In the rapidly evolving field of computational drug discovery, one of the most persistent challenges is accurately predicting how small molecules—potential drug candidates—interact with biological targets like proteins. Traditional physics-based docking methods are often accurate but computationally expensive, while many machine learning (ML) alternatives sacrifice chemical realism for speed, leading to physically implausible predictions such as steric clashes or incorrect chirality.
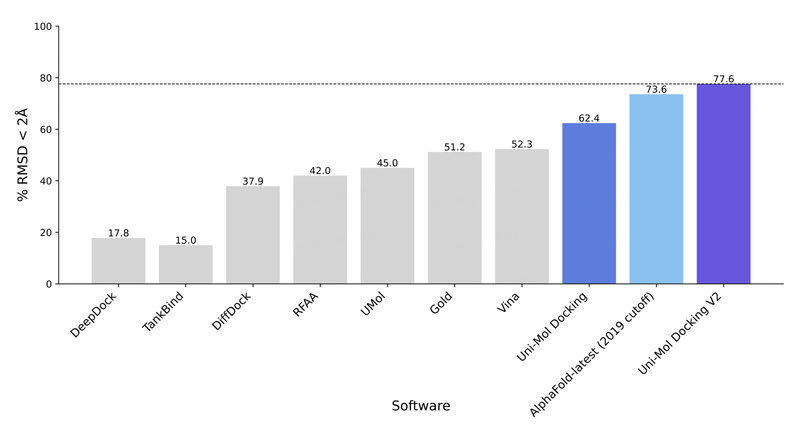
Enter Uni-Mol, a universal 3D molecular representation learning framework that bridges this gap. Developed by DP Technology, Uni-Mol leverages deep learning to deliver both high accuracy and chemical plausibility across a wide range of molecular tasks—from property prediction and conformation generation to protein-ligand binding pose estimation. Its latest iteration, Uni-Mol Docking V2, achieves state-of-the-art results on the rigorous PoseBusters benchmark, with over 77% of ligands predicted within 2.0 Å RMSD and 75% passing all structural quality checks.
What makes Uni-Mol especially compelling for project and technical decision-makers is its balance of scientific rigor, industrial applicability, and accessibility. Whether you’re running virtual screening campaigns, optimizing lead compounds, or building downstream ML pipelines for chemistry, Uni-Mol offers a robust, open-source foundation that integrates seamlessly into real-world workflows.
Why Uni-Mol Stands Out in Molecular AI
Chemically Faithful Predictions at Scale
Unlike earlier ML-based docking models that prioritize numerical metrics over physical realism, Uni-Mol Docking V2 is explicitly designed to avoid common pitfalls like steric overlaps and chirality inversions. This means its predictions aren’t just numerically close to crystallographic poses—they’re chemically sensible, making them far more trustworthy in practical drug design settings.
This fidelity stems from Uni-Mol’s dual pretraining strategy: one model is trained on 209 million 3D molecular conformations, while another is trained on 3 million protein pocket structures. When combined for docking tasks, they jointly capture both ligand flexibility and binding site geometry, enabling highly accurate and physically grounded pose predictions.
Benchmark-Leading Performance Across Tasks
Uni-Mol isn’t just strong in docking—it excels across the molecular AI landscape:
- Property Prediction: Outperforms prior methods on 14 out of 15 standard benchmarks.
- Docking Accuracy: Uni-Mol Docking V2 achieves >77% success rate (RMSD < 2.0 Å) on PoseBusters—a significant jump from 62% in the original version.
- Quantum Chemical Estimation: With Uni-Mol+, the framework ranks #1 on major benchmarks like OGB-LSC and OC20 by iteratively optimizing 3D conformations before property prediction.
- Scalability: Uni-Mol2 scales from 84 million to 1.1 billion parameters, allowing users to choose the right model size for their compute budget and accuracy needs.
These results aren’t just academic—they translate directly into higher-quality virtual screening hits and more reliable structure-based design.
Real-World Applications That Benefit from Uni-Mol
Accelerating Early-Stage Drug Discovery
In virtual screening, where millions of compounds must be evaluated rapidly, Uni-Mol provides a fast yet accurate alternative to slow physics-based docking. Its ability to generate realistic binding poses means fewer false positives and better prioritization of compounds for experimental testing.
Lead Optimization with Reliable Binding Insights
During lead optimization, knowing how a molecule binds is as important as whether it binds. Uni-Mol Docking V2’s high-resolution pose predictions (including sub-1.5 Å accuracy for many cases) help medicinal chemists make informed decisions about chemical modifications—without worrying about artifacts from the model itself.
Quantum Property Prediction Without Quantum Costs
Uni-Mol+ enables data-driven estimation of quantum mechanical properties—such as energy, dipole moments, or partial charges—using only 2D molecular graphs as input. By first generating and refining a 3D conformation (e.g., via RDKit), then applying Uni-Mol+’s learned physics-aware representations, teams can bypass expensive quantum chemistry calculations while maintaining high accuracy.
Seamless Integration into ML Pipelines
For teams building custom molecular ML systems, Uni-Mol provides high-quality 3D embeddings out of the box. These representations can be used as input features for downstream tasks like solubility prediction, toxicity classification, or reaction yield modeling—greatly reducing the need for hand-crafted descriptors.
Getting Started: Practical Pathways for Technical Teams
Uni-Mol is designed for adoption, not just admiration. Here’s how you can start using it today:
1. Use the Unified Python Package
Install unimol-tools via pip:
pip install unimol-tools
This package provides high-level APIs for molecular representation, property prediction, and docking inference—ideal for rapid prototyping or integration into existing data pipelines.
2. Access the Hosted Docking Service
For teams without dedicated GPU infrastructure, the Uni-Mol Docking V2 service on Bohrium (https://bohrium.dp.tech/apps/unimoldockingv2) offers a no-code way to run high-accuracy docking jobs—just upload your protein pocket and ligand file.
3. Fine-Tune or Extend the Open-Source Models
All code, pretrained weights, and training data are publicly available on GitHub (https://github.com/dptech-corp/Uni-Mol). Researchers and engineers can fine-tune models on proprietary datasets or adapt the architecture for specialized tasks like covalent docking or multi-ligand binding.
4. Combine with Physics-Based Methods for Best Results
As noted in the Uni-Mol Docking V2 paper, hybrid approaches (e.g., using Uni-Mol for initial pose generation followed by refinement with Uni-Dock or other physics-based scorers) often yield the highest-quality predictions. This makes Uni-Mol a complementary tool—not a replacement—for established computational chemistry workflows.
Limitations and Strategic Considerations
While Uni-Mol is powerful, it’s important to understand its boundaries:
- Pocket-Dependent Docking: Uni-Mol Docking requires a predefined binding pocket. It does not perform blind docking across the entire protein surface.
- Dependence on Initial Conformations: Components like Uni-Mol+ rely on an initial 3D conformation (often from RDKit), which may be suboptimal for highly flexible or macrocyclic molecules.
- Compute Requirements for Large Models: Uni-Mol2’s 1.1B-parameter variant delivers top performance but demands significant GPU memory—teams should evaluate whether smaller variants (e.g., 84M or 300M) meet their needs.
- Not a Full Replacement for Physics: For highly sensitive applications (e.g., binding affinity ranking), combining Uni-Mol with physics-based scoring remains the gold standard.
Summary
Uni-Mol represents a significant step forward in making 3D molecular AI both accurate and chemically trustworthy. By unifying representation learning, docking, and quantum property prediction under a single scalable framework, it empowers drug discovery teams to move faster without sacrificing scientific rigor. With open-source code, a user-friendly toolkit, and a hosted service, Uni-Mol lowers the barrier to adopting state-of-the-art molecular AI—making it a compelling choice for any project where molecular structure, interaction, or property matters.