM separates each weight matrix into two parts:
- A dense component, heavily quantized (e.g., to 3-bit) with minimal quality loss.
- A sparse component, stored in an efficient sparse format, preserving only the most sensitive or outlier weights in higher precision.
This hybrid representation ensures that the model retains its reasoning fidelity while achieving ultra-low memory usage. In practice, this means SqueezeLLM’s 3-bit quantized LLaMA models close the perplexity gap with FP16 by up to 2.1× compared to state-of-the-art baselines under the same memory budget.
Ideal Scenarios for Adopting SqueezeLLM
SqueezeLLM shines in environments where memory efficiency and model quality must coexist:
- Single-GPU deployment: Run LLaMA-13B or Vicuna-13B on a single A6000 without offloading or quantization-induced quality drops.
- Cost-sensitive cloud inference: Serve more model instances per GPU, reducing cloud spend while maintaining MMLU scores (e.g., SqueezeLLM’s Vicuna variant achieves 2% higher MMLU than FP16 baseline despite using half the memory).
- Edge or on-prem AI servers: Deploy capable LLMs on hardware with limited VRAM but sufficient compute (e.g., A5000/A6000-class GPUs).
- High-throughput serving with vLLM: Thanks to native integration with the vLLM framework, SqueezeLLM models can be production-ready with minimal integration effort.
Getting Started: From Installation to Inference
SqueezeLLM is designed for practical adoption. Here’s how to begin:
Installation
conda create --name sqllm python=3.9 -y conda activate sqllm git clone https://github.com/SqueezeAILab/SqueezeLLM cd SqueezeLLM pip install -e . cd squeezellm python setup_cuda.py install
Running Pre-Quantized Models
SqueezeLLM provides ready-to-use quantized checkpoints for popular models. For example, to evaluate a 3-bit LLaMA-7B model:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python llama.py {original_model_path} c4 --wbits 3 --load sq-llama-7b-w3-s0.pt --eval
For models with sparse components (e.g., sq-llama-7b-w3-s5.pt), add the --include_sparse flag.
Note: LLaMA v1 and Vicuna v1.1 require you to first convert the original HF-compatible model. However, LLaMA-2, Mistral, Vicuna v1.3, and XGen work out-of-the-box—no original weights needed.
Supported Models and Configurations
SqueezeLLM supports:
- Models: LLaMA (7B–65B), LLaMA-2 (7B/13B), Vicuna (7B/13B/30B), Mistral (7B), XGen (7B), and OPT (1.3B–30B).
- Bitwidths: 3-bit and 4-bit.
- Sparsity levels: 0% (dense-only), 0.05%, and 0.45% (varies by model; e.g., LLaMA-2 currently only offers dense variants).
Quantizing custom models is also possible using their open-sourced pipeline.
Practical Considerations and Limitations
While SqueezeLLM delivers strong results, keep these points in mind:
- Hardware: Tested on NVIDIA A5000/A6000 GPUs with CUDA 11.3 and cuDNN 8.2. Performance on other architectures may vary.
- Model coverage: Not every model supports all sparsity levels. For example, LLaMA-2 and Mistral currently only offer dense (0% sparsity) quantizations.
- Workflow integration: For production serving, leverage the official vLLM integration for optimized throughput and compatibility.
Summary
SqueezeLLM redefines what’s possible with low-bit LLM deployment. By combining sensitivity-aware quantization with Dense-and-Sparse decomposition, it achieves higher accuracy at lower bitwidths—enabling teams to run powerful LLMs on fewer GPUs without quality degradation. Whether you’re optimizing cloud costs, enabling single-GPU research, or scaling inference infrastructure, SqueezeLLM offers a compelling path to efficient, high-fidelity LLM serving.