Creating natural-sounding spoken dialogues between two people has long been a pain point in AI-driven voice applications. Traditional approaches either rely on stitching pre-recorded audio clips (limiting flexibility) or use slow, auto-regressive speech synthesis models that struggle with speaker-switch timing and voice consistency. Enter ZipVoice-Dialog: a breakthrough non-autoregressive model that generates high-quality, zero-shot two-party spoken dialogues—fast, from text alone, and without any speaker enrollment.
Built on flow matching and part of the ZipVoice family of text-to-speech (TTS) models, ZipVoice-Dialog is designed specifically for scenarios where realistic turn-taking, distinct speaker voices, and rapid inference matter. Whether you’re prototyping a conversational assistant, generating synthetic call-center data, or building immersive audio experiences for games or simulations, ZipVoice-Dialog offers a practical, open-source solution that just works—out of the box.
Why ZipVoice-Dialog Stands Out
Non-Autoregressive Speed Without Sacrificing Quality
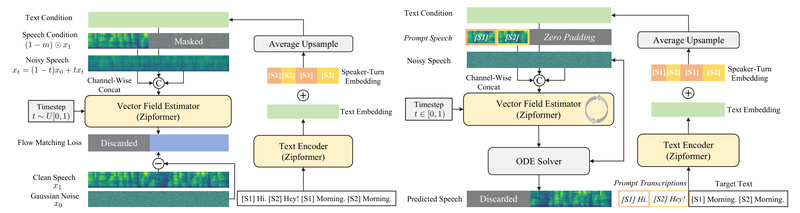
Unlike conventional spoken dialogue systems that generate speech token-by-token (auto-regressively), ZipVoice-Dialog uses a non-autoregressive flow matching architecture. This means entire dialogue utterances are synthesized in parallel, drastically reducing inference time while maintaining high intelligibility and naturalness. For product teams under tight iteration cycles or researchers running large-scale evaluations, this speed advantage translates directly into faster experimentation and deployment.
Precise Speaker Turn-Taking with Speaker-Turn Embeddings
A common flaw in dialogue TTS is unnatural or misaligned speaker switches—e.g., overlapping speech or incorrect attribution. ZipVoice-Dialog introduces speaker-turn embeddings that explicitly encode which speaker ([S1] or [S2]) is talking at each point in the dialogue. This ensures clean, well-timed alternation between voices, mimicking real human conversation rhythm.
Zero-Shot Voice Cloning That Actually Works
You don’t need hours of a target speaker’s audio. With just a short prompt (as brief as a few seconds), ZipVoice-Dialog clones speaker timbre with impressive fidelity. Benchmarks show state-of-the-art performance in speaker similarity, intelligibility, and naturalness—even in zero-shot settings. This makes it ideal for applications where collecting speaker-specific data isn’t feasible.
Mono and Stereo Output Options
Need spatial audio? ZipVoice-Dialog comes in two variants:
- ZipVoice-Dialog: Generates single-channel (mono) dialogues with alternating speaker segments.
- ZipVoice-Dialog-Stereo: Outputs two-channel stereo audio, with each speaker assigned to a separate channel—perfect for VR, gaming, or accessibility tools.
Trained on Real-World Data: The OpenDialog Dataset
To address the scarcity of large-scale spoken dialogue corpora, the team behind ZipVoice-Dialog curated OpenDialog, a 6,800-hour dataset extracted from in-the-wild conversational speech. Models trained on this data generalize better to natural dialogue patterns, pauses, and overlapping cues than those trained on scripted or synthetic data.
Ideal Use Cases for Practitioners
ZipVoice-Dialog shines in scenarios where speed, realism, and flexibility are non-negotiable:
- Conversational AI Prototyping: Quickly build voice assistants that don’t just respond—but converse—with users, complete with natural back-and-forth rhythm.
- Synthetic Training Data Generation: Create massive volumes of realistic call-center or customer-service dialogues to train downstream ASR or dialogue understanding systems—without recording real calls.
- Interactive Media and Gaming: Generate dynamic in-game dialogues between characters using only script text and short voice prompts, enabling localized or adaptive storytelling.
- Multilingual Dialogue Systems: Leverage built-in support for both English and Chinese to prototype cross-lingual conversational agents—no retraining required.
Because it operates in zero-shot mode, you avoid the overhead of fine-tuning or maintaining speaker-specific models. Just provide a prompt and dialogue script, and ZipVoice-Dialog handles the rest.
Getting Started: Practical, No-PhD Required
Using ZipVoice-Dialog is intentionally straightforward:
-
Install the package:
git clone https://github.com/k2-fsa/ZipVoice.git pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Prepare your dialogue script:
Format your text using[S1]and[S2]tags to indicate speaker turns:[S1] Hello, how can I help you today? [S2] I'd like to check my account balance.
-
Provide speaker prompts:
You can use either:- Merged prompt format: A single audio file containing both speakers’ voices, with a corresponding transcription like
[S1] Hi. [S2] How are you? - Split prompt format: Separate audio files and transcriptions for each speaker
- Merged prompt format: A single audio file containing both speakers’ voices, with a corresponding transcription like
-
Run inference:
python3 -m zipvoice.bin.infer_zipvoice_dialog --model-name zipvoice_dialog --test-list test.tsv --res-dir results
The pre-trained model automatically downloads from Hugging Face on first use.
For faster CPU inference, consider using the zipvoice_dialog_stereo variant with threading (--num-thread 4)—though note that ONNX acceleration is not yet available for dialogue models.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While powerful, ZipVoice-Dialog has sensible boundaries to keep in mind:
- Language support is currently limited to English and Chinese. Other languages are not supported out of the box.
- Stereo output requires the
zipvoice_dialog_stereomodel—the basezipvoice_dialogonly produces mono. - Very short utterances (e.g., single words) may be cut off; use
--speed 0.3to extend duration if needed. - Long prompt audios (>10 seconds) can degrade quality and slow inference—stick to concise prompts.
- No ONNX support for dialogue models yet, so speed optimizations on CPU are limited to multi-threading.
These constraints are transparently documented, allowing you to assess fit early—no hidden surprises.
Summary
ZipVoice-Dialog solves a real, persistent problem: generating realistic, multi-speaker spoken dialogues quickly and without speaker-specific training data. By combining non-autoregressive speed, accurate turn-taking, zero-shot voice cloning, and real-world training data, it delivers a rare balance of quality, speed, and usability. For developers, researchers, and product teams building voice-enabled applications, it removes major roadblocks in dialogue audio generation—making it not just another TTS model, but a practical tool for real-world innovation.
With open-source code, pre-trained models, and the OpenDialog dataset all publicly available, there’s never been a better time to experiment.