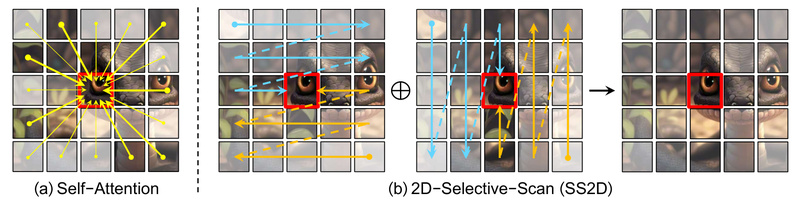
In the rapidly evolving landscape of computer vision, model efficiency and scalability are no longer optional—they’re essential. Enter VMamba, a vision backbone built on the principles of state-space models (SSMs), originally pioneered in language modeling with Mamba. VMamba reimagines how visual data is processed by replacing attention-based mechanisms with a 2D Selective Scan (SS2D) module, enabling linear time complexity with respect to input size. This makes VMamba exceptionally well-suited for tasks involving high-resolution imagery, large batches, or resource-constrained environments—without sacrificing accuracy.
Accepted as a NeurIPS 2024 Spotlight paper, VMamba isn’t just theoretically elegant—it delivers state-of-the-art or competitive results across ImageNet classification, COCO object detection, and ADE20K semantic segmentation, often outperforming established architectures like Swin Transformer in both speed and accuracy.
What Makes VMamba Unique?
Linear Complexity for Real-World Scalability
Unlike Transformers, whose self-attention mechanism scales quadratically with sequence length (or image resolution), VMamba processes visual tokens in linear time. This becomes a decisive advantage when working with larger images—common in medical imaging, satellite vision, or industrial inspection—where quadratic growth in compute quickly becomes prohibitive.
2D Selective Scan: Bridging 1D SSMs and 2D Vision
The core innovation of VMamba lies in its Visual State-Space (VSS) block, which features the SS2D module. Traditional SSMs scan sequences in a single direction (e.g., left-to-right), which doesn’t naturally align with 2D image structure. SS2D solves this by scanning the image along four directional paths (e.g., left-to-right, right-to-left, top-to-bottom, bottom-to-top). This multi-directional traversal enables VMamba to capture long-range spatial dependencies and global contextual information effectively—mimicking the receptive field of Transformers, but with far greater efficiency.
Performance That Competes—and Often Wins
Extensive benchmarks confirm VMamba’s practical value:
- On ImageNet-1K, VMamba-B achieves 83.9% top-1 accuracy, surpassing Swin-B (83.5%) with similar parameters and FLOPs.
- In COCO object detection with Mask R-CNN, VMamba-S reaches 48.7 bbox AP, outperforming Swin-S (44.8).
- For ADE20K semantic segmentation, VMamba-S delivers 50.6 mIoU (single-scale), again ahead of Swin-S (47.6).
Crucially, VMamba achieves these results while offering higher throughput—e.g., 877 images/sec on A100 for VMamba-S vs. 718 for Swin-S—making it not just accurate, but faster during both training and inference.
Ideal Use Cases for VMamba
VMamba excels in scenarios where efficiency, scalability, and strong visual understanding intersect:
- Real-time object detection in robotics or autonomous systems, where low latency is critical.
- Semantic segmentation of high-resolution aerial or medical images, where quadratic models become impractical.
- Cloud-based vision pipelines where compute cost scales with model complexity—linear models like VMamba reduce operational expenses.
- Edge deployment on devices with limited GPU memory, thanks to its predictable memory footprint and absence of attention bottlenecks.
If your project involves variable input resolutions or requires training on large batches, VMamba’s linear scaling behavior provides a clear operational advantage over attention-based backbones.
Getting Started: Simplicity by Design
One of VMamba’s standout practical features is its minimal setup. As the repository proudly states: “Use VMamba with only one file and in fewest steps!”
Quick Setup
git clone https://github.com/MzeroMiko/VMamba.git cd VMamba conda create -n vmamba python=3.10 conda activate vmamba pip install torch==2.2 torchvision torchaudio triton einops timm==0.4.12 pip install https://github.com/state-spaces/mamba/releases/download/v2.2.4/mamba_ssm-2.2.4+cu12torch2.2cxx11abiTRUE-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl python vmamba.py
This streamlined installation gets you running inference or training within minutes. Pretrained models are provided for ImageNet, and integration with Mask R-CNN (detection) and UperNet (segmentation) is supported via standard OpenMMLab tooling.
Training and Evaluation
- For classification, use
main.pywith distributed training. - For detection/segmentation, leverage the provided configs with
mmdetectionormmsegmentationvia simpledist_train.shanddist_test.shscripts. - Built-in analysis tools let you visualize effective receptive fields, “attention-like” activation maps, and throughput metrics—helping you validate model behavior without external dependencies.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While VMamba offers compelling advantages, adopters should note a few caveats:
- Hardware/Software Dependencies: Optimal performance requires PyTorch ≥ 2.0, CUDA ≥ 11.8, and the custom
mamba_ssmkernel. Lower versions may work but with reduced speed. - cuDNN Interference: A known issue noted in the repo: enabling
torch.backends.cudnn.enabled=Truecan significantly slow down VMamba. Disabling cuDNN (or leaving it off by default, as in the sample script) is recommended. - Ecosystem Maturity: As a newer architecture (first released in early 2024), VMamba has less third-party integration compared to Transformers. Community tooling, tutorials, and pretrained variants are still growing—though active development (including NeurIPS 2024 acceptance) signals strong long-term support.
These are manageable trade-offs for teams prioritizing performance-per-watt or scalability on large inputs.
Summary
VMamba redefines what’s possible in efficient vision modeling. By adapting the state-space paradigm to 2D data through its innovative 2D Selective Scan, it achieves Transformer-level accuracy with CNN-like efficiency and linear scaling—a rare and powerful combination.
For technical decision-makers evaluating next-generation backbones, VMamba offers a production-ready, benchmark-validated, and hardware-conscious alternative to attention-based models. Whether you’re building scalable cloud services, deploying to edge devices, or pushing the limits of high-resolution vision, VMamba delivers the performance you need—without the computational bloat.
With active maintenance, NeurIPS recognition, and straightforward integration, now is the time to test VMamba in your pipeline.