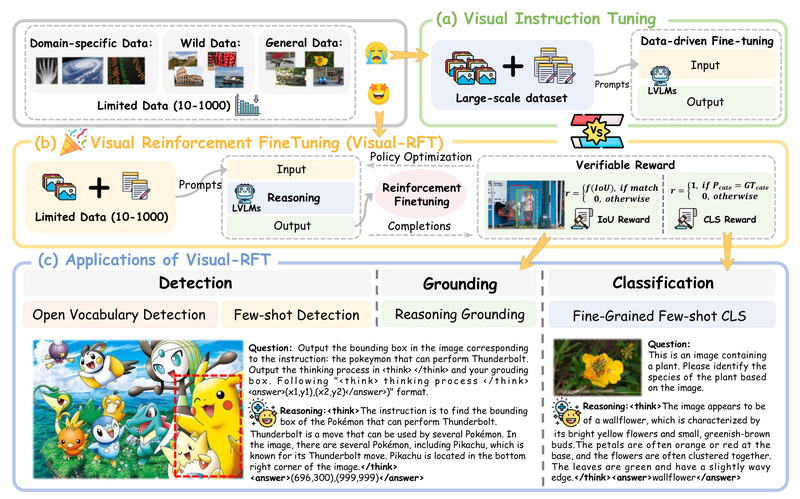
When labeled visual data is scarce—think dozens or hundreds of examples per category—traditional supervised fine-tuning (SFT) often falls short. Enter Visual-RFT (Visual Reinforcement Fine-Tuning): a novel, data-efficient method that adapts reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards to Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs). Inspired by the success of DeepSeek-R1 and OpenAI o1 in language reasoning, Visual-RFT extends this reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) paradigm to multimodal tasks like object detection, visual grounding, and fine-grained classification—delivering significant performance gains even with extremely limited training data.
Developed by researchers at leading AI labs and accepted to ICCV 2025, Visual-RFT is not just theoretical—it’s fully open-sourced, complete with training code, curated datasets, and evaluation scripts. If you’re building or adapting LVLMs for niche visual tasks where annotation is expensive or impractical, Visual-RFT offers a compelling alternative to conventional fine-tuning.
What Problem Does Visual-RFT Solve?
Supervised fine-tuning requires large, high-quality labeled datasets. In many real-world scenarios—such as medical imaging, industrial inspection, or specialized robotics—collecting thousands of annotated images per class is infeasible. Even few-shot SFT often struggles to generalize.
Visual-RFT tackles this by replacing human-labeled targets with automated, task-specific reward functions. For example:
- In object detection, it uses Intersection over Union (IoU) between predicted and ground-truth bounding boxes.
- In classification, it checks whether the final answer matches the ground truth.
Because these rewards are verifiable and differentiable, they enable policy gradient updates without manual labels. The model learns to refine its internal reasoning (including intermediate “thought” tokens) to maximize these rewards—effectively teaching itself how to solve structured visual problems with minimal supervision.
How Visual-RFT Works
Visual-RFT builds on Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), a stable reinforcement learning algorithm designed for language models. The workflow is straightforward:
- Response Generation: Given an image and a prompt, the LVLM (e.g., Qwen2-VL-2B/7B) generates multiple reasoning trajectories—each ending in a final answer (e.g., a bounding box or class label).
- Reward Assignment: A task-specific reward function evaluates each output. For detection, IoU determines the score; for classification, it’s binary accuracy.
- Policy Update: GRPO uses these rewards to update the model, favoring trajectories that lead to higher scores. A KL divergence constraint ensures updates remain close to the original model, preserving general knowledge.
Crucially, the reward is computed automatically—no human in the loop. This makes the approach scalable, consistent, and ideal for domains where expert labeling is costly.
Proven Performance Gains
Visual-RFT demonstrates remarkable improvements across multiple benchmarks:
- +24.3% accuracy over SFT in one-shot fine-grained image classification (e.g., distinguishing aircraft models with only ~100 samples).
- +21.9 mAP on COCO two-shot object detection.
- +15.4 mAP on LVIS few-shot detection.
These results highlight Visual-RFT’s ability to extract maximum utility from minimal data—making it especially valuable for low-resource or rapidly evolving visual domains.
Getting Started: Practical Integration
Visual-RFT is designed for ease of adoption:
Base Models
Currently supports Qwen2-VL and Qwen2.5-VL (2B and 7B variants).
Data Format
You can use either:
- HuggingFace Datasets (pre-built for COCO, LVIS, Flowers, Cars, etc.)
- Custom JSON files with fields:
image,problem, andsolution
The project includes scripts to build your own dataset from scratch (dataset/build_dataset.ipynb).
Training
Training is lightweight:
- For datasets with ~100–1,000 samples, 200 optimization steps are often sufficient.
- Use the provided
grpo.pyscript with GRPO configuration. - Multi-GPU support via
torchrunand DeepSpeed (ZeRO-3).
Memory Tips: If you hit OOM errors:
- Reduce
--num_generations(default: 8 → try 4) - Enable
--gradient_checkpointing - Use
zero3_offload.jsonfor CPU offloading - Lower image resolution via
--max_pixels
Evaluation
Built-in evaluation suites for:
- COCO and LVIS object detection
- Fine-grained classification (Flowers, Aircraft, Cars, Pets)
- Reasoning grounding (e.g., LISA dataset)
Each evaluation script outputs standard metrics (mAP, accuracy) and supports multi-GPU inference.
When to Use (and Not Use) Visual-RFT
✅ Ideal For:
- Few-shot or one-shot visual tasks with limited labeled data
- Structured output tasks where correctness is objectively measurable (e.g., bounding boxes, class labels)
- Domain adaptation where collecting new labels is expensive
- Projects requiring transparent, reward-driven learning without human feedback
⚠️ Limitations to Consider:
- Base model dependency: Only Qwen2-VL variants are officially supported.
- Reward design requirement: Your task must have a clear, automated metric (e.g., IoU, exact match). Tasks without verifiable outputs (e.g., subjective image captioning) aren’t suitable.
- Hardware needs: Training and evaluation benefit from multi-GPU setups (≥2 GPUs recommended).
- License: Code and data are for non-commercial research only (CC BY-NC 4.0).
Summary
Visual-RFT redefines how we fine-tune vision-language models under data scarcity. By replacing manual labels with automated, task-specific rewards and leveraging stable policy optimization, it unlocks strong performance in few-shot detection, grounding, and classification—areas where traditional methods falter. With full code, data, and evaluation tooling open-sourced, it’s ready for integration into research pipelines tackling real-world visual reasoning challenges. If your project operates in a low-data, high-stakes visual domain, Visual-RFT is a powerful tool worth exploring.