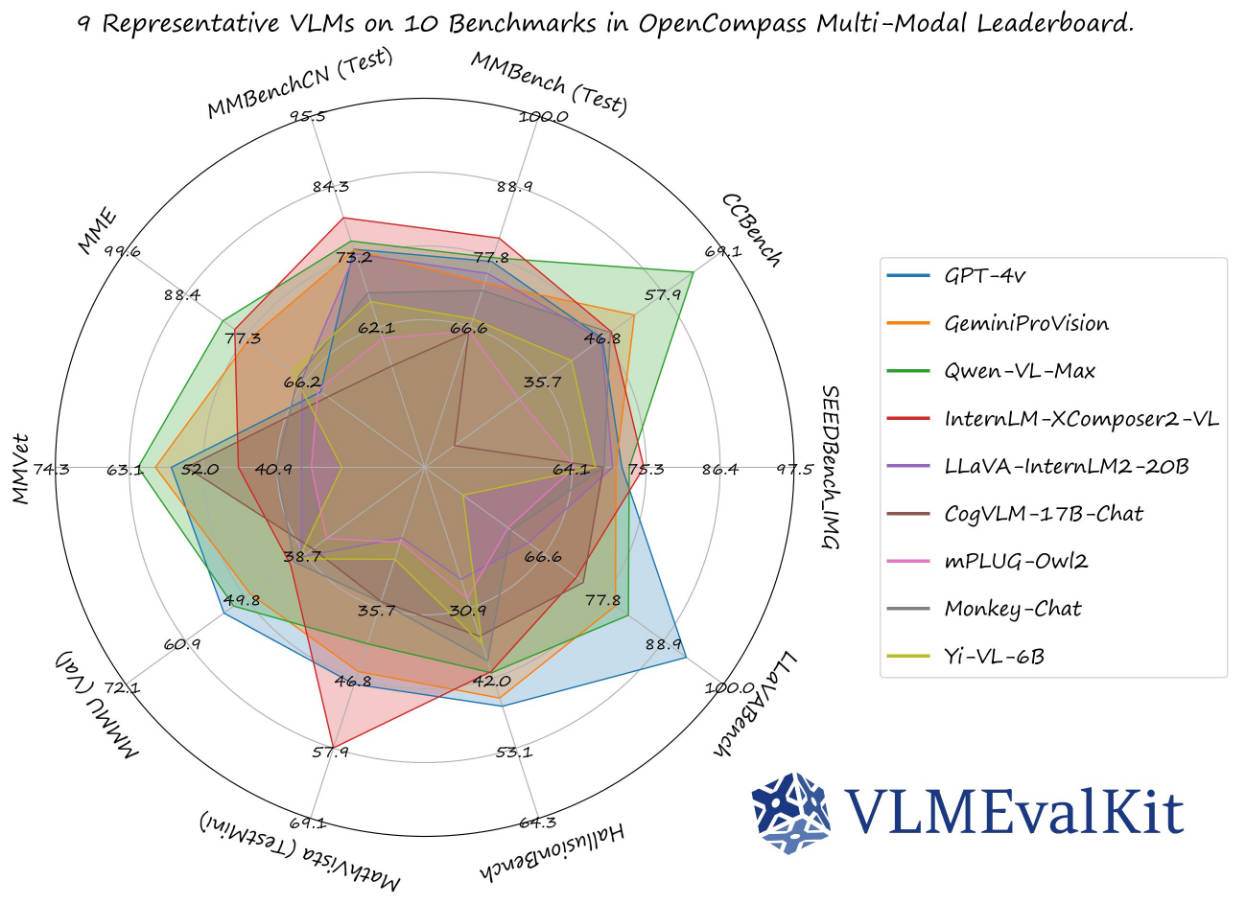
Evaluating large vision-language models (LVLMs) used to be a fragmented, time-consuming chore—juggling dozens of benchmark repositories, writing custom data loaders, and debugging mismatched evaluation protocols. VLMEvalKit changes all that. Built as an open-source PyTorch-based toolkit, it delivers a unified, reproducible, and user-friendly framework for evaluating any multi-modal model on more than 80 standardized benchmarks—using just a single command. Whether you’re a researcher comparing state-of-the-art models or a developer validating your own LVLM, VLMEvalKit eliminates the engineering overhead so you can focus on what matters: performance, fairness, and progress.
Why VLMEvalKit Solves Real Evaluation Pain Points
Traditional multi-modal evaluation workflows suffer from three core problems:
- Fragmentation: Each benchmark (e.g., MMBench, VQAv2, OCRBench) often ships with its own data format, preprocessing logic, and scoring script.
- Reproducibility gaps: Even minor differences in prompts, post-processing, or inference settings lead to inconsistent results.
- Scalability bottlenecks: Running evaluations across dozens of models and benchmarks requires significant scripting and compute orchestration.
VLMEvalKit directly addresses these by enforcing a standardized evaluation pipeline—generation-based inference paired with consistent post-processing (exact matching or LLM-assisted answer extraction)—while automating everything from data download to metric computation.
Evaluate Any Model on Any Benchmark—With One Command
VLMEvalKit supports over 80 multi-modal benchmarks, spanning image understanding, video reasoning, OCR, physics-based QA, medical imaging, and more. This includes widely used suites like MME, MMMU, and MM-Vet, as well as newer challenges like SeePhys, PhyX, and NaturalBench.
Thanks to its modular design, switching between benchmarks requires no code changes—just specify the dataset name in your evaluation command. The toolkit handles the rest: downloading data (with optional ModelScope integration for video benchmarks), formatting inputs, running inference, and computing official metrics.
Out-of-the-Box Support for 200+ Vision-Language Models
From open-source stalwarts like LLaVA, InternVL, and QwenVL to proprietary APIs such as Gemini-2.5-Pro, Kimi-VL, and Grok, VLMEvalKit includes built-in wrappers for 200+ multi-modal models. Each model is pre-configured with its recommended tokenizer, image processor, and prompt template, ensuring fair and consistent comparisons.
This breadth enables direct benchmarking across open and closed models—something rarely possible with fragmented evaluation setups. Results are aggregated on the OpenVLM Leaderboard, offering a transparent, community-tracked view of LVLM progress.
Adding Your Custom Model Takes Just One Function
For model developers, VLMEvalKit dramatically lowers the barrier to standardized evaluation. To integrate a new vision-language model, you only need to implement a single method: generate_inner(), which defines how your model processes a list of images and a text prompt to produce a response.
Once that’s done, VLMEvalKit automatically manages:
- Distributed inference (including multi-node support via LMDeploy or vLLM)
- Batched data loading
- Prediction caching and post-processing
- Metric calculation across all supported benchmarks
This design ensures your model is evaluated under the same conditions as every other entry—making your results directly comparable and reproducible by others.
Practical Features for Real-World Evaluation Scenarios
VLMEvalKit isn’t just theoretically clean—it’s built for the messy realities of modern LVLMs:
- Thinking-mode support: Many models (e.g., InternVL) output intermediate reasoning steps wrapped in
<think>...</think>tags. By settingSPLIT_THINK=True, VLMEvalKit cleanly separates reasoning from final answers, preventing contamination of evaluation metrics. - Long-response handling: Models generating 16k+ or 32k+ tokens risk truncation in Excel-based prediction files. Setting
PRED_FORMAT=tsvswitches output to TSV format, preserving full-length responses. - Accelerated inference: For large or slow models, enable
use_lmdeployoruse_vllmin your model config to leverage optimized serving backends—slashing evaluation time without code changes.
Important Limitations to Understand
VLMEvalKit prioritizes consistency and ease of use—but this comes with trade-offs:
- Generation-based evaluation only: Unlike benchmarks that use perplexity (PPL) or multiple-choice scoring (e.g., SEEDBench), VLMEvalKit treats all tasks as open-ended generation. While this enables cross-benchmark uniformity, absolute scores may differ from original papers. The toolkit transparently reports both exact-match and LLM-extracted scores where applicable.
- Shared prompt templates: By default, all models on a benchmark use the same prompt. Some models perform better with custom templates (e.g., system messages or CoT prompts). The toolkit encourages—but doesn’t enforce—model-specific prompt implementations.
- Version-sensitive dependencies: Certain models require exact versions of
transformers,torchvision, orflash-attn. The documentation provides clear version mappings (e.g.,transformers==4.37.0for LLaVA series) to avoid runtime errors.
Getting Started Is Remarkably Simple
You can start evaluating in seconds. Here’s a minimal example:
from vlmeval.config import supported_VLM model = supported_VLM['idefics_9b_instruct']() response = model.generate(['assets/apple.jpg', 'What is in this image?']) print(response) # "The image features a red apple with a leaf on it."
For full benchmark runs, the QuickStart guide provides CLI commands that handle everything from model loading to result reporting—no scripting needed.
Who Should Use VLMEvalKit?
- Researchers tracking LVLM progress across diverse tasks.
- Model developers validating new architectures or fine-tuned variants.
- Engineering teams building reproducible evaluation pipelines for production models.
- Benchmark creators seeking standardized integration and community adoption.
If your work involves comparing, validating, or deploying vision-language models, VLMEvalKit removes the evaluation bottleneck—so you spend less time wiring scripts and more time advancing the field.
Summary
VLMEvalKit delivers on a simple but powerful promise: standardized, one-command evaluation for the entire ecosystem of vision-language models. By unifying data handling, inference, and scoring across 200+ models and 80+ benchmarks, it makes reproducible multi-modal evaluation accessible to everyone—from students to industry labs. With active maintenance, community contributions, and support for emerging modalities like video, it’s quickly becoming the de facto toolkit for LVLM assessment.